ASIC Monitoring
Cumulus Linux provides an ASIC monitoring tool that collects and distributes data about the state of the ASIC. The monitoring tool polls for data at specific intervals and takes certain actions so that you can identify and respond to problems, such as:
- Microbursts that result in longer packet latency.
- Packet buffer congestion that might lead to packet drops.
- Network problems with a particular switch, port, or traffic class.
Cumulus Linux provides:
- The egress queue length histogram, which shows information about egress buffer utilization over time.
- The ingress queue lengths histogram, which shows information about ingress buffer utilization over time.
- The counter histogram, which shows information about bandwidth utilization for a port over time.
- Packet drops due to errors (Linux only).
Cumulus Linux supports:
- The egress queue length histogram on Spectrum 1 and later.
- The ingress queue length histogram on Spectrum-2 and later.
- The counter histogram (transmitted packet, transmitted byte, received packet, received byte, and CRC counters) on Spectrum-2 and later.
- The counter histogram (layer 1 received byte counters and layer 1 transmitted byte counters) on Spectrum-4 only.
Histogram Collection Example
The NVIDIA Spectrum ASIC provides a mechanism to measure and report ingress and egress queue lengths, and counters in histograms (a graphical representation of data, which it divides into intervals or bins). Each queue reports through a histogram with 10 bins, where each bin represents a range of queue lengths.
You configure the histogram with a minimum size boundary (Min) and a histogram size. You then derive the maximum size boundary (Max) by adding the minimum size boundary and the histogram size.
The 10 bins have numbers 0 through 9. Bin 0 represents queue lengths up to the Min specified, including queue length 0. Bin 9 represents queue lengths of Max and above. Bins 1 through 8 represent equal-sized ranges between the Min and Max (by dividing the histogram size by 8).
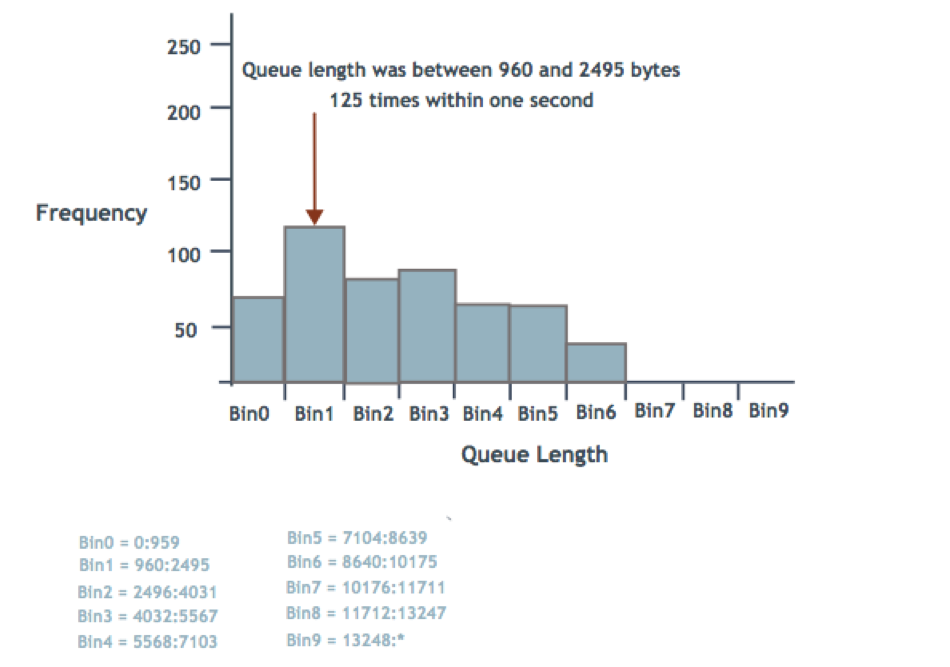
For example, consider the following histogram queue length ranges, in bytes:
- Min = 960
- Histogram size = 12288
- Max = 13248
- Range size = 1536
- Bin 0: 0:959
- Bin 1: 960:2495
- Bin 2: 2496:4031
- Bin 3: 4032:5567
- Bin 4: 5568:7103
- Bin 5: 7104:8639
- Bin 6: 8640:10175
- Bin 7: 10176:11711
- Bin 8: 11712:13247
- Bin 9: 13248:*
The following illustration demonstrates a histogram showing how many times the queue length for a port was in the ranges specified by each bin. The example shows that the queue length was between 960 and 2495 bytes 125 times within one second.
Configure ASIC Monitoring
To configure ASIC monitoring, you specify:
- The type of data to collect.
- The switch ports to monitor.
- For the egress queue length histogram, you can specify the traffic class you want to monitor for a port or range of ports.
- For the ingress queue length histogram, you can specify the priority group you want to monitor for a port or range of ports.
- How and when to start reading the ASIC: at a specific queue length, number of packets or bytes received or transmitted.
- What actions to take: create a snapshot file, send a message to the
/var/log/syslogfile, or both.
Enable ASIC Monitoring
To enable ASIC monitoring:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry enable on
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
The asic-monitor service manages the ASIC monitoring tool (systemd manages the asic-monitor service). The asic-monitor service reads the /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf configuration file to determine what statistics to collect and when to trigger. The service always starts; however, if the configuration file is empty, the service exits.
Restarting the asic-monitor service does not disrupt traffic or require you to restart switchd.
Histogram Settings
Histogram settings include the type of data you want to collect, the ports you want the histogram to monitor, the sampling time of the histogram, the histogram size, and the minimum boundary size for the histogram.
- The ingress queue length histogram can monitor a specific priority group for a port or range of ports.
- The egress queue length histogram can monitor a specific traffic class for a port or range of ports. Traffic class 0 through 7 is for unicast traffic and traffic class 8 through 15 is for multicast traffic.
- The counter histogram can monitor the following counter types:
- Received packet counters (
rx-packet) - Transmitted packet counters (
tx-packet) - Received byte counters (
rx-byte) - Transmitted byte counters (
tx-byte) - CRC counters (
crc) - Layer 1 received byte counters (
l1-rx-byte). The byte count includes layer 1IPG bytes. - Layer 1 transmitted byte counters (
l1-tx-byte). The byte count includes layer 1IPG bytes.
- Received packet counters (
- You can enable up to two counter histogram counter types per physical interface. The counter histogram does not support bonds or virtual interfaces.
- The value for the minimum boundary size must be a multiple of 96. Adding this number to the size of the histogram produces the maximum boundary size. These values represent the range of queue lengths per bin. The default minimum boundary size is 960 bytes.
- The default value for the sampling time is 1024 nanoseconds.
The histogram type can be egress-buffer, ingress-buffer, or counter.
- To change global histogram settings, run the
nv set service telemetry histogram <type>command. - To enable histograms on interfaces or to change interface level settings, run the
nv set interface <interface> telemetry histogram <type>command.
The following example configures the egress queue length histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960, the histogram size to 12288, and the sampling interval to 1024. These settings apply to interfaces that have the egress-buffer histogram enabled and do not have different values configured for these settings at the interface level:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram egress-buffer bin-min-boundary 960
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram egress-buffer histogram-size 12288
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram egress-buffer sample-interval 1024
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
The following example enables the egress queue length histogram for traffic class 0 on swp1 through swp8 with the globally applied minimum boundary, histogram size, and sample interval. The example also enables the egress queue length histogram for traffic class 1 on swp9 through swp16 and sets the minimum boundary to 768 bytes, the histogram size to 9600 bytes, and the sampling interval to 2048 nanoseconds.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry enable on
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp1-8 telemetry histogram egress-buffer traffic-class 0
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-16 telemetry histogram egress-buffer traffic-class 1 bin-min-boundary 768
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-16 telemetry histogram egress-buffer traffic-class 1 histogram-size 9600
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-16 telemetry histogram egress-buffer traffic-class 1 sample-interval 2048
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
The following example configures the ingress queue length histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960 bytes, the histogram size to 12288 bytes, and the sampling interval to 1024 nanoseconds. These settings apply to interfaces that have the ingress-buffer histogram enabled and do not have different values configured for these settings at the interface level:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry enable on
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram ingress-buffer bin-min-boundary 960
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram ingress-buffer histogram-size 12288
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram ingress-buffer sample-interval 1024
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
The following example enables the ingress queue length histogram for priority group 0 on swp1 through swp8 with the globally applied minimum boundary, histogram size, and sample interval. The example also enables the ingress queue length histogram for priority group 1 on swp9 through swp16 and sets the minimum boundary to 768 bytes, the histogram size to 9600 bytes, and the sampling interval to 2048 nanoseconds.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp1-8 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 0
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-16 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 1 bin-min-boundary 768
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-16 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 1 histogram-size 9600
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-16 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 1 sample-interval 2048
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
The following example configures the counter histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960, the histogram size to 12288, and the sampling interval to 1024. The histogram monitors all counter types. These settings apply to interfaces that have the counter histogram enabled and do not have different values configured for these settings at the interface level:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram counter bin-min-boundary 960
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram counter histogram-size 12288
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry histogram counter sample-interval 1024
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
The following example enables the counter histogram on swp1 through swp8 and uses the global settings for the minimum boundary size, histogram size, and the sampling interval. The histogram monitors all received packet counters on ports 1 through 8:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp1-swp8 telemetry histogram counter counter-type rx-packet
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
Edit settings in the /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf file, then restart the asic-monitor service with the systemctl restart asic-monitor.service command. The asic-monitor service reads the new configuration file and then runs until you stop the service with the systemctl stop asic-monitor.service command.
The following table describes the ASIC monitor settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
port_group_list |
Specifies the names of the monitors (port groups) you want to use to collect data, such as histogram_pg. You can provide any name you want for the port group. You must use the same name for all the port group settings.Example: monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_pg,discards_pg,buffers_pg, all_packets_pg]Note: You must specify at least one port group. If the port group list is empty, systemd shuts down the asic-monitor service. |
<port_group_name>.port_set |
Specifies the range of ports you want to monitor; for example, swp4,swp8,swp10-swp50.Example: monitor.histogram_pg.port_set = swp1-swp50 |
<port_group_name>.stat_type |
Specifies the type of data that the port group collects. For egress queue length histograms, specify histogram_tc. For example:monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = histogram_tcFor ingress queue length histograms, specify histogram_pg. For example: monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = histogram_pgFor counter histograms, specify histogram_counter. For example:monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = histogram_counter. |
<port_group_name>.cos_list |
For histogram monitoring, each CoS (Class of Service) value in the list has its own histogram on each port. The global limit on the number of histograms is an average of one histogram per port. Example: monitor.histogram_pg.cos_list = [0] |
<port_group_name>.counter_type |
Specifies the counter type for counter histogram monitoring. The counter types can be tx-pkt,rx-pkt,tx-byte,rx-byte.Example: monitor.histogram_pg.counter_type = [rx_byte] |
<port_group_name>.trigger_type |
Specifies the type of trigger that initiates data collection. The only option is timer. At least one port group must have a configured timer, otherwise no data is ever collected. Example: monitor.histogram_pg.trigger_type = timer |
<port_group_name>.timer |
Specifies the frequency at which data collects; for example, a setting of 1s indicates that data collects one time per second. You can set the timer to the following: 1 to 60 seconds: 1s, 2s, and so on up to 60s 1 to 60 minutes: 1m, 2m, and so on up to 60m 1 to 24 hours: 1h, 2h, and so on up to 24h 1 to 7 days: 1d, 2d and so on up to 7d Example: monitor.histogram_pg.timer = 4s |
<port_group_name>.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary |
For histogram monitoring. The minimum boundary size for the histogram in bytes. On a Spectrum switch, this number must be a multiple of 96. Adding this number to the size of the histogram produces the maximum boundary size. These values represent the range of queue lengths per bin. Example: monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960 |
<port_group_name>.histogram.histogram_size_bytes |
For histogram monitoring. The size of the histogram in bytes. Adding this number and the minimum_bytes_boundary value together produces the maximum boundary size. These values represent the range of queue lengths per bin. Example: monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288 |
<port_group_name>.histogram.sample_time_ns |
For histogram monitoring. The sampling time of the histogram in nanoseconds. Example: monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024 |
The following example configures the egress queue length histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960, the histogram size to 12288, and the sampling interval to 1024. The histogram collects data every second for traffic class 0 through 15 on all ports:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf
...
monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_pg]
monitor.histogram_pg.port_set = allports
monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = histogram_tc
monitor.histogram_pg.cos_list = [0-15]
monitor.histogram_pg.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_pg.timer = 1s
...
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
The following example configures the egress queue length histogram and sets the minimum boundary to 960 bytes, the histogram size to 12288 bytes, and the sampling interval to 1024 nanoseconds. The histogram collects data every second for traffic class 0 on swp1 through swp8, and for traffic class 1 on swp9 through swp16.
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf
...
monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_gr1, histogram_gr2]
monitor.histogram_gr1.port_set = swp1-swp8
monitor.histogram_gr1.stat_type = histogram_tc
monitor.histogram_gr1.cos_list = [0]
monitor.histogram_gr1.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_gr1.timer = 1s
...
monitor.histogram_gr1.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_gr1.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_gr1.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
monitor.histogram_gr2.port_set = swp9-swp16
monitor.histogram_gr2.stat_type = histogram_tc
monitor.histogram_gr2.cos_list = [1]
monitor.histogram_gr2.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_gr2.timer = 1s
…
monitor.histogram_gr2.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_gr2.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_gr2.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
The following example configures the ingress queue length histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960 bytes, the histogram size to 12288 bytes, and the sampling interval to 1024 nanoseconds. The histogram collects data every second for priority group 1 through 15 on all ports.
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf
...
monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_pg]
monitor.histogram_pg.port_set = allports
monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = histogram_pg
monitor.histogram_pg.cos_list = [0-15]
monitor.histogram_pg.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_pg.timer = 1s
...
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
The following example configures the ingress queue length histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960, the histogram size to 12288, and the sampling interval to 1024. The histogram monitors priority group 0 on ports 1 through 8 and priority group 1 on ports 9 through 16:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf
...
monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_gr1, histogram_gr2]
monitor.histogram_gr1.port_set = swp1-swp8
monitor.histogram_gr1.stat_type = histogram_pg
monitor.histogram_gr1.cos_list = [0]
monitor.histogram_gr1.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_gr1.timer = 1s
...
monitor.histogram_gr1.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_gr1.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_gr1.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
monitor.histogram_gr2.port_set = swp9-swp16
monitor.histogram_gr2.stat_type = histogram_pg
monitor.histogram_gr2.cos_list = [1]
monitor.histogram_gr2.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_gr2.timer = 1s
…
monitor.histogram_gr2.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_gr2.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_gr2.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
The following example configures the counter histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960, the histogram size to 12288, and the sampling interval to 1024. The histogram monitors all counter types:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf
...
monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_pg]
monitor.histogram_pg.port_set = allports
monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = histogram_counter
monitor.histogram_pg.counter_type = [tx-pkt,rx-pkt,tx-byte,rx-byte]
monitor.histogram_pg.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_pg.timer = 1s
...
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
The following example configures the counter histogram and sets the minimum boundary size to 960, the histogram size to 12288, and the sampling interval to 1024. The histogram monitors all received packets on ports 1 through 8:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf
...
monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_pg]
monitor.histogram_pg.port_set = swp1-swp8
monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = histogram_counter
monitor.histogram_pg.counter_type = [tx-pkt]
monitor.histogram_pg.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_pg.timer = 1s
...
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
In the following example:
- Packet drops on swp1 through swp50 collect every two seconds.
- If the number of packet drops is greater than 100, the results write to the
/var/lib/cumulus/discard_statssnapshot file and the system sends a message to the/var/log/syslogfile.
monitor.port_group_list = [discards_pg]
monitor.discards_pg.port_set = swp1-swp50
monitor.discards_pg.stat_type = packet
monitor.discards_pg.action_list = [snapshot,log]
monitor.discards_pg.trigger_type = timer
monitor.discards_pg.timer = 2s
monitor.discards_pg.log.packet_error_drops = 100
monitor.discards_pg.snapshot.packet_error_drops = 100
monitor.discards_pg.snapshot.file = /var/lib/cumulus/discard_stats
monitor.discards_pg.snapshot.file_count = 16
A collect action triggers the collection of additional information. You can daisy chain multiple monitors (port groups) into a single collect action.
In the following example:
- Queue length histograms collect for swp1 through swp50 every second.
- The results write to the
/var/lib/cumulus/histogram_statssnapshot file. - When the queue length reaches 500 bytes, the system sends a message to the /var/log/syslog file and collects additional data; buffer occupancy and all packets per port.
- Buffer occupancy data writes to the
/var/lib/cumulus/buffer_statssnapshot file and all packets per port data writes to the/var/lib/cumulus/all_packet_statssnapshot file. - In addition, packet drops on swp1 through swp50 collect every two seconds. If the number of packet drops is greater than 100, the monitor writes the results to the
/var/lib/cumulus/discard_statssnapshot file and sends a message to the/var/log/syslogfile.
monitor.port_group_list = [histogram_pg,discards_pg]
monitor.histogram_pg.port_set = swp1-swp50
monitor.histogram_pg.stat_type = buffer
monitor.histogram_pg.cos_list = [0]
monitor.histogram_pg.trigger_type = timer
monitor.histogram_pg.timer = 1s
monitor.histogram_pg.action_list = [snapshot,collect,log]
monitor.histogram_pg.snapshot.file = /var/lib/cumulus/histogram_stats
monitor.histogram_pg.snapshot.file_count = 64
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.minimum_bytes_boundary = 960
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.histogram_size_bytes = 12288
monitor.histogram_pg.histogram.sample_time_ns = 1024
monitor.histogram_pg.log.queue_bytes = 500
monitor.histogram_pg.collect.queue_bytes = 500
monitor.histogram_pg.collect.port_group_list = [buffers_pg,all_packet_pg]
monitor.buffers_pg.port_set = swp1-swp50
monitor.buffers_pg.stat_type = buffer
monitor.buffers_pg.action_list = [snapshot]
monitor.buffers_pg.snapshot.file = /var/lib/cumulus/buffer_stats
monitor.buffers_pg.snapshot.file_count = 8
monitor.all_packet_pg.port_set = swp1-swp50
monitor.all_packet_pg.stat_type = packet_all
monitor.all_packet_pg.action_list = [snapshot]
monitor.all_packet_pg.snapshot.file = /var/lib/cumulus/all_packet_stats
monitor.all_packet_pg.snapshot.file_count = 8
monitor.discards_pg.port_set = swp1-swp50
monitor.discards_pg.stat_type = packet
monitor.discards_pg.action_list = [snapshot,log]
monitor.discards_pg.trigger_type = timer
monitor.discards_pg.timer = 2s
monitor.discards_pg.log.packet_error_drops = 100
monitor.discards_pg.snapshot.packet_error_drops = 100
monitor.discards_pg.snapshot.file = /var/lib/cumulus/discard_stats
monitor.discards_pg.snapshot.file_count = 16
Bandwidth Gauge
Cumulus Linux supports the bandwidth gauge option on the Spectrum-4 switch only.
To track bandwidth usage for an interface, you can enable the bandwidth gauge option with the nv set interface <interface-id> telemetry bw-gauge enable on command:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp1 telemetry bw-gauge enable on
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
To disable the bandwidth gauge setting, run the nv set interface <interface-id> telemetry bw-gauge enable off command.
To show the bandwidth gauge setting for an interface, run the nv show interface <interface> telemetry bw-gauge command:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show interface swp1 telemetry bw-gauge
operational applied
------ ----------- -------
enable on on
To show a summary of the bandwidth for an interface, run the nv show service telemetry bw-gauge interface command:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show service telemetry bw-gauge interface
Interface Tx (Mbps) Rx (Mbps)
--------- --------- ---------
swp1 4 4
Snapshots
To create a snapshot:
- Set how often to write to a snapshot file. The default value is 1 second.
- Provide the snapshot file name and location. The default location and file name is
/var/lib/cumulus/histogram_stats. - Configure the number of snapshots you can create before Cumulus Linux overwrites the first snapshot file. For example, if you set the snapshot file count to 30, the first snapshot file is
histogram_stats_0and the 30th snapshot ishistogram_stats_30. After the 30th snapshot, Cumulus Linux overwrites the original snapshot file (histogram_stats_0) and the sequence restarts. The default value is 64.
Snapshots provide you with more data; however, they can occupy a lot of disk space on the switch. To reduce disk usage, you can use a volatile partition for the snapshot files; for example, /var/run/cumulus/histogram_stats.
The following example creates the /var/lib/cumulus/histogram_stats snapshot every 5 seconds. The number of snapshots that you can create before the first snapshot file is overwritten is set to 30.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry snapshot-file name /var/lib/cumulus/histogram_stats
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry snapshot-file count 30
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set service telemetry snapshot-interval 5
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
Edit the snapshot.file settings in the /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf file, then restart the asic-monitor service with the systemctl restart asic-monitor.service command. The asic-monitor service reads the new configuration file and then runs until you stop the service with the systemctl stop asic-monitor.service command.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
<port_group_name>.action_list |
Specifies one or more actions that occur when data collects:snapshot writes a snapshot of the data collection results to a file. If you specify this action, you must also specify a snapshot file (described below). You can also specify a threshold that initiates the snapshot action.Example: monitor.histogram_pg.action_list = [snapshot] collect gathers additional data. If you specify this action, you must also specify the port groups for the additional data you want to collect.Example: monitor.histogram_pg.action_list = [collect log sends a message to the /var/log/syslog file. If you specify this action, you must also specify a threshold that initiates the log action.Example: monitor.histogram_pg.action_list = [log]You can use all three of these actions in one monitoring step. For example monitor.histogram_pg.action_list = [snapshot,collect,log]Note: If an action appears in the action list but does not have the required settings (such as a threshold for the log action), the ASIC monitor stops and reports an error. |
<port_group_name>.snapshot.file |
Specifies the name for the snapshot file. All snapshots use this name, with a sequential number appended to it. See the snapshot.file_count setting.Example: monitor.histogram_pg.snapshot.file = /var/lib/cumulus/histogram_stats |
<port_group_name>.snapshot.file_count |
Specifies the number of snapshots you can create before Cumulus Linux overwrites the first snapshot file. In the following example, because the snapshot file count is set to 64, the first snapshot file is histogram_stats_0 and the 64th snapshot is histogram_stats_63. After the 65th snapshot, Cumulus Linux overwrites the original snapshot file (histogram_stats_0) and the sequence restarts.Example: monitor.histogram_pg.snapshot.file_count = 64Note: While more snapshots provide you with more data, they can occupy a lot of disk space on the switch. |
- To show an ingress queue snapshot, run the
nv show interface <interface> telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group <value> snapshotcommand - To show an egress queue snapshot, run the
nv show interface <interface> telemetry histogram egress-buffer traffic-class <type> snapshot - To show a counter snapshot, run the
nv show interface <interface> telemetry histogram counter counter-type <type> snapshot
The following example shows an ingress queue snapshot:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show interface swp1 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 0 snapshot
Sl.No Date-Time Bin-0 Bin-1 Bin-2 Bin-3 Bin-4 Bin-5 Bin-6 Bin-7 Bin-8 Bin-9
----- ------------------- ------ ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------- -------- ---------
0 - (<864) (<2304) (<3744) (<5184) (<6624) (<8064) (<9504) (<10944) (<12384) (>=12384)
1 2023-12-13 11:02:44 980318 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 2023-12-13 11:02:43 980318 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 2023-12-13 11:02:42 980318 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 2023-12-13 11:02:41 980318 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 2023-12-13 11:02:40 980488 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 2023-12-13 11:02:39 980149 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
7 2023-12-13 11:02:38 979809 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
8 2023-12-13 11:02:37 980488 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
9 2023-12-13 11:02:36 980318 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Parsing the snapshot file and finding the information you need can be tedious; use a third-party analysis tool to analyze the data in the file.
Log files
In addition to snapshots, you can configure the switch to send log messages to the /var/log/syslog file when the queue length reaches a specified number of bytes or the number of counters reach a specified value.
The following example sends a message to the /var/log/syslog file after the ingress queue length for priority group 1 on ports swp9 through swp16 reaches 5000 bytes:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-swp16 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 1 threshold action log
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp9-swp16 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 1 threshold value 5000
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
Set the log options in the /etc/cumulus/datapath/monitor.conf file, then restart the asic-monitor service with the systemctl restart asic-monitor.service command. The asic-monitor service reads the new configuration file and then runs until you stop the service with the systemctl stop asic-monitor.service command.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
<port_group_name>.log.action_list |
Set this option to log to create a log message when the queue length or counter number reaches the threshold set. |
<port_group_name>.log.queue_bytes |
Specifies the length of the queue in bytes after which the switch sends a log message. |
<port_group_name>.log.count |
Specifies the number of counters to reach after which the switch sends a log message. |
...
monitor.histogram_pg.action_list = [log]
...
monitor.histogram_pg.log.queue_bytes = 5000
The following shows an example syslog message:
2018-02-26T20:14:41.560840+00:00 cumulus asic-monitor-module INFO: 2018-02-26 20:14:41.559967: Egress queue(s) greater than 500 bytes in monitor port group histogram_pg.
When collecting data, the switch uses both the CPU and SDK process, which can affect switchd. Snapshots and logs can occupy a lot of disk space if you do not limit their number.
Show Histogram Information
To show a list of the interfaces with enabled histograms, run the nv show service telemetry histogram interface command:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show service telemetry histogram interface
Interface ingress-buffer egress-buffer counter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swp1 0,1,2 - tx-byte,rx-byte
swp2 - 0,1,8 tx-byte,tx-byte
To show the egress queue depth histogram samples collected at the configured interval for a traffic class for a port, run the nv show interface <interface> telemetry histogram egress-buffer traffic-class <traffic-class> command.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show interface swp1 telemetry histogram egress-buffer traffic-class 0
Time 0-863 864:2303 2304:3743. 3744:5183 5184:6623 6624:8063 8064:9503 9. 504:10943 10944:12383
12384:*
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
08:56:19 978065 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
08:56:20 978532 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
To show the ingress queue depth histogram samples collected at the configured interval for a priority group for a port, run the nv show interface <interface> telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group <priority-group> command.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show interface swp1 telemetry histogram ingress-buffer priority-group 0
Time 0-863 864:2303 2304:3743 3744:5183 5184:6623 6624:8063 8064:9503 9. 504:10943 10944:12383
12384:*
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
08:56:19 978065 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
08:56:20 978532 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0