Bridge Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
A VXLAN connects layer 2 domains across a layer 3 fabric; however, layer 2 protocol packets, such as LLDP, LACP, STP, and CDP stop at the ingress VTEP. If you want the VXLAN to behave more like a wire or hub, where the switch tunnels protocol packets instead of terminating them locally, you can enable bridge layer 2 protocol tunneling.
Configure Bridge Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
To configure bridge layer 2 protocol tunneling for all protocols:
cumulus@switch:~$ net add interface swp1 bridge l2protocol-tunnel all
cumulus@switch:~$ net add interface vni10 bridge l2protocol-tunnel all
cumulus@switch:~$ net pending
cumulus@switch:~$ net commit
Add bridge-l2protocol-tunnel all to the interface stanza and the VNI stanza of the /etc/network/interfaces file:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
bridge-l2protocol-tunnel all
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp4
iface swp4
...
interface vni10
bridge-access 10
bridge-l2protocol-tunnel all
bridge-learning off
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
mstpctl-portbpdufilter yes
vxlan-id 10
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.1
To configure bridge layer 2 protocol tunneling for a specific protocol, such as LACP:
cumulus@switch:~$ net add interface swp1 bridge l2protocol-tunnel lacp
cumulus@switch:~$ net add interface vni10 bridge l2protocol-tunnel lacp
cumulus@switch:~$ net pending
cumulus@switch:~$ net commit
Add bridge-l2protocol-tunnel <protocol> to the interface stanza and the VNI stanza of the /etc/network/interfaces file:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
bridge-l2protocol-tunnel lacp
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp4
iface swp4
...
interface vni10
bridge-access 10
bridge-l2protocol-tunnel lacp
bridge-learning off
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
mstpctl-portbpdufilter yes
vxlan-id 10
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.1
You must enable layer 2 protocol tunneling on the VXLAN link in addition to the interface so that the packets get bridged and forwarded correctly.
LLDP Example
Here is another example configuration for Link Layer Discovery Protocol. You can verify the configuration with lldpcli.
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo lldpcli show neighbors
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LLDP neighbors:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interface: swp23, via LLDP, RID: 13, TIme: 0 day, 00:58:20
Chassis:
ChassisID: mac e4:1d:2d:f7:d5:52
SysName: H1
MgmtIP: 10.0.2.207
MgmtIP: fe80::e61d:2dff:fef7:d552
Capability: Bridge, off
Capability: Router, on
Port:
PortID: ifname swp14
PortDesc: swp14
TTL: 120
PMD autoneg: support: yes, enabled: yes
Adv: 1000Base-T, HD: no, FD: yes
MAU oper type: 40GbaseCR4 - 40GBASE-R PCS/PMA over 4 lane shielded copper balanced cable
...
LACP Example
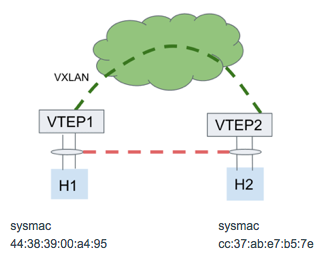
H2 bond0:
Bonding Mode: IEEE 802.3ad Dynamic link aggregation
Transmit Hash Policy: layer 3+4(1)
802.3ad: info
LACP rate: fast
Min links: 1
Aggregator selection policy (ad_select): stable
System priority: 65535
System MAC address: cc:37:ab:e7:b5:7e
Active Aggregator Info:
Aggregator ID: 1
Number of ports: 2
Slave Interface: eth0
...
details partner lacp pdu:
system priority: 65535
system MAC address: 44:38:39:00:a4:95
...
Slave Interface: eth1
...
details partner lacp pdu:
system priority: 65535
system MAC address: 44:38:39:00:a4:95
Pseudowire Example
In this example:
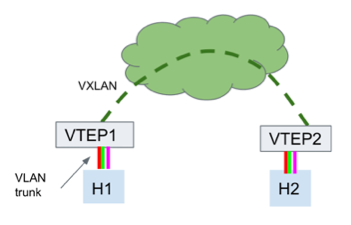
- Only two VTEPs are in the VXLAN. VTEP1 and VTEP2 point to each other as the only remote VTEP.
- The bridge on each VTEP is in 802.1ad mode.
- The host interface is an 802.1Q VLAN trunk.
- The setting for
bridge-l2protocol-tunnelisall. - The VTEP host-facing port is in access mode and the PVID maps to the VNI.
Considerations
Use caution when enabling bridge layer 2 protocol tunneling:
- Layer 2 protocol tunneling is not a full-featured pseudo-wire solution; End-to-end link status tracking or feedback does not exist.
- Layer 2 protocols typically run on a link-local scope. Running the protocols through a tunnel across a layer 3 fabric incurs higher latency, which require you to tune protocol timers.
- The lack of end to end link or tunnel status feedback and the higher protocol timeout values make for a higher protocol convergence time when there are changes.
- If the remote endpoint is a Cisco endpoint using LACP, you must configure
etherchannel misconfig guardon the Cisco device.