Open Shortest Path First v2 - OSPFv2
This topic describes OSPFv2, which is a link-state routing protocol for IPv4. For IPv6 commands, refer to Open Shortest Path First v3 - OSPFv3.
Basic OSPFv2 Configuration
You can configure OSPF using either numbered interfaces or unnumbered interfaces.
OSPFv2 Numbered
To configure OSPF using numbered interfaces, you specify the router ID, IP subnet prefix, and area address. You must put all the interfaces on the switch with an IP address that matches the network subnet into the specified area. OSPF attempts to discover other OSPF routers on those interfaces. Cumulus Linux adds all matching interface network addresses to a type-1 LSA and advertises to discovered neighbors for proper reachability.
If you do not want to bring up an OSPF adjacency on certain interfaces, but want to advertise those networks in the OSPF database, you can configure the interfaces as passive interfaces. A passive interface creates a database entry but does not send or receive OSPF hello packets. For example, in a data center topology, the host-facing interfaces do not need to run OSPF, however, you need to advertise the corresponding IP addresses to neighbors.
Network statements can be as inclusive or generic as necessary to cover the interface networks.
The following example commands configure OSPF numbered on leaf01 and spine01.
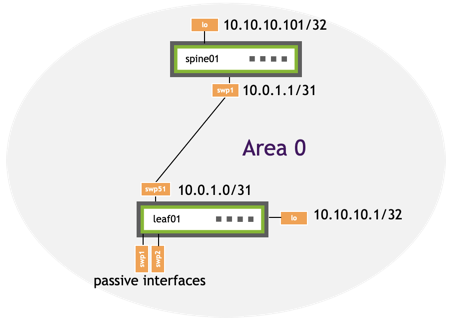
| leaf01 | spine01 |
|---|---|
|
|
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.1/32
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51 ip address 10.0.1.0/31
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf router-id 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf area 0 network 10.10.10.1/32
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf area 0 network 10.0.1.0/31
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp1 router ospf passive on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp2 router ospf passive on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.101/32
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1 ip address 10.0.1.1/31
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf router-id 10.10.10.101
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf area 0 network 10.10.10.101/32
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf area 0 network 10.0.1.1/31
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv config apply
-
Edit the
/etc/frr/daemonsfile to enable theospfdaemon, then start the FRR service (see FRRouting). -
Edit the
/etc/network/interfacesfile to configure the IP address for the loopback and swp51:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.1/32
auto swp51
iface swp51
address 10.0.1.0/31
-
Run the
ifreload -acommand to load the new configuration:cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo ifreload -a -
From the vtysh shell, configure OSPF:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh ... leaf01# configure terminal leaf01(config)# router ospf leaf01(config-router)# ospf router-id 10.10.10.1 leaf01(config-router)# network 10.10.10.1/32 area 0 leaf01(config-router)# network 10.0.1.0/31 area 0 leaf01(config-router)# passive-interface swp1 leaf01(config-router)# passive-interface swp2 leaf01(config-router)# exit leaf01(config)# exit leaf01# write memory leaf01# exit
You can use the passive-interface default command to set all interfaces as passive and selectively bring up protocol adjacency on certain interfaces:
leaf01(config)# router ospf
leaf01(config-router)# passive-interface default
leaf01(config-router)# no passive-interface swp51
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
router ospf
ospf router-id 10.10.10.1
network 10.10.10.1/32 area 0
network 10.0.1.0/31 area 0
passive-interface swp1
passive-interface swp2
...
-
Edit the
/etc/frr/daemonsfile to enable theospfdaemon, then start the FRR service (see FRRouting). -
Edit the
/etc/network/interfacesfile to configure the IP address for the loopback and swp1:cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces ... auto lo iface lo inet loopback address 10.10.10.101/32auto swp51 iface swp51 address 10.0.1.1/31
-
Run the
ifreload -acommand to load the new configuration:cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo ifreload -a -
From the vtysh shell, configure OSPF:
cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo vtysh ... spine01# configure terminal spine01(config)# router ospf spine01(config-router)# ospf router-id 10.10.101.1 spine01(config-router)# network 10.10.10.101/32 area 0 spine01(config-router)# network 10.0.1.1/31 area 0 spine01(config-router)# exit spine01(config)# exit spine01# write memory spine01# exit
You can use the passive-interface default command to set all interfaces as passive and selectively bring up protocol adjacency on certain interfaces:
spine01(config)# router ospf
spine01(config-router)# passive-interface default
spine01(config-router)# no passive-interface swp1
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
router ospf
ospf router-id 10.10.10.101
network 10.10.10.101/32 area 0
network 10.0.1.1/31 area 0
...
OSPFv2 Unnumbered
Unnumbered interfaces are interfaces without unique IP addresses; multiple interfaces share the same IP address. In OSPFv2, unnumbered interfaces do not need unique IP addresses on leaf and spine interfaces and simplify the OSPF database, which reduces the memory footprint and improves SPF convergence times.
To configure an unnumbered interface, take the IP address of loopback interface (called the anchor) and use that as the IP address of the unnumbered interface.
OSPF unnumbered supports point-to-point interfaces only and does not support network statements.
The following example commands configure OSPF unnumbered on leaf01 and spine01.
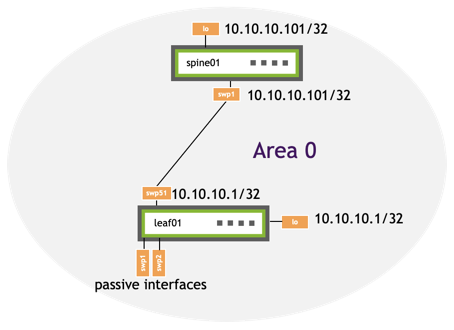
| leaf01 | spine01 |
|---|---|
|
|
Configure the unnumbered interface:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.1/32
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51 ip address 10.10.10.1/32
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
Configure OSPF:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf router-id 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface lo router ospf area 0
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf area 0
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp1 router ospf passive on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp2 router ospf passive on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf network-type point-to-point
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
Configure the unnumbered interface:
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.101/32
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1 ip address 10.10.10.101/32
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv config apply
Configure OSPF:
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf router-id 10.10.10.101
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface lo router ospf area 0
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1 router ospf area 0
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1 router ospf network-type point-to-point
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv config apply
-
Edit the
/etc/frr/daemonsfile to enable theospfdaemon, then start the FRR service (see FRRouting). -
Edit the
/etc/network/interfacesfile to configure the loopback and unnumbered interface address:cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces ... auto lo iface lo inet loopback address 10.10.10.1/32auto swp51 iface swp51 address 10.10.10.1/32
-
Run the
ifreload -acommand to load the new configuration:cumulus@leaf01:~$ ifreload -a -
From the vtysh shell, configure OSPF:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh ... leaf01# configure terminal leaf01(config)# router ospf leaf01(config-router)# ospf router-id 10.10.10.1 leaf01(config-router)# interface swp51 leaf01(config-if)# ip ospf area 0 leaf01(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# interface lo leaf01(config-if)# ip ospf area 0 leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# router ospf leaf01(config-router)# passive-interface swp1,swp2 leaf01(config-router)# end leaf01# write memory leaf01# exitYou can use the
passive-interface defaultcommand to set all interfaces as passive and selectively bring up protocol adjacency on certain interfaces:leaf01(config)# router ospf leaf01(config-router)# passive-interface default leaf01(config-router)# no passive-interface swp51
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
interface lo
ip ospf area 0
interface swp51
ip ospf area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
router ospf
ospf router-id 10.10.10.1
passive-interface swp1,swp2
...
-
Edit the
/etc/frr/daemonsfile to enable theospfdaemon, then start the FRR service (see FRRouting). -
Edit the
/etc/network/interfacesfile to configure the loopback and unnumbered interface address:cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces ... auto lo iface lo inet loopback address 10.10.10.101/32auto swp1 iface swp1 address 10.10.10.101/32
-
Run the
ifreload -acommand to load the new configuration:cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo ifreload -a -
From the vtysh shell, configure OSPF:
cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo vtysh ... spine01# configure terminal spine01(config)# router ospf spine01(config)# ospf router-id 10.10.10.101 spine01(config)# interface swp1 spine01(config-if)# ip ospf area 0 spine01(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point spine01(config-if)# exit spine01(config)# interface lo spine01(config-if)# ip ospf area 0 spine01(config-if)# exit spine01(config-if)# end spine01# write memory spine01# exitYou can use the
passive-interface defaultcommand to set all interfaces as passive and selectively bring up protocol adjacency on certain interfaces:spine01(config)# router ospf spine01(config-router)# passive-interface default spine01(config-router)# no passive-interface swp1
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
interface lo
ip ospf area 0
interface swp1
ip ospf area 0
ip ospf network point-to-point
router ospf
ospf router-id 10.10.10.101
...
Optional OSPFv2 Configuration
This section describes optional configuration. The steps provided in this section assume that you already configured basic OSPFv2 as described in Basic OSPF Configuration, above.
Interface Parameters
You can define the following OSPF parameters per interface:
- Network type (point-to-point or broadcast). Broadcast is the default setting. Configure the interface as point-to-point unless you intend to use the Ethernet media as a LAN with multiple connected routers. Point-to-point provides a simplified adjacency state machine so there is no need for DR/BDR election and LSA reflection. See RFC5309 for a more information.
Cumulus Linux requires Point-to-point for OSPFv2 unnumbered.
- Hello interval. The number of seconds between hello packets sent on the interface. The default is 10 seconds.
- Dead interval. The number of seconds before neighbors declare the router down after they stop hearing hello packets. The default is 40 seconds.
- Priority in becoming the OSPF Designated Router (DR) on a broadcast interface. The default is priority 1.
The following command example sets the network type to point-to-point.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf network-type point-to-point
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface swp51
switch(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point
switch(config-if)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example
...
interface swp51
ip ospf network point-to-point
...
The following command example sets the hello interval to 5 seconds and the dead interval to 60 seconds. The hello interval and dead interval can be any value between 1 and 65535 seconds.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf timers hello-interval 5
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface swp51
switch(config-if)# ip ospf network hello-interval 5
switch(config-if)# ip ospf network dead-interval 60
switch(config-if)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example
...
interface swp51
ip ospf hello-interval 5
ip ospf dead-interval 60
...
The following command example sets the priority to 5 for swp51. The priority can be any value between 0 to 255. 0 configures the interface to never become the OSPF Designated Router (DR) on a broadcast interface.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf priority 5
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface swp51
switch(config-if)# ip ospf network priority 5
switch(config-if)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example
...
interface swp51
ip ospf priority 5
...
To see the configured OSPF interface parameter values, run the vtysh show ip ospf interface command.
SPF Timer Defaults
OSPF uses the following default timers to prevent consecutive SPF from overburdening the CPU:
- 0 milliseconds from the initial event until SPF runs
- 50 milliseconds between consecutive SPF runs (the number doubles with each SPF, until it reaches the maximum time between SPF runs)
- 5000 milliseconds maximum between SPFs
The following example commands change the number of milliseconds from the initial event until SPF runs to 80, the number of milliseconds between consecutive SPF runs to 100, and the maximum number of milliseconds between SPFs to 6000.
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set router ospf timers spf delay 80
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set router ospf timers spf holdtime 100
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set router ospf timers spf max-holdtime 6000
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# timers throttle spf 80 100 6000
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
router ospf
ospf router-id 10.10.10.1
passive-interface swp1
passive-interface swp2
network 10.10.10.1/32 area 0
timers throttle spf 80 100 6000
...
To see the configured SPF timer values, run the vtysh show ip ospf command.
MD5 Authentication
To configure MD5 authentication on the switch, you need to create a key and a key ID, then enable MD5 authentication. The key ID must be a value between 1 and 255 that represents the key used to create the message digest. This value must be consistent across all routers on a link. The key must be a value with an upper range of 16 characters (longer strings truncate) that represents the actual message digest.
The following example commands create key ID 1 with the key thisisthekey and enable MD5 authentication on swp51 on leaf01 and on swp1 on spine01.
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf authentication message-digest-key 1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf authentication md5-key thisisthekey
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf authentication enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1 router ospf authentication message-digest-key 1
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1 router ospf authentication md5-key thisisthekeynet
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1 router ospf authentication enable on
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
...
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# interface swp51
leaf01(config-if)# ip ospf authentication message-digest
leaf01(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 thisisthekey
leaf01(config-if)# end
leaf01# write memory
leaf01# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
interface swp51
ip ospf authentication message-digest
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 thisisthekey
...
cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo vtysh
...
spine01# configure terminal
spine01(config)# interface swp1
spine01(config-if)# ip ospf authentication message-digest
spine01(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 thisisthekey
spine01(config-if)# end
spine01# write memory
spine01# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
interface swp1
ip ospf authentication message-digest
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 thisisthekey
...
To remove existing MD5 authentication hashes, run the vtysh no ip ospf command (no ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 thisisthekey).
Summarization and Prefix Range
By default, an ABR creates a summary (type-3) LSA for each route in an area and advertises it in adjacent areas. Prefix range configuration optimizes this behavior by creating and advertising one summary LSA for multiple routes. OSPF only allows for route summarization between areas on a ABR.
The following example shows a topology divided into area 0 and area 1. border01 and border02 are ABRs that have links to multiple areas and perform a set of specialized tasks, such as SPF computation per area and summarization of routes across areas.
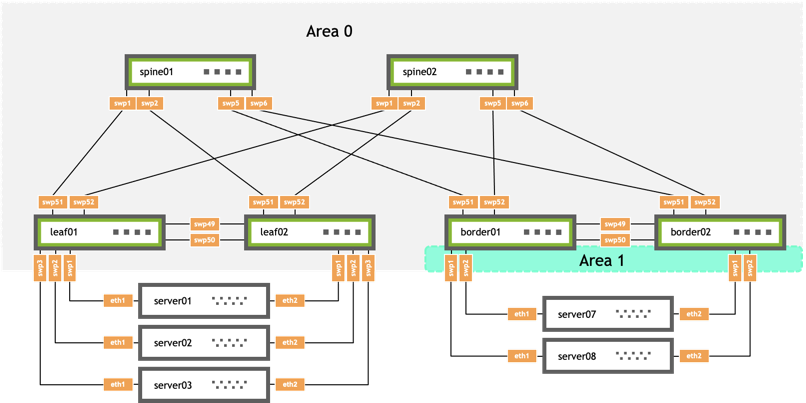
On border01:
- swp1 is in area 1 with IP addresses 10.0.0.24/31, 172.16.1.1/32, 172.16.1.2/32, and 172.16.1.3/32
- swp51 is in area 0 with IP address 10.0.1.9/31
These commands create a summary route for all the routes in the range 172.16.1.0/24 in area 0:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf area 0 range 172.16.1.0/24
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
...
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# router ospf
leaf01(config-router)# area 0 range 172.16.1.0/24
leaf01(config-router)# end
leaf01# write memory
leaf01# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
cumulus@border01:mgmt:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
interface lo
ip ospf area 0
interface swp1
ip ospf area 1
interface swp2
ip ospf area 1
interface swp51
ip ospf area 0
interface swp52
ip ospf area 0
router ospf
ospf router-id 10.10.10.63
area 0 range 172.16.1.0/24
Stub Areas
External routes are the routes redistributed into OSPF from another protocol. They have an AS-wide flooding scope. Typically, external link states make up a large percentage of the link-state database (LSDB). Stub areas reduce the LSDB size by not flooding AS-external LSAs.
All routers must agree that an area is a stub, otherwise they do not become OSPF neighbors.
To configure a stub area:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf area 1 type stub
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# area 1 stub
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
router ospf
router-id 10.10.10.63
area 1 stub
...
Stub areas still receive information about networks that belong to other areas of the same OSPF domain. If summarization is not configured (or is not comprehensive), the information can be overwhelming for the nodes. Totally stubby areas address this issue. Routers in totally stubby areas keep information about routing within their area in their LSDB.
To configure a totally stubby area:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf area 1 type totally-stub
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# area 1 stub no-summary
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
router ospf
router-id 10.10.10.63
area 1 stub no-summary
...
Here is a brief summary of the area type differences:
| Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Normal non-zero area | LSA types 1, 2, 3, 4 area-scoped, type 5 externals, inter-area routes summarized |
| Stub area | LSA types 1, 2, 3, 4 area-scoped, no type 5 externals, inter-area routes summarized |
| Totally stubby area | LSA types 1, 2 area-scoped, default summary, no type 3, 4, 5 LSA types allowed |
Auto-cost Reference Bandwidth
When you set the auto-cost reference bandwidth, Cumulus Linux dynamically calculates the OSPF interface cost to support higher speed links. The default value is 100000 for 100Gbps link speed. The cost of interfaces with link speeds lower than 100Gbps is higher.
To avoid routing loops, set the bandwidth to a consistent value across all OSPF routers.
The following example commands configure the auto-cost reference bandwidth for 90Gbps link speed:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf reference-bandwidth 9000
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth 90000
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
router ospf
router-id 10.10.10.1
auto-cost reference-bandwidth 90000
...
Administrative Distance
Cumulus Linux uses the administrative distance to choose which routing protocol to use when two different protocols provide route information for the same destination. The smaller the distance, the more reliable the protocol. For example, if the switch receives a route from OSPF with an administrative distance of 110 and the same route from BGP with an administrative distance of 100, the switch chooses BGP.
Cumulus Linux provides several commands to change the distance for OSPF routes. The default value is 110.
The following example commands set the distance for an entire group of routes:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# distance 254
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The following example commands change the OSPF administrative distance to 150 for internal routes and 220 for external routes:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf distance intra-area 150
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf distance inter-area 150
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf distance external 220
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# distance ospf intra-area 150 inter-area 150 external 220
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The following example commands change the OSPF administrative distance to 150 for internal routes to a subnet or network inside the same area as the router:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf distance intra-area 150
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# distance ospf intra-area 150
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The following example commands change the OSPF administrative distance to 150 for internal routes to a subnet in an area of which the router is not a part:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf distance inter-area 150
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# distance ospf inter-area 150
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
The vtysh commands save the configuration to the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. For example:
...
router ospf
ospf router-id 10.10.10.1
distance ospf intra-area 150 inter-area 150 external 220
...
Topology Changes and OSPF Reconvergence
When you remove a router or OSPF interface, LSA updates trigger throughout the network to inform all routers of the topology change. When the switch receives the LSA and runs OSPF, a routing update occurs. This can cause short-duration outages while the network detects the failure and updates the OSPF database.
With a planned outage (such as during a maintenance window), you can configure the OSPF router with an OSPF max-metric to notify its neighbors not to use it as part of the OSPF topology. While the network converges, all traffic forwarded to the max-metric router is still forwarded. After you update the network, the max-metric router no longer receives any traffic and you can configure the max-metric setting. To remove a single interface, you can configure the OSPF cost for that specific interface.
For failure events, traffic loss can occur during reconvergence (until SPF on all nodes computes an alternative path around the failed link or node to each of the destinations).
To configure the max-metric (for all interfaces):
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set vrf default router ospf max-metric administrative on
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router ospf
switch(config-router)# max-metric router-lsa administrative
switch(config-router)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
To configure the cost (for a specific interface):
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface swp51 router ospf cost 65535
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface swp51
switch(config-if)# ospf cost 65535
switch(config-if)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
Troubleshooting
Cumulus Linux provides several OSPF troubleshooting commands:
| Description | vtysh Command |
|---|---|
| Show neighbor states | show ip ospf neighbor |
| Verify that the LSDB synchronizes across all routers in the network | show ip ospf database |
| Determine why Cumulus Linux does not forward an OSPF route properly | show ip route ospf |
| Show OSPF interfaces | show ip ospf interface |
| Show information about the OSPF process | show ip ospf |
The following example shows the show ip ospf neighbor command output:
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$sudo vtysh
...
leaf01# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface RXmtL RqstL DBsmL
10.10.10.101 1 Full/Backup 30.307s 10.0.1.1 swp51:10.0.1.0 0 0 0
The following example shows the show ip route ospf command output:
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ sudo vtysh
...
leaf01# show ip route ospf
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP,
O - OSPF, I - IS-IS, B - BGP, E - EIGRP, N - NHRP,
T - Table, v - VNC, V - VNC-Direct, A - Babel, D - SHARP,
F - PBR, f - OpenFabric,
> - selected route, * - FIB route, q - queued route, r - rejected route
O 10.0.1.0/31 [110/100] is directly connected, swp51, weight 1, 00:02:37
O 10.10.10.1/32 [110/0] is directly connected, lo, weight 1, 00:02:37
O>* 10.10.10.101/32 [110/100] via 10.0.1.1, swp51, weight 1, 00:00:57
To capture OSPF packets, run the sudo tcpdump -v -i swp1 ip proto ospf command.
Related Information
- FRR OSPFv2
- Perlman, Radia (1999); Interconnections: Bridges, Routers, Switches, and Internetworking Protocols (2 ed.); Addison-Wesley
- Moy, John T.; OSPF: Anatomy of an Internet Routing Protocol; Addison-Wesley
- RFC 2328 OSPFv2
- RFC 3101 OSPFv2 Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA)