Static VXLAN Tunnels
Static VXLAN tunnels serve to connect two VTEPs in a given environment. Static VXLAN tunnels are the simplest deployment mechanism for small scale environments and are interoperable with other vendors that adhere to VXLAN standards. Because you map which VTEPs are in a particular VNI, you can avoid the tedious process of defining connections to every VLAN on every other VTEP on every other rack.
Cumulus Linux supports more than one VXLAN ID per VLAN-aware bridge but does not support more than one VXLAN ID per traditional bridge.
Configure Static VXLAN Tunnels
To configure static VXLAN tunnels, you create VXLAN devices. Cumulus Linux supports:
- Traditional VXLAN devices, where you configure unique VXLAN devices and add each device to the bridge.
- Single VXLAN devices, where all VXLAN tunnels with the same settings (local tunnel IP address and VXLAN remote IP addresses) can share the same VXLAN device and you only need to add the single VXLAN device to the bridge.
The configuration examples use the following topology. Each IP address corresponds to the loopback address of the switch.
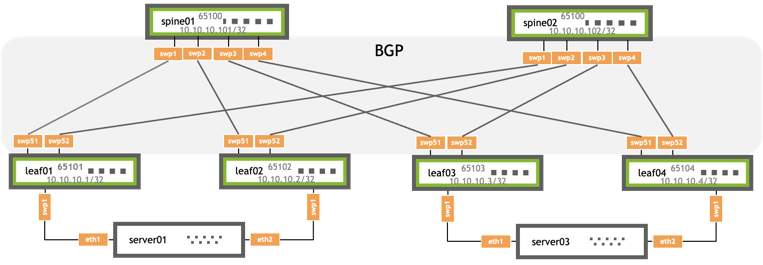
Traditional VXLAN Device
The following traditional VXLAN device configuration:
- Sets the loopback address on each leaf
- Creates two unique VXLAN devices (vni10 and vni20)
- Configures the local tunnel IP address to be the loopback address of the switch
- Enables bridge learning on the each VXLAN device
- Creates the tunnels on each VXLAN device by specifying the loopback addresses of the other leafs
- Adds both VXLAN devices (vni10 and vni20) to the bridge called
bridge
Edit the /etc/network/interfaces file, then run the ifreload -a command.
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.1/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.1
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vni10
iface vni10
bridge-access 10
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.2
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.3
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.4
vxlan-id 10
auto vni20
iface vni20
bridge-access 20
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.2
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.3
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.4
vxlan-id 20
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vni10 vni20
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.2/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.2
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vni10
iface vni10
bridge-access 10
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.1
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.3
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.4
vxlan-id 10
auto vni20
iface vni20
bridge-access 20
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.1
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.3
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.4
vxlan-id 20
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vni10 vni20
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.3/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.3
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vni10
iface vni10
bridge-access 10
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.1
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.2
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.4
vxlan-id 10
auto vni20
iface vni20
bridge-access 20
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.1
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.2
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.4
vxlan-id 20
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vni10 vni20
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.4/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.3
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vni10
iface vni10
bridge-access 10
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.1
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.2
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.3
vxlan-id 10
auto vni20
iface vni20
bridge-access 20
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.1
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.2
vxlan-remoteip 10.10.10.3
vxlan-id 20
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vni10 vni20
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
Single VXLAN Device
The following single VXLAN device example configuration:
- Sets the loopback address on each leaf
- Creates a single VXLAN device (
vxlan48), and mapsvlan 10toVNI 10andvlan 20toVNI 20 - Enables bridge learning on the single VXLAN device
- Adds the VXLAN device to the default bridge
br_default - Configures the local tunnel IP address to be the loopback address of the switch
- Creates the static VXLAN tunnels by specifying the loopback addresses of the other leafs
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.1/32
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan mac-learning on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.2/32
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set nve vxlan mac-learning on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface swp2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.3/32
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set nve vxlan mac-learning on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface swp2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.4/32
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan mac-learning on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20 flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface swp2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv config apply
Edit the /etc/network/interfaces file, then run the sudo ifreload -a command.
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.1/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.1
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
vxlan-remoteip-map 10=10.10.10.2 10=10.10.10.3 20=10.10.10.4
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20
bridge-vids 10 20
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:aa
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.2/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.2
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
vxlan-remoteip-map 10=10.10.10.1 10=10.10.10.3 20=10.10.10.4
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20
bridge-vids 10 20
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:ab
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.3/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.3
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
vxlan-remoteip-map 10=10.10.10.1 10=10.10.10.2 20=10.10.10.4
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20
bridge-vids 10 20
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:bb
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.4/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.4
auto swp1
iface swp1
bridge-access 10
auto swp2
iface swp2
bridge-access 20
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
vxlan-remoteip-map 10=10.10.10.1 10=10.10.10.2 20=10.10.10.3
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20
bridge-vids 10 20
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:c1
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
The simulation starts with the example static VXLAN configuration. The demo is pre-configured using NVUE commands.
To validate the configuration, run the verification commands shown below.
The above NVUE commands specify a different flooding list for each VNI. If you want to set the same flooding list for all VNIs, you can use the nv set nve vxlan flooding head-end-replication command; for example:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.1/32
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan mac-learning on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan flooding head-end-replication 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
The above commands create this configuration in the /etc/network/interfaces file:
...
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
vxlan-remoteip-map 10=10.10.10.2 10=10.10.10.3 10=10.10.10.4 20=10.10.10.2 20=10.10.10.3 20=10.10.10.4
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20
bridge-learning on
...
Verify the Configuration
After you configure all the leafs, run the following command to check for replication entries. The command output is different for traditional and single VXLAN devices.
For traditional VXLAN devices:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo bridge fdb show | grep 00:00:00:00:00:00
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vni10 dst 10.10.10.3 self permanent
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vni10 dst 10.10.10.2 self permanent
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vni20 dst 10.10.10.4 self permanent
For a single VXLAN devices:
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ sudo bridge fdb show | grep 00:00:00:00:00:00
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan48 dst 10.10.10.2 src_vni 10 self permanent
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan48 dst 10.10.10.3 src_vni 10 self permanent
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan48 dst 10.10.10.4 src_vni 20 self permanent
Cumulus Linux disables bridge learning and enables ARP suppression by default on VXLAN interfaces. You can change the default behavior to set bridge learning on and ARP suppression off for all VNIs by creating a policy file called bridge.json in the /etc/network/ifupdown2/policy.d/ directory. For example:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/network/ifupdown2/policy.d/bridge.json
{
"bridge": {
"module_globals": {
"bridge_vxlan_port_learning" : "on",
"bridge-vxlan-arp-nd-suppress" : "off"
}
}
}
After you create the file, run ifreload -a to load the new configuration.