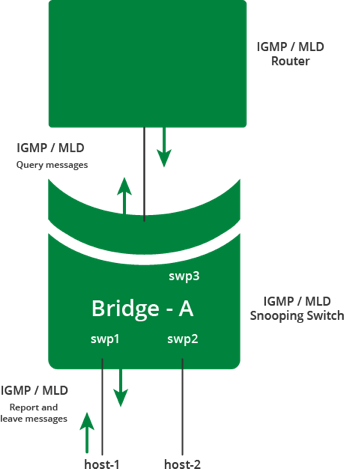
IGMP and MLD Snooping
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) and MLD (Multicast Listener Discovery) snooping are implemented in the bridge driver of the Cumulus Linux kernel and are enabled by default. IGMP snooping processes IGMP v1, v2, and v3 reports received on a bridge port in a bridge to identify the hosts that want to receive multicast traffic destined to that group.
In Cumulus Linux 3.7.4 and later, IGMP and MLD snooping is supported over VXLAN bridges; however, this feature is not enabled by default. To enable IGMP and MLD over VXLAN, see Configure IGMP/MLD Snooping over VXLAN.
When an IGMPv2 leave message is received, a group specific query is sent to identify if there are any other hosts interested in that group, before the group is deleted.
An IGMP query message received on a port is used to identify the port that is connected to a router and is interested in receiving multicast traffic.
MLD snooping processes MLD v1/v2 reports, queries and v1 done messages for IPv6 groups. If IGMP or MLD snooping is disabled, multicast traffic gets flooded to all the bridge ports in the bridge. Similarly, in the absence of receivers in a VLAN, multicast traffic would be flooded to all ports in the VLAN. The multicast group IP address is mapped to a multicast MAC address and a forwarding entry is created with a list of ports interested in receiving multicast traffic destined to that group.
Configure IGMP/MLD Snooping over VXLAN
On Broadcom switches, Cumulus Linux 3.7.4 and later supports IGMP/MLD snooping over VXLAN bridges, where VXLAN ports are set as router ports. On Mellanox Spectrum switches, IGMP/MLD snooping over VXLAN bridges is supported in Cumulus Linux 3.7.9 and later.
To enable IGMP/MLD snooping over VXLAN, run the net add bridge <bridge> mcsnoop yes command:
cumulus@switch:~$ net add bridge mybridge mcsnoop yes
cumulus@switch:~$ net pending
cumulus@switch:~$ net commit
Consider also configuring IGMP/MLD querier. See Configure IGMP/MLD Querier below.
To disable IGMP/MLD snooping over VXLAN, run the net add bridge <bridge> mcsnoop no command.
Additional Configuration for Spectrum Switches
In Cumulus Linux 3.7.13 and earlier, in addition to enabling IGMP/MLD snooping over VXLAN, you need to perform an additional configuration step, described below. This additional configuration step is not required for Cumulus Linux 3.7.14 and later.
For Spectrum switches, the IGMP reports received over VXLAN from remote hosts are not forwarded to the kernel, which, in certain cases, might result in local receivers not responding to the IGMP query. To workaround this issue, you need to apply certain ACL rules to avoid the IGMP report packets being sent across to the hosts:
Add the following lines to the /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/23_acl_test.rules file (where <swp> is the port connected to the access host), then run the cl-acltool -i command:
[ebtables]
-A FORWARD -p IPv4 -o #<swp> --ip-proto igmp -j ACCEPT --ip-destination 224.0.0.0/24
-A FORWARD -p IPv4 -o #<swp> --ip-proto igmp -j DROP
DIP-based Multicast Forwarding
DIP-based multicast forwarding is supported on Broadcom switches only.
Cumulus Linux 3.7.10 and earlier performs layer 2 multicast bridging using the destination MAC address (DMAC) of the packet, which is programmed in the layer 2 table of the ASIC. Cumulus Linux 3.7.11 and later provides the option of using IP-based layer 2 multicast forwarding (DIP), where layer 2 multicast packets are forwarded based on the layer 3 forwarding table, using the VLAN as the key.
DIP-based multicast forwarding is a good solution if you want to have a separate bridge domain and multicast flood domain for two groups that map to the same MAC address. In multicast, there can be multiple group addresses that map to the same MAC address as the address is derived from the three octets of the group; out of the allowed multicast range, you have 16 group addresses with the same MAC address.
DIP-based multicast forwarding is also a good solution if you use a group that falls in to the link local address range (for example, 228.0.0.1), which is not forwarded with DMAC-based multicast forwarding.
DIP-based multicast forwarding is not supported with IGMP Snooping over VXLAN or with IPv6 addresses (DMAC-based forwarding is used for IPv6 addresses).
To enable DIP-based multicast forwarding:
-
Edit the
/etc/cumulus/switchd.conffile to set thebridge.dip_based_l2multicastfield toTRUE, then uncomment the line. -
Restart the
switchdservice:cumulus@switch:~$ sudo systemctl restart switchd.service
Restarting the
switchdservice causes all network ports to reset, interrupting network services, in addition to resetting the switch hardware configuration.
The following example shows that the bridge.dip_based_l2multicast field is set to TRUE and the line is uncommented in the /etc/cumulus/switchd.conf file:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/switchd.conf
...
# configure IP based forwarding for L2 Multicast
bridge.dip_based_l2multicast = TRUE
...
Configure IGMP/MLD Querier
If no multicast router is sending queries to configure IGMP/MLD querier
on the switch, you can add a configuration similar to the following in
/etc/network/interfaces. To enable IGMP and MLD snooping for a bridge,
set bridge-mcquerier to 1 in the bridge stanza. By default, the
source IP address of IGMP queries is 0.0.0.0. To set the source IP
address of the queries to be the bridge IP address, configure
bridge-mcqifaddr 1.
For an explanation of the relevant parameters, see the
ifupdown-addons-interfaces man page.
For a VLAN-aware bridge, use a configuration like the following:
auto bridge.100
vlan bridge.100
bridge-igmp-querier-src 123.1.1.1
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 swp3
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 100 200
bridge-pvid 1
bridge-mcquerier 1
For a VLAN-aware bridge, like bridge in the above example, to enable
querier functionality for VLAN 100 in the bridge, set bridge-mcquerier
to 1 in the bridge stanza and set bridge-igmp-querier-src to
123.1.1.1 in the bridge.100 stanza.
You can specify a range of VLANs as well. For example:
auto bridge.[1-200]
vlan bridge.[1-200]
bridge-igmp-querier-src 123.1.1.1
For a bridge in traditional mode, use a configuration like the following:
auto br0
iface br0
address 192.0.2.10/24
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 swp3
bridge-vlan-aware no
bridge-mcquerier 1
bridge-mcqifaddr 1
Disable IGMP and MLD Snooping
To disable IGMP and MLD snooping, set the bridge-mcsnoop value to 0.
The example NCLU commands below create a VLAN-aware bridge interface for a VRR-enabled network:
cumulus@switch:~$ net add bridge bridge mcsnoop no
cumulus@switch:~$ net pending
cumulus@switch:~$ net commit
The commands above add the bridge-mcsnoop line to the following
example bridge in /etc/network/interfaces:
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-mcquerier 1
bridge-mcsnoop 0
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 swp3
bridge-pvid 1
bridge-vids 100 200
bridge-vlan-aware yes
Troubleshooting
To show the IGMP/MLD snooping bridge state, run brctl showstp <bridge>:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo brctl showstp bridge
bridge
bridge id 8000.7072cf8c272c
designated root 8000.7072cf8c272c
root port 0 path cost 0
max age 20.00 bridge max age 20.00
hello time 2.00 bridge hello time 2.00
forward delay 15.00 bridge forward delay 15.00
ageing time 300.00
hello timer 0.00 tcn timer 0.00
topology change timer 0.00 gc timer 263.70
hash elasticity 4096 hash max 4096
mc last member count 2 mc init query count 2
mc router 1 mc snooping 1
mc last member timer 1.00 mc membership timer 260.00
mc querier timer 255.00 mc query interval 125.00
mc response interval 10.00 mc init query interval 31.25
mc querier 0 mc query ifaddr 0
flags
swp1 (1)
port id 8001 state forwarding
designated root 8000.7072cf8c272c path cost 2
designated bridge 8000.7072cf8c272c message age timer 0.00
designated port 8001 forward delay timer 0.00
designated cost 0 hold timer 0.00
mc router 1 mc fast leave 0
flags
swp2 (2)
port id 8002 state forwarding
designated root 8000.7072cf8c272c path cost 2
designated bridge 8000.7072cf8c272c message age timer 0.00
designated port 8002 forward delay timer 0.00
designated cost 0 hold timer 0.00
mc router 1 mc fast leave 0
flags
swp3 (3)
port id 8003 state forwarding
designated root 8000.7072cf8c272c path cost 2
designated bridge 8000.7072cf8c272c message age timer 0.00
designated port 8003 forward delay timer 8.98
designated cost 0 hold timer 0.00
mc router 1 mc fast leave 0
flags
To show the groups and bridge port state, run the NCLU net show bridge mdb command or the Linux bridge mdb show
command. To show detailed router ports and group information, run the bridge -d -s mdb show command:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo bridge -d -s mdb show
dev bridge port swp2 grp 234.10.10.10 temp 241.67
dev bridge port swp1 grp 238.39.20.86 permanent 0.00
dev bridge port swp1 grp 234.1.1.1 temp 235.43
dev bridge port swp2 grp ff1a::9 permanent 0.00
router ports on bridge: swp3