EVPN BUM Traffic with PIM-SM
Without EVPN and PIM-SM, HER is the default way to replicate BUM traffic to remote VTEPs, where the ingress VTEP generates the same number of copies as VTEPs for each overlay BUM packet. In certain deployments, this is not optimal.
The following example shows a EVPN-PIM configuration, where underlay multicast distributes BUM traffic. An MDT optimizes the flow of overlay BUM traffic in the underlay network.
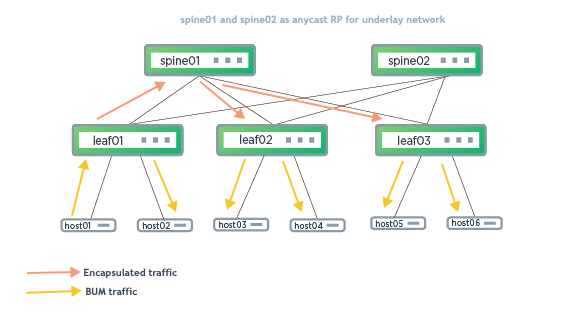
In the above example, host01 sends an ARP request to resolve host03. leaf01 (in addition to flooding the packet to host02) sends an encapsulated packet over the underlay network, which the spine forwards using the MDT to leaf02 and leaf03.
For PIM-SM, type-3 routes do not result in any forwarding entries. Cumulus Linux does not advertise type-3 routes for a layer 2 VNI when BUM mode for that VNI is PIM-SM.
If you use a PIM-SM based MDT for EVPN BUM replication, NVIDIA recommends that you use EVPN multihoming.
Configure Multicast VXLAN Tunnels
To configure multicast VXLAN tunnels, you need to configure PIM-SM in the underlay:
- Enable PIM-SM on the appropriate layer 3 interfaces.
- Configure static RP on all the PIM routers.
- Configure MSDP on the RPs for RP redundancy.
For the configuration steps to configure PIM-SM in the underlay, refer to Protocol Independent Multicast - PIM.
In addition to the PIM-SM configuration, you need to run the following commands on each VTEP to provide the layer 2 VNI to MDT mapping.
Run the nv set nve vxlan flooding multicast-group <ip-address> command. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set nve vxlan flooding multicast-group 224.0.0.10
Edit the /etc/network/interfaces file and add vxlan-mcastgrp <ip-address> to the interface stanza. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto vxlan10
iface vxlan10
vxlan-id 10
vxlan-mcastgrp 224.0.0.10
...
Run the ifreload -a command to load the new configuration:
cumulus@switch:~$ ifreload -a
One multicast group per layer 2 VNI is optimal configuration for underlay bandwidth utilization. However, you can specify the same multicast group for more than one layer 2 VNI.
Verify EVPN-PIM
Run the net show mroute command or the vtysh show ip mroute command to review the multicast route information in FRR. When using EVPN-PIM, every VTEP acts as both source and destination for a VNI-MDT group, therefore, mroute entries on each VTEP should look like this:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# show ip mroute
IP Multicast Routing Table
Flags: S - Sparse, C - Connected, P - Pruned
R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set
Source Group Flags Proto Input Output TTL Uptime
* 224.0.0.10 S IGMP swp54 pimreg 1 23:20:54
ipmr-lo 1
10.10.10.1 224.0.0.10 SFT PIM lo swp51 1 23:20:56
* 224.0.0.20 S IGMP swp53 pimreg 1 23:20:54
ipmr-lo 1
10.10.10.1 224.0.0.20 SFT PIM lo swp52 1 23:20:56
* 224.0.0.30 S IGMP swp51 pimreg 1 23:20:54
ipmr-lo 1
10.10.10.1 224.0.0.30 SFT PIM lo swp53 1 23:20:56
(*,G) entries should show ipmr-lo in the OIL (Outgoing Interface List) and (S,G) entries should show lo as the Source interface or incoming interface and ipmr-lo in the OIL.
Run the ip mroute command to review the multicast route information in the kernel. The kernel information should match the FRR information.
cumulus@switch:~$ ip mroute
(10.10.10.1,224.0.0.30) Iif: lo Oifs: swp53 State: resolved
(10.10.10.1,224.0.0.20) Iif: lo Oifs: swp52 State: resolved
(10.10.10.1,224.0.0.10) Iif: lo Oifs: swp51 State: resolved
(0.0.0.0,224.0.0.10) Iif: swp54 Oifs: pimreg ipmr-lo swp54 State: resolved
(0.0.0.0,224.0.0.20) Iif: swp53 Oifs: pimreg ipmr-lo swp53 State: resolved
(0.0.0.0,224.0.0.30) Iif: swp51 Oifs: pimreg ipmr-lo swp51 State: resolved
Run the bridge fdb show | grep 00:00:00:00:00:00 command to verify that all zero MAC addresses for every VXLAN device point to the correct multicast group destination.
cumulus@switch:~$ bridge fdb show | grep 00:00:00:00:00:00
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan10 dst 224.0.0.10 self permanent
00:00:00:00:00:00 dev vxlan20 dst 224.0.0.20 self permanent
The show ip mroute count command, often used to check multicast packet counts does not update for encapsulated BUM traffic originating or terminating on the VTEPs.
Run the net show evpn vni <vni> command or the vtysh show evpn vni <vni> command to ensure that your layer 2 VNI has the correct flooding information:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
switch# show evpn vni 10
VNI: 10
Type: L2
Tenant VRF: default
VxLAN interface: vni10
VxLAN ifIndex: 18
Local VTEP IP: 10.10.10.1
Mcast group: 224.0.0.10 <<<<<<<
Remote VTEPs for this VNI:
10.10.10.3 flood: -
Number of MACs (local and remote) known for this VNI: 6
Number of ARPs (IPv4 and IPv6, local and remote) known for this VNI: 14
Advertise-gw-macip: No
Example Configuration
The following example shows an EVPN-PIM configuration on the VTEP, where:
- PIM is on swp51 thru swp54 and the loopback interface (see the example
/etc/frr/frr.conffile below). - The group mapping 10.10.100.100 is for a static RP (see the top of the
/etc/frr/frr.conffile example below). - Multicast group 224.0.0.10 maps to VNI10, multicast group 224.0.0.20 maps to VNI20, and multicast group 224.0.0.30 maps to VNI30 (see the example
/etc/network/interfacesfile below).
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
ip pim rp 10.10.100.100
ip pim keep-alive-timer 3600
ip pim ecmp
service integrated-vtysh-config
vrf BLUE
vni 4002
exit-vrf
vrf RED
vni 4001
exit-vrf
vrf mgmt
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.200.1
exit-vrf
interface swp51
ip pim
interface swp52
ip pim
interface swp53
ip pim
interface swp54
ip pim
interface lo
ip igmp
ip pim
ip pim use-source 10.10.10.1
router bgp 65101
bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
neighbor underlay peer-group
neighbor underlay remote-as external
neighbor swp51 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp52 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp53 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp54 interface peer-group underlay
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor underlay activate
advertise-all-vni
exit-address-family
!
router bgp 65101 vrf RED
bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
!
router bgp 65101 vrf BLUE
bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.1/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.1
auto eth0
iface eth0
vrf mgmt
address 192.168.200.11/24
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
vrf-table auto
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
auto RED
iface RED
vrf-table auto
auto BLUE
iface BLUE
vrf-table auto
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports bond1 bond2 bond3
bridge-ports vni10 vni20 vni30 vniRED vniBLUE
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-vlan-aware yes
auto vni10
iface vni10
bridge-access 10
vxlan-id 10
mstpctl-portbpdufilter yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
bridge-learning off
bridge-arp-nd-suppress on
vxlan-mcastgrp 224.0.0.10
auto vni20
iface vni20
bridge-access 20
vxlan-id 20
mstpctl-portbpdufilter yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
bridge-learning off
bridge-arp-nd-suppress on
vxlan-mcastgrp 224.0.0.20
auto vni30
iface vni30
bridge-access 30
vxlan-id 30
mstpctl-portbpdufilter yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
bridge-learning off
bridge-arp-nd-suppress on
vxlan-mcastgrp 224.0.0.30
auto vniRED
iface vniRED
bridge-access 4001
vxlan-id 4001
mstpctl-portbpdufilter yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
bridge-learning off
bridge-arp-nd-suppress on
auto vniBLUE
iface vniBLUE
bridge-access 4002
vxlan-id 4002
mstpctl-portbpdufilter yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
bridge-learning off
bridge-arp-nd-suppress on
auto vlan10
iface vlan10
address 10.1.10.2/24
address-virtual 00:00:00:00:00:10 10.1.10.1/24
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device bridge
vlan-id 10
auto vlan20
iface vlan20
address 10.1.20.2/24
address-virtual 00:00:00:00:00:20 10.1.20.1/24
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device bridge
vlan-id 20
auto vlan30
iface vlan30
address 10.1.30.2/24
address-virtual 00:00:00:00:00:30 10.1.30.1/24
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device bridge
vlan-id 30
auto vlan4001
iface vlan4001
hwaddress 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device bridge
vlan-id 4001
auto vlan4002
iface vlan4002
hwaddress 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device bridge
vlan-id 4002
auto swp51
iface swp51
alias to spine
auto swp52
iface swp52
alias to spine
auto swp53
iface swp53
alias to spine
auto swp54
iface swp54
alias to spine
auto swp1
iface swp1
alias bond member of bond1
auto bond1
iface bond1
bond-slaves swp1
bridge-access 10
mtu 9000
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
mstpctl-portadminedge yes
auto swp2
iface swp2
alias bond member of bond2
auto bond2
iface bond2
bond-slaves swp2
bridge-access 20
mtu 9000
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
mstpctl-portadminedge yes
auto swp3
iface swp3
alias bond member of bond3
auto bond3
iface bond3
bond-slaves swp3
bridge-access 30
mtu 9000
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
mstpctl-bpduguard yes
mstpctl-portadminedge yes
Configure EVPN-PIM in VXLAN Active-active Mode
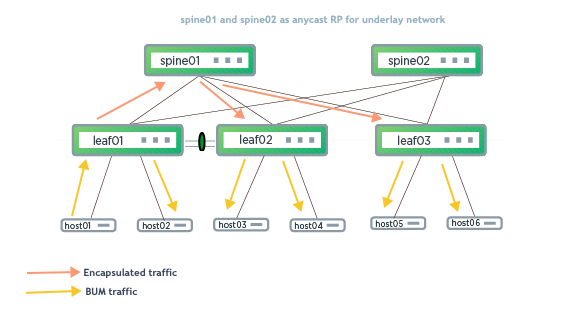
To configure EVPN-PIM with an MLAG pair in VXLAN active-active mode, enable PIM on the peer link subinterface of each MLAG peer switch (in addition to the configuration described in Configure Multicast VXLAN Tunnels, above).
Run the nv set interface <peerlink> router pim command. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set interface peerlink.4094 router pim
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
In the vtysh shell, run the following commands:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# interface peerlink.4094
switch(config-if)# ip pim
switch(config-if)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
cumulus@switch:~$