EVPN Multihoming
EVPN multihoming (EVPN-MH) provides support for all-active server redundancy. It is a standards-based replacement for MLAG in data centers deploying Clos topologies. Replacing MLAG provides these benefits:
- Eliminates the need for peerlinks or inter-switch links between the top of rack switches
- Allows more than two ToR switches a redundancy group
- Provides a single BGP-EVPN control plane
- Allows multi-vendor interoperability
EVPN-MH uses BGP-EVPN type-1, type-2 and type-4 routes to discover Ethernet segments (ES) and to forward traffic to those Ethernet segments. The MAC and neighbor databases synchronize between the Ethernet segment peers through these routes as well. An Ethernet segment is a group of switch links that attach to the same server. Each Ethernet segment has an unique Ethernet segment ID (ESI) across the entire PoD.
To configure EVPN-MH, you set an Ethernet segment system MAC address and a local Ethernet segment ID on a static or LACP bond. These two parameters generate the unique MAC-based ESI value (type-3) automatically:
-
The Ethernet segment system MAC address is the LACP system identifier.
-
The local Ethernet segment ID configuration defines a local discriminator to uniquely enumerate each bond that shares the same Ethernet segment system MAC address.
-
The resulting 10-byte ESI value has the following format, where the MMs denote the 6-byte Ethernet segment system MAC address and the XXs denote the 3-byte local Ethernet segment ID value:
03:MM:MM:MM:MM:MM:MM:XX:XX:XX
While you can specify a different system MAC address on different Ethernet segments attached to the same switch, the Ethernet segment system MAC address must be the same on the downlinks attached to the same server.
On Spectrum-2 and later, an Ethernet segment can span more than two switches. Each Ethernet segment is a distinct redundancy group. However, on Spectrum A1 switches, you can include a maximum of two switches in a redundancy group or Ethernet segment.
Required and Supported Features
This section describes features that you must enable to use EVPN multihoming. Other supported and unsupported features are also described.
Required Features
You must enable the following features to use EVPN-MH:
Cumulus Linux uses HER by default with EVPN multihoming. If you prefer to use EVPN BUM traffic handling with EVPN-PIM on multihomed sites through Type-4/ESR routes, configure EVPN-PIM as described in EVPN BUM Traffic with PIM-SM. You cannot configure both EVPN-PIM and HER at the same time with EVPN-MH; use either EVPN-PIM or HER.
On Spectrum A1 switches, NVIDIA recommends that you use a PIM-SM underlay to distribute BUM traffic with EVPN multihoming for better performance. To check if you have a Spectrum A1 switch, run the sudo decode-syseeprom version | egrep -i "tlv|--|device version" command. If the command output shows the Device Version value at 16 or higher, you have a Spectrum A1 switch:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo decode-syseeprom version | egrep -i "tlv|--|device version"
TlvInfo Header:
Id String: TlvInfo
TLV Name Code Len Value
-------------------- ---- --- -----
Device Version 0x26 1 16
To use EVPN-MH, you must remove any MLAG configuration on the switch:
- Remove the
clag-idfrom all interfaces in the/etc/network/interfacesfile. - Remove the peerlink interfaces in the
/etc/network/interfacesfile. - Remove any existing
hwaddress(from a Cumulus Linux 3.x MLAG configuration) oraddress-virtual(from a Cumulus Linux 4.x MLAG configuration) entries from all SVIs corresponding to a layer 3 VNI in the/etc/network/interfacesfile. - Remove any
clagd-vxlan-anycast-ipconfiguration in the/etc/network/interfacesfile. - Run the
sudo ifreloadcommand to reload the configuration.
Supported Features
- Known unicast traffic multihoming through type-1/EAD (Ethernet auto discovery) routes and type-2 (non-zero ESI) routes. Includes all-active redundancy using aliasing and support for fast failover.
- LACP Bypass.
- When an EVPN-MH bond enters LACP bypass state, BGP stops advertising EVPN type-1 and type-4 routes for that bond. The switch disables split-horizon and designated forwarder filters.
- When an EVPN-MH bond exits the LACP bypass state, BGP starts advertising EVPN type-1 and type-4 routes for that bond. The switch enables split-horizon and designated forwarder filters.
- EVI - Cumulus Linux supports VLAN-based service only, so the EVI is just a layer 2 VNI.
- Supported ASICs include NVIDIA Spectrum A1, Spectrum-2 and later.
Supported EVPN Route Types
EVPN multihoming supports the following route types.
| Route Type | Description | RFC or Draft |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ethernet auto-discovery (A-D) route | RFC 7432 |
| 2 | MAC/IP advertisement route | RFC 7432 |
| 3 | Inclusive multicast route | RFC 7432 |
| 4 | Ethernet segment route | RFC 7432 |
| 5 | IP prefix route | draft-ietf-bess-evpn-prefix-advertisement-04 |
Unsupported Features
The following features are not supported with EVPN-MH:
- Traditional bridge mode
- Distributed asymmetric routing
- Centralized routing
- Duplicate address detection
- Multihomed networks, such as STP bridge domains that are MH connected. EVPN-MH bonds are for multihomed end-node device (server) connectivity.
Basic Configuration
To configure EVPN-MH, you must complete all the following steps:
- Enable EVPN multihoming.
- Configure an ESI on each EVPN-MH bond interface.
- Configure multihoming uplinks.
You can associate static and LACP bonds with an ESI.
The switch selects a designated forwarder (DF) for each Ethernet segment. The DF forwards flooded traffic received through the VXLAN overlay to the locally attached Ethernet segment. Specify a preference on an Ethernet segment for the DF election, as this leads to predictable failure scenarios. The EVPN VTEP with the highest DF preference setting becomes the DF. The DF preference setting defaults to 32767.
NVUE generates the EVPN-MH configuration and reloads FRR and ifupdown2. The configuration appears in both the /etc/network/interfaces file and in /etc/frr/frr.conf file.
When you enable EVPN-MH, all SVI MAC addresses advertise as type-2 routes. You do not need to configure a unique SVI IP address or configure the BGP EVPN address family with advertise-svi-ip.
Enable EVPN-MH
NVIDIA recommends that you enable EVPN-MH on all VTEPs throughout the fabric to avoid duplicate packets.
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set evpn multihoming enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
When you enable multihoming on the Spectrum A1 switch with the nv set evpn multihoming enable on command, NVUE restarts the switchd service, which causes all network ports to reset in addition to resetting the switch hardware configuration.
On a switch with the Spectrum A1 ASIC, set the evpn.multihoming.enable variable in the /etc/cumulus/switchd.conf file to TRUE. On a switch with Spectrum-2 and later, no action is required.
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/switchd.conf
...
evpn.multihoming.enable = TRUE
...
Restart switchd with the sudo systemctl restart switchd.service command.
Configure the EVPN-MH Bonds
To configure bond interfaces for EVPN-MH:
You can either set both the local Ethernet segment ID and the segment MAC address to generate a unique ESI automatically or set the 10-byte Ethernet segment ID manually, then set the segment MAC address. You can see both options below.
The following example commands configure each bond interface with the local Ethernet segment ID and the segment MAC address to generate a unique ESI automatically:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp2
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp3
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 evpn multihoming segment local-id 1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 evpn multihoming segment local-id 2
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 evpn multihoming segment local-id 3
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment df-preference 50000
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
The following example commands configure each bond interface with the Ethernet segment ID manually. The ID must be a 10-byte (80-bit) integer and must be unique. When you configure the 10-byte Ethernet segment ID, ensure that the local ID is not present. You must also configure the segment MAC address. The example configures a global segment MAC address for use on all the Ethernet segment bonds.
In Cumulus Linux 5.6 and later, NVUE no longer supports a 10-byte ESI value starting with a non 00 hex value.
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp2
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp3
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 evpn multihoming segment identifier 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:01
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 evpn multihoming segment identifier 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:02
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 evpn multihoming segment identifier 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:03
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment df-preference 50000
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set evpn multihoming segment mac-address 44:38:39:ff:ff:01
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
The following example commands configure each bond interface with the local Ethernet segment ID and the segment MAC address to generate a unique ESI automatically:
-
Configure the ESI on each bond interface with the local Ethernet segment ID and the segment MAC address:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh leaf01# configure terminal leaf01(config)# interface bond1 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-id 1 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# interface bond2 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-id 2 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# interface bond3 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-id 3 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# write memory leaf01(config)# exit leaf01# exit cumulus@leaf01:~$The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the
/etc/frr/frr.conffile.cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf ... ! interface bond1 evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 evpn mh es-id 1 evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA ! interface bond2 evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 evpn mh es-id 2 evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA ! interface bond3 evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 evpn mh es-id 3 evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA ! -
Add the segment MAC address to the bond interfaces in the
/etc/network/interfacesfile, then run theifreload -acommand.cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces ... interface bond1 bond-slaves swp1 es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA interface bond2 bond-slaves swp2 es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA interface bond3 bond-slaves swp3 es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AAcumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo ifreload -a
The following example commands configure each bond interface with the Ethernet segment ID manually. The ID must be a 10-byte (80-bit) integer and must be unique. When you configure the 10-byte Ethernet segment ID, ensure that the local ID is not present. You must also configure the segment MAC address separately. The example configures a global segment MAC address for use on all the Ethernet segment bonds.
In Cumulus Linux 5.6 and later, NVUE no longer supports a 10-byte ESI value starting with a non 00 hex value.
-
Configure each bond interface with the Ethernet segment ID manually:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh leaf01# configure terminal leaf01(config)# interface bond1 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-id 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:01 leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# interface bond2 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-id 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:02 leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# interface bond3 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh es-id 00:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03 leaf01(config-if)# exit leaf01(config)# write memory leaf01(config)# exit leaf01# exit cumulus@leaf01:~$The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the
/etc/frr/frr.conffile.cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf ... interface bond1 evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 evpn mh es-id 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:01 interface bond2 evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 evpn mh es-id 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:02 interface bond3 evpn mh es-df-pref 50000 evpn mh es-id 00:44:38:39:BE:EF:AA:00:00:03 ... -
Add the segment MAC address to the bond interfaces in the
/etc/network/interfacesfile, then run theifreload -acommand.cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces ... interface bond1 bond-slaves swp1 es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA interface bond2 bond-slaves swp2 es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA interface bond3 bond-slaves swp3 es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
Enable uplink Tracking
When all uplinks go down, the VTEP loses connectivity to the VXLAN overlay. To prevent traffic loss, Cumulus Linux tracks the operational state of the uplink. When all the uplinks are down, the Ethernet segment bonds on the switch are in a protodown or error-disabled state. An MH uplink is any routed interface to which the switch routes locally encapsulated VXLAN traffic (after encapsulation) or any routed interface receiving VXLAN traffic (before decapsulation) that the local device decapsulates.
Split-horizon and Designated-Forwarder filters only apply to interfaces that are MH uplinks. If you configure EVPN-MH without MH uplinks, BUM traffic duplicates or loops back to the same ES. This can cause MAC flaps or other issues on multihomed devices.
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51-54 evpn multihoming uplink on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
If you are configuring EVPN multihoming with EVPN-PIM, be sure to configure PIM on the interfaces.
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
...
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# interface swp51
leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh uplink
leaf01(config-if)# exit
leaf01(config)# interface swp52
leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh uplink
leaf01(config-if)# exit
leaf01(config)# interface swp53
leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh uplink
leaf01(config-if)# exit
leaf01(config)# interface swp54
leaf01(config-if)# evpn mh uplink
leaf01(config-if)# exit
leaf01(config)# write memory
leaf01(config)# exit
leaf01# exit
cumulus@leaf01:~$
The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
!
interface swp1
evpn mh uplink
!
interface swp2
evpn mh uplink
!
interface swp3
evpn mh uplink
!
interface swp4
evpn mh uplink
!
...
To show if uplinks are down, run the nv show interface status command:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv show interface status
Interface Admin Status Oper Status Protodown Protodown Reason
----------- ------------ ----------- --------- ----------------
br_default up up disabled
br_l3vni up up disabled
eth0 up up disabled
bond3 up down disabled
bond4 up down disabled
bond5 up down disabled
bond6 up up disabled
lo up unknown disabled
mgmt up up disabled
swp5 up down enabled frr <<<< part of bond3
swp6 up down enabled frr
swp7 up down enabled frr
Optional EVPN MH Configuration
Global Settings
You can set these global settings for EVPN-MH:
mac-holdtimespecifies the duration for which a switch maintains SYNC MAC entries after the switch deletes the EVPN type-2 route of the Ethernet segment peer. During this time, the switch attempts to independently establish reachability of the MAC address on the local Ethernet segment. The hold time can be between 0 and 86400 seconds. The default is 1080 seconds.neigh-holdtimespecifies the duration for which a switch maintains SYNC neighbor entries after the switch deletes the EVPN type-2 route of the Ethernet segment peer. During this time, the switch attempts to independently establish reachability of the host on the local Ethernet segment. The hold time can be between 0 and 86400 seconds. The default is 1080 seconds.redirect-offdisables fast failover of traffic destined to the access port through the VXLAN overlay. This only applies to Cumulus VX.startup-delayspecifies the duration for which a switch holds the Ethernet segment-bond in a protodown state after a reboot or process restart. This allows the initialization of the VXLAN overlay to complete. The delay can be between 0 and 216000 seconds. The default is 180 seconds.
To configure a MAC hold time for 1000 seconds, run the following commands:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set evpn multihoming mac-holdtime 1000
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# evpn mh mac-holdtime 1000
leaf01(config)# exit
leaf01# write memory
The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh mac-holdtime 1000
To configure a neighbor hold time for 600 seconds, run the following commands:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set evpn multihoming neighbor-holdtime 600
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# evpn mh neigh-holdtime 600
leaf01(config)# exit
leaf01# write memory
The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh neigh-holdtime 600
To configure a startup delay for 1800 seconds, run the following commands:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set evpn multihoming startup-delay 1800
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# evpn mh startup-delay 1800
leaf01(config)# exit
leaf01# write memory
The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh startup-delay 1800
To disable fast failover of traffic destined to the access port through the VXLAN overlay (for Cumulus VX):
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# evpn mh redirect-off
leaf01(config)# exit
leaf01# write memory
The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh redirect-off
Enable FRR Debugging
You can add debug statements to the /etc/frr/frr.conf file to debug the Ethernet segments, routes, and routing protocols (via Zebra).
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo vtysh
...
leaf01# configure terminal
leaf01(config)# debug bgp evpn mh es
leaf01(config)# debug bgp evpn mh route
leaf01(config)# debug bgp zebra
leaf01(config)# debug zebra evpn mh es
leaf01(config)# debug zebra evpn mh mac
leaf01(config)# debug zebra evpn mh neigh
leaf01(config)# debug zebra evpn mh nh
leaf01(config)# debug zebra vxlan
leaf01(config)# write memory
leaf01(config)# exit
leaf01# exit
cumulus@leaf01:~$
The vtysh commands create the following configuration in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file:
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
!
debug bgp evpn mh es
debug bgp evpn mh route
debug bgp zebra
debug zebra evpn mh es
debug zebra evpn mh mac
debug zebra evpn mh neigh
debug zebra evpn mh nh
debug zebra vxlan
!
...
Fast failover
When an Ethernet segment link goes down, the attached VTEP notifies all other VTEPs using a single EAD-ES withdraw. Cumulus Linux uses an Ethernet segment bond redirect.
Fast failover also triggers:
- When you reboot a leaf switch or VTEP.
- When there is an uplink failure. When all uplinks are down, the Ethernet segment bonds on the switch are protodown or error disabled.
Disable Next Hop Group Sharing in the ASIC
When you configure EVPN-MH, container sharing for both layer 2 and layer 3 next hop groups is on by default. The switch stores these settings in the evpn.multihoming.shared_l2_groups and evpn.multihoming.shared_l3_groups variables.
Disabling container sharing allows for faster failover when an Ethernet segment link flaps.
To disable either setting, edit the switchd.conf file, set the variable to FALSE, then restart the switchd service. For example, to disable container sharing for layer 3 next hop groups:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo nano /etc/cumulus/switchd.conf
...
evpn.multihoming.shared_l3_groups = FALSE
...
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo systemctl restart switchd.service
Disable EAD-per-EVI Route Advertisements
RFC 7432 requires the switch to advertise type-1/EAD (Ethernet Auto-discovery) routes:
- As EAD-per-ES (Ethernet Auto-discovery per Ethernet segment) routes
- As EAD-per-EVI (Ethernet Auto-discovery per EVPN instance) routes
Some third party switch vendors do not advertise EAD-per-EVI routes; they only advertise EAD-per-ES routes. To interoperate with these vendors, you need to disable EAD-per-EVI route advertisements.
To remove the dependency on EAD-per-EVI routes and activate the VTEP upon receiving the EAD-per-ES route:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set evpn multihoming ead-evi-route rx off
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
To suppress the advertisement of EAD-per-EVI routes, run:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv set evpn multihoming ead-evi-route tx off
cumulus@switch:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router bgp
switch(config-router)# address-family l2vpn evpn
switch(config-router-af)# disable-ead-evi-rx
switch(config-router-af)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
cumulus@switch:~$
To suppress the advertisement of EAD-per-EVI routes, run:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# router bgp
switch(config-router)# address-family l2vpn evpn
switch(config-router-af)# disable-ead-evi-tx
switch(config-router-af)# end
switch# write memory
switch# exit
cumulus@switch:~$
Troubleshooting
Use the following commands to troubleshoot your EVPN multihoming configuration.
Show Global EVPN-MH Information
To show global EVPN-MH information, such as the uplink count, startup delay timer, neighbor hold time, and MAC entry hold time, run the NVUE nv show evpn multihoming command:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show evpn multihoming
operational applied
------------------- ----------- -------
enable on
mac-holdtime 1080 1080
neighbor-holdtime 1080 1080
startup-delay 180 180
ead-evi-route
rx on
tx on
segment
df-preference 32767
startup-delay-timer --:--:--
uplink-active 2
uplink-count 2
Show Ethernet Segment Information
To show the Ethernet segments across all VNIs, run the nv show evpn multihoming esi command or the vtysh show evpn es command. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show evpn multihoming esi
SInterface - Local interface, NHG - Nexthop group ID, DFPref - Designated
forwarder preference, VNICnt - ESI EVPN instances, MacCnt - Mac entries using
this ES as destination, RemoteVTEPs - Remote tunnel Endpoint
ESI ESInterface NHG DFPref VNICnt MacCnt Flags RemoteVTEPs
----------------------------- ----------- --------- ------ ------ ------ ------ -----------
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01 bond1 536870913 50000 1 2 local 10.10.10.2
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02 bond2 536870914 50000 1 2 local 10.10.10.2
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03 bond3 536870915 50000 1 2 local 10.10.10.2
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:01 536870916 0 0 2 remote 10.10.10.3
10.10.10.4
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# show evpn es
Type: B bypass, L local, R remote, N non-DF
ESI Type ES-IF VTEPs
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01 LR bond1 10.10.10.2
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02 LR bond2 10.10.10.2
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03 LR bond3 10.10.10.2
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:01 R - 10.10.10.3,10.10.10.4
You can also show the Ethernet segments across all VNIs with NVUE in json format:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show evpn multihoming esi -o json
{
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01": {
"df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"bridge-port": "on",
"designated-forward": "on",
"local": "on",
"nexthop-group-active": "on",
"oper-up": "on",
"ready-for-bgp": "on",
"remote": "on"
},
"local-interface": "bond1",
"mac-count": 2,
"nexthop-group-id": 536870913,
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.2": {
"df-algorithm": "preference",
"df-preference": 50000,
"nexthop-group-id": 268435462
}
},
"vni-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02": {
"df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"bridge-port": "on",
"designated-forward": "on",
"local": "on",
"nexthop-group-active": "on",
"oper-up": "on",
"ready-for-bgp": "on",
"remote": "on"
},
"local-interface": "bond2",
"mac-count": 2,
"nexthop-group-id": 536870914,
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.2": {
"df-algorithm": "preference",
"df-preference": 50000,
"nexthop-group-id": 268435462
}
},
"vni-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03": {
"df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"bridge-port": "on",
"designated-forward": "on",
"local": "on",
"nexthop-group-active": "on",
"oper-up": "on",
"ready-for-bgp": "on",
"remote": "on"
},
"local-interface": "bond3",
"mac-count": 2,
"nexthop-group-id": 536870915,
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.2": {
"df-algorithm": "preference",
"df-preference": 50000,
"nexthop-group-id": 268435462
}
},
"vni-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:01": {
"df-preference": 0,
"flags": {
"nexthop-group-active": "on",
"remote": "on"
},
"mac-count": 2,
"nexthop-group-id": 536870916,
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.3": {
"nexthop-group-id": 268435461
},
"10.10.10.4": {
"nexthop-group-id": 268435463
}
},
"vni-count": 0
}
}
To show information about a specific ESI:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show evpn multihoming esi 03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01
operational
-------------------- -----------
df-preference 50000
local-interface bond1
mac-count 2
nexthop-group-id 5.369e+08
vni-count 1
flags
bridge-port on
designated-forward on
local on
oper-up on
ready-for-bgp on
remote on
[remote-vtep] 10.10.10.2
Show Ethernet Segment per VNI Information
To display the Ethernet segments learned for each VNI, run the vtysh show evpn es-evi command. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# show evpn es-evi
Type: L local, R remote
VNI ESI Type
20 03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02 L
30 03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03 L
10 03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01 L
To show the Ethernet segments for a specific VNI, run the NVUE nv show evpn vni <vni> multihoming esi command. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show evpn vni 10 multihoming esi
ESI Local Remote
----------------------------- ----- ------
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01 yes no
Show BGP Ethernet Segment Information
To show the Ethernet segments across all VNIs learned through type-1 and type-4 routes, run the NVUE nv show evpn multihoming bgp-info esi command or the vtysh show bgp l2vpn evpn es command. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show evpn multihoming bgp-info esi
SrcIP - Originator IP, VNICnt - VNI Count, VRFCnt - VRF Count, MACIPCnt - MAC IP
path count, MacGlblCnt - Mac global count, VTEP - Remote VTEP ID, FragID -
Fragments ID
ESI RD SrcIP VNICnt VRFCnt MACIPCnt MacGlblCnt Local Remote VTEP FragID
----------------------------- ------------ ---------- ------ ------ -------- ---------- ----- ------ ---------- ------------
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01 10.10.10.1:3 10.10.10.1 1 1 3 6 yes yes 10.10.10.2 10.10.10.1:3
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02 10.10.10.1:4 10.10.10.1 1 1 2 4 yes yes 10.10.10.2 10.10.10.1:4
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03 10.10.10.1:5 10.10.10.1 1 1 2 4 yes yes 10.10.10.2 10.10.10.1:5
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:01 0.0.0.0 1 1 0 12 yes 10.10.10.3
10.10.10.4
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:02 0.0.0.0 1 1 0 0 yes
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:03 0.0.0.0 1 1 0 0 yes
cumulus@switch:~$ show bgp l2vpn evpn es
ES Flags: B - bypass, L local, R remote, I inconsistent
VTEP Flags: E ESR/Type-4, A active nexthop
ESI Flags RD #VNIs VTEPs
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01 LR 10.10.10.1:3 1 10.10.10.2(EA)
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02 LR 10.10.10.1:4 1 10.10.10.2(EA)
03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03 LR 10.10.10.1:5 1 10.10.10.2(EA)
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:01 R (null) 1 10.10.10.3(A),10.10.10.4(A)
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:02 R (null) 1
03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:03 R (null) 1
You can also show the Ethernet segments across all VNIs learned through type-1 and type-4 routes with NVUE in json format:
cumulus@switch:~$ nv show evpn multihoming bgp-info esi -o json
{
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01": {
"es-df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"advertise-evi": "on",
"up": "on"
},
"fragments": {
"10.10.10.1:3": {
"evi-count": 1
}
},
"inconsistent-vni-count": 0,
"macip-global-path-count": 8,
"macip-path-count": 4,
"originator-ip": "10.10.10.1",
"rd": "10.10.10.1:3",
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.2": {
"df-algorithm": "preference",
"df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"active": "on",
"esr": "on"
}
}
},
"type": {
"local": "on",
"remote": "on"
},
"vni-count": 1,
"vrf-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02": {
"es-df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"advertise-evi": "on",
"up": "on"
},
"fragments": {
"10.10.10.1:4": {
"evi-count": 1
}
},
"inconsistent-vni-count": 0,
"macip-global-path-count": 6,
"macip-path-count": 3,
"originator-ip": "10.10.10.1",
"rd": "10.10.10.1:4",
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.2": {
"df-algorithm": "preference",
"df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"active": "on",
"esr": "on"
}
}
},
"type": {
"local": "on",
"remote": "on"
},
"vni-count": 1,
"vrf-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03": {
"es-df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"advertise-evi": "on",
"up": "on"
},
"fragments": {
"10.10.10.1:5": {
"evi-count": 1
}
},
"inconsistent-vni-count": 0,
"macip-global-path-count": 6,
"macip-path-count": 3,
"originator-ip": "10.10.10.1",
"rd": "10.10.10.1:5",
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.2": {
"df-algorithm": "preference",
"df-preference": 50000,
"flags": {
"active": "on",
"esr": "on"
}
}
},
"type": {
"local": "on",
"remote": "on"
},
"vni-count": 1,
"vrf-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:01": {
"inconsistent-vni-count": 0,
"macip-global-path-count": 16,
"macip-path-count": 0,
"originator-ip": "0.0.0.0",
"remote-vtep": {
"10.10.10.3": {
"flags": {
"active": "on"
}
},
"10.10.10.4": {
"flags": {
"active": "on"
}
}
},
"type": {
"remote": "on"
},
"vni-count": 1,
"vrf-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:02": {
"inconsistent-vni-count": 0,
"macip-global-path-count": 0,
"macip-path-count": 0,
"originator-ip": "0.0.0.0",
"type": {
"remote": "on"
},
"vni-count": 1,
"vrf-count": 1
},
"03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:03": {
"inconsistent-vni-count": 0,
"macip-global-path-count": 0,
"macip-path-count": 0,
"originator-ip": "0.0.0.0",
"type": {
"remote": "on"
},
"vni-count": 1,
"vrf-count": 1
}
}
Show BGP Ethernet Segment per VNI Information
To display the Ethernet segments per VNI learned through type-1 and type-4 routes, run the vtysh show bgp l2vpn evpn es-evi command.
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# show bgp l2vpn evpn es-evi
Flags: L local, R remote, I inconsistent
VTEP-Flags: E EAD-per-ES, V EAD-per-EVI
VNI ESI Flags VTEPs
20 03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02 LR 10.10.10.2(V)
20 03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:02 R 10.10.10.3(V),10.10.10.4(V)
30 03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03 LR 10.10.10.2(V)
30 03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:03 R 10.10.10.3(V),10.10.10.4(V)
10 03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01 LR 10.10.10.2(V)
10 03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:01 R 10.10.10.3(V),10.10.10.4(V)
...
Show EAD Route Types
To view type-1 EAD routes, run the NVUE vtysh show bgp l2vpn evpn route type ead command. For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ sudo vtysh
...
switch# show bgp l2vpn evpn route type ead
BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 10.10.10.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
EVPN type-1 prefix: [1]:[ESI]:[EthTag]:[IPlen]:[VTEP-IP]
EVPN type-2 prefix: [2]:[EthTag]:[MAClen]:[MAC]:[IPlen]:[IP]
EVPN type-3 prefix: [3]:[EthTag]:[IPlen]:[OrigIP]
EVPN type-4 prefix: [4]:[ESI]:[IPlen]:[OrigIP]
EVPN type-5 prefix: [5]:[EthTag]:[IPlen]:[IP]
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Extended Community
Route Distinguisher: 10.10.10.1:2
*> [1]:[0]:[03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02]:[128]:[0.0.0.0]
10.10.10.1 32768 i
ET:8 RT:65101:20
Route Distinguisher: 10.10.10.1:6
*> [1]:[0]:[03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03]:[128]:[0.0.0.0]
10.10.10.1 32768 i
ET:8 RT:65101:30
Route Distinguisher: 10.10.10.1:7
*> [1]:[0]:[03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01]:[128]:[0.0.0.0]
10.10.10.1 32768 i
ET:8 RT:65101:10
Route Distinguisher: 10.10.10.2:2
*> [1]:[0]:[03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:02]:[32]:[0.0.0.0]
10.10.10.2 0 65199 65102 i
RT:65102:20 ET:8
Route Distinguisher: 10.10.10.2:6
*> [1]:[0]:[03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:03]:[32]:[0.0.0.0]
10.10.10.2 0 65199 65102 i
RT:65102:30 ET:8
Route Distinguisher: 10.10.10.2:7
*> [1]:[0]:[03:44:38:39:be:ef:aa:00:00:01]:[32]:[0.0.0.0]
10.10.10.2 0 65199 65102 i
RT:65102:10 ET:8
Route Distinguisher: 10.10.10.3:2
*> [1]:[0]:[03:44:38:39:be:ef:bb:00:00:02]:[32]:[0.0.0.0]
10.10.10.3 0 65199 65103 i
RT:65103:20 ET:8
...
Considerations
If you enable EVPN-MH and configure VLAN match rules in ebtables with a {{mark}} target, the ebtables rule might overwrite the {{mark}} set by traffic class rules you configure for EVPN-MH on ingress. Egress EVPN MH traffic class rules that match the ingress traffic class {{mark}} might not get hit. To work around this issue, add ebtable rules to {{ACCEPT}} the packets already marked by EVPN-MH traffic class rules on ingress.
Configuration Example
The following configuration examples use the topology illustrated below and configure EVPN multihoming with head end replication using single VXLAN devices. The examples provide configuration for server01 through server04. The configuration for server05 and server06 are not included for simplicity.
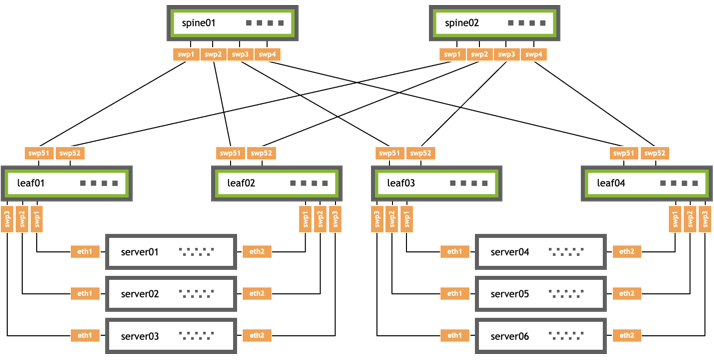
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.1/32
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp1-3,swp51-52
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp2
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp3
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default access 30
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf RED
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 30 vni 30
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf RED evpn vni 4001
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf BLUE evpn vni 4002
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65101
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set router bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay remote-as external
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp51 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp52 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp autonomous-system 65101
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp autonomous-system 65101
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set evpn multihoming enable on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1 evpn multihoming segment local-id 1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond2 evpn multihoming segment local-id 2
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond3 evpn multihoming segment local-id 3
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment df-preference 50000
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set interface swp51-52 evpn multihoming uplink on
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.2/32
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface swp1-3,swp51-52
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp2
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp3
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default access 30
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf RED
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 30 vni 30
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf RED evpn vni 4001
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf BLUE evpn vni 4002
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65102
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set router bgp router-id 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay remote-as external
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp51 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp52 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp autonomous-system 65102
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp router-id 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp autonomous-system 65102
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp router-id 10.10.10.2
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set evpn multihoming enable on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1 evpn multihoming segment local-id 1
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond2 evpn multihoming segment local-id 2
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond3 evpn multihoming segment local-id 3
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment df-preference 50000
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv set interface swp51-52 evpn multihoming uplink on
cumulus@leaf02:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.3/32
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface swp1-3,swp51-52
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp2
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp3
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default access 30
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.4/24
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.4/24
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.4/24
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf RED
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 30 vni 30
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf RED evpn vni 4001
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf BLUE evpn vni 4002
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65103
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set router bgp router-id 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay remote-as external
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp51 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp52 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp autonomous-system 65103
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp router-id 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp autonomous-system 65103
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp router-id 10.10.10.3
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set evpn multihoming enable on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1 evpn multihoming segment local-id 1
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond2 evpn multihoming segment local-id 2
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond3 evpn multihoming segment local-id 3
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment df-preference 50000
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv set interface swp51-52 evpn multihoming uplink on
cumulus@leaf03:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.4/32
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface swp1-3,swp51-52
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp2
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp3
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond lacp-bypass on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default access 10
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond2 bridge domain br_default access 20
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default access 30
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.5/24
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.5/24
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.5/24
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf RED
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 30 vni 30
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrf RED
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf RED evpn vni 4001
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf BLUE evpn vni 4002
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65104
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set router bgp router-id 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay remote-as external
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp51 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp52 peer-group underlay
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp autonomous-system 65104
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp router-id 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp autonomous-system 65104
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp router-id 10.10.10.4
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set vrf BLUE router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set evpn multihoming enable on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1 evpn multihoming segment local-id 1
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond2 evpn multihoming segment local-id 2
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond3 evpn multihoming segment local-id 3
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface bond1-3 evpn multihoming segment df-preference 50000
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv set interface swp51-52 evpn multihoming uplink on
cumulus@leaf04:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.101/32
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set interface swp1-4
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65199
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set router bgp router-id 10.10.10.101
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay remote-as external
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@spine01:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.102/32
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set interface swp1-4
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65199
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set router bgp router-id 10.10.10.102
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay remote-as external
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 peer-group underlay
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group underlay address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
cumulus@spine02:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:~$ cat /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml
- set:
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
vlan:
'10':
vni:
'10': {}
'20':
vni:
'20': {}
'30':
vni:
'30': {}
evpn:
enable: on
multihoming:
enable: on
interface:
bond1:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp1: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 10
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 1
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond2:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp2: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 20
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 2
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond3:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp3: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 30
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 3
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
lo:
ip:
address:
10.10.10.1/32: {}
type: loopback
swp1:
type: swp
swp2:
type: swp
swp3:
type: swp
swp51:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
swp52:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
vlan10:
ip:
address:
10.1.10.2/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.10.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 10
vlan20:
ip:
address:
10.1.20.2/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.20.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 20
vlan30:
ip:
address:
10.1.30.2/24: {}
vrf: BLUE
vrr:
address:
10.1.30.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 30
nve:
vxlan:
arp-nd-suppress: on
enable: on
source:
address: 10.10.10.1
router:
bgp:
autonomous-system: 65101
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.1
vrr:
enable: on
system:
global:
anycast-mac: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
vrf:
BLUE:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4002': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65101
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.1
RED:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4001': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65101
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.1
default:
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
enable: on
neighbor:
swp51:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp52:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
peer-group:
underlay:
address-family:
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
remote-as: external
cumulus@leaf02:~$ cat /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml
- set:
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
vlan:
'10':
vni:
'10': {}
'20':
vni:
'20': {}
'30':
vni:
'30': {}
evpn:
enable: on
multihoming:
enable: on
interface:
bond1:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp1: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 10
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 1
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond2:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp2: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 20
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 2
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond3:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp3: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 30
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 3
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
lo:
ip:
address:
10.10.10.2/32: {}
type: loopback
swp1:
type: swp
swp2:
type: swp
swp3:
type: swp
swp51:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
swp52:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
vlan10:
ip:
address:
10.1.10.3/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.10.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 10
vlan20:
ip:
address:
10.1.20.3/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.20.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 20
vlan30:
ip:
address:
10.1.30.3/24: {}
vrf: BLUE
vrr:
address:
10.1.30.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 30
nve:
vxlan:
arp-nd-suppress: on
enable: on
source:
address: 10.10.10.2
router:
bgp:
autonomous-system: 65102
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.2
vrr:
enable: on
system:
global:
anycast-mac: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
vrf:
BLUE:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4002': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65102
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.2
RED:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4001': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65102
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.2
default:
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
enable: on
neighbor:
swp51:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp52:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
peer-group:
underlay:
address-family:
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
remote-as: external
cumulus@leaf03:~$ cat /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml
- set:
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
vlan:
'10':
vni:
'10': {}
'20':
vni:
'20': {}
'30':
vni:
'30': {}
evpn:
enable: on
multihoming:
enable: on
interface:
bond1:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp1: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 10
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 1
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond2:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp2: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 20
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 2
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond3:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp3: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 30
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 3
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
lo:
ip:
address:
10.10.10.3/32: {}
type: loopback
swp1:
type: swp
swp2:
type: swp
swp3:
type: swp
swp51:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
swp52:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
vlan10:
ip:
address:
10.1.10.4/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.10.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 10
vlan20:
ip:
address:
10.1.20.4/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.20.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 20
vlan30:
ip:
address:
10.1.30.4/24: {}
vrf: BLUE
vrr:
address:
10.1.30.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 30
nve:
vxlan:
arp-nd-suppress: on
enable: on
source:
address: 10.10.10.3
router:
bgp:
autonomous-system: 65103
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.3
vrr:
enable: on
system:
global:
anycast-mac: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
vrf:
BLUE:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4002': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65103
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.3
RED:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4001': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65103
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.3
default:
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
enable: on
neighbor:
swp51:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp52:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
peer-group:
underlay:
address-family:
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
remote-as: external
cumulus@leaf04:~$ cat /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml
- set:
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
vlan:
'10':
vni:
'10': {}
'20':
vni:
'20': {}
'30':
vni:
'30': {}
evpn:
enable: on
multihoming:
enable: on
interface:
bond1:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp1: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 10
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 1
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond2:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp2: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 20
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 2
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
bond3:
bond:
lacp-bypass: on
member:
swp3: {}
bridge:
domain:
br_default:
access: 30
evpn:
multihoming:
segment:
df-preference: 50000
enable: on
local-id: 3
mac-address: 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
link:
mtu: 9000
type: bond
lo:
ip:
address:
10.10.10.4/32: {}
type: loopback
swp1:
type: swp
swp2:
type: swp
swp3:
type: swp
swp51:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
swp52:
evpn:
multihoming:
uplink: on
type: swp
vlan10:
ip:
address:
10.1.10.5/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.10.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 10
vlan20:
ip:
address:
10.1.20.5/24: {}
vrf: RED
vrr:
address:
10.1.20.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 20
vlan30:
ip:
address:
10.1.30.5/24: {}
vrf: BLUE
vrr:
address:
10.1.30.1/24: {}
enable: on
state:
up: {}
type: svi
vlan: 30
nve:
vxlan:
arp-nd-suppress: on
enable: on
source:
address: 10.10.10.4
router:
bgp:
autonomous-system: 65104
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.4
vrr:
enable: on
system:
global:
anycast-mac: 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
vrf:
BLUE:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4002': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65104
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.4
RED:
evpn:
enable: on
vni:
'4001': {}
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
route-export:
to-evpn:
enable: on
autonomous-system: 65104
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.4
default:
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
enable: on
neighbor:
swp51:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp52:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
peer-group:
underlay:
address-family:
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
remote-as: external
cumulus@spine01:~$ cat /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml
- set:
interface:
lo:
ip:
address:
10.10.10.101/32: {}
type: loopback
swp1:
type: swp
swp2:
type: swp
swp3:
type: swp
swp4:
type: swp
router:
bgp:
autonomous-system: 65199
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.101
vrf:
default:
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
enable: on
neighbor:
swp1:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp2:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp3:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp4:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
peer-group:
underlay:
address-family:
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
remote-as: external
cumulus@spine02:~$ cat /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml
- set:
interface:
lo:
ip:
address:
10.10.10.102/32: {}
type: loopback
swp1:
type: swp
swp2:
type: swp
swp3:
type: swp
swp4:
type: swp
router:
bgp:
autonomous-system: 65199
enable: on
router-id: 10.10.10.102
vrf:
default:
router:
bgp:
address-family:
ipv4-unicast:
enable: on
redistribute:
connected:
enable: on
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
enable: on
neighbor:
swp1:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp2:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp3:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
swp4:
peer-group: underlay
type: unnumbered
peer-group:
underlay:
address-family:
l2vpn-evpn:
enable: on
remote-as: external
cumulus@leaf01:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.1/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.1
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto RED
iface RED
vrf-table auto
auto BLUE
iface BLUE
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp51
iface swp51
auto swp52
iface swp52
auto bond1
iface bond1
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
bond-slaves swp1
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 10
auto bond2
iface bond2
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
bond-slaves swp2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 20
auto bond3
iface bond3
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
bond-slaves swp3
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 30
auto vlan10
iface vlan10
address 10.1.10.2/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.10.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:b1
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 10
auto vlan20
iface vlan20
address 10.1.20.2/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.20.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:b1
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 20
auto vlan30
iface vlan30
address 10.1.30.2/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.30.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:b1
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 30
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20 30=30
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-learning off
auto vlan220_l3
iface vlan220_l3
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 220
auto vlan297_l3
iface vlan297_l3
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 297
auto vxlan99
iface vxlan99
bridge-vlan-vni-map 220=4001 297=4002
bridge-vids 220 297
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports bond1 bond2 bond3 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:b1
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-pvid 1
auto br_l3vni
iface br_l3vni
bridge-ports vxlan99
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:b1
bridge-vlan-aware yes
cumulus@leaf02:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.2/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.2
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto RED
iface RED
vrf-table auto
auto BLUE
iface BLUE
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp51
iface swp51
auto swp52
iface swp52
auto bond1
iface bond1
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
bond-slaves swp1
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 10
auto bond2
iface bond2
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
bond-slaves swp2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 20
auto bond3
iface bond3
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
bond-slaves swp3
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 30
auto vlan10
iface vlan10
address 10.1.10.3/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.10.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:af
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 10
auto vlan20
iface vlan20
address 10.1.20.3/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.20.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:af
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 20
auto vlan30
iface vlan30
address 10.1.30.3/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.30.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:af
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 30
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20 30=30
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-learning off
auto vlan220_l3
iface vlan220_l3
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 220
auto vlan297_l3
iface vlan297_l3
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 297
auto vxlan99
iface vxlan99
bridge-vlan-vni-map 220=4001 297=4002
bridge-vids 220 297
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports bond1 bond2 bond3 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:af
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-pvid 1
auto br_l3vni
iface br_l3vni
bridge-ports vxlan99
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:af
bridge-vlan-aware yes
cumulus@leaf03:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.3/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.3
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto RED
iface RED
vrf-table auto
auto BLUE
iface BLUE
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp51
iface swp51
auto swp52
iface swp52
auto bond1
iface bond1
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
bond-slaves swp1
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 10
auto bond2
iface bond2
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
bond-slaves swp2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 20
auto bond3
iface bond3
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
bond-slaves swp3
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 30
auto vlan10
iface vlan10
address 10.1.10.4/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.10.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:bb
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 10
auto vlan20
iface vlan20
address 10.1.20.4/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.20.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:bb
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 20
auto vlan30
iface vlan30
address 10.1.30.4/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.30.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:bb
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 30
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20 30=30
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-learning off
auto vlan220_l3
iface vlan220_l3
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 220
auto vlan297_l3
iface vlan297_l3
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 297
auto vxlan99
iface vxlan99
bridge-vlan-vni-map 220=4001 297=4002
bridge-vids 220 297
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports bond1 bond2 bond3 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:bb
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-pvid 1
auto br_l3vni
iface br_l3vni
bridge-ports vxlan99
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:bb
bridge-vlan-aware yes
cumulus@leaf04:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.4/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.4
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto RED
iface RED
vrf-table auto
auto BLUE
iface BLUE
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp51
iface swp51
auto swp52
iface swp52
auto bond1
iface bond1
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
bond-slaves swp1
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 10
auto bond2
iface bond2
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
bond-slaves swp2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 20
auto bond3
iface bond3
mtu 9000
es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
bond-slaves swp3
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-lacp-bypass-allow yes
bridge-access 30
auto vlan10
iface vlan10
address 10.1.10.5/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.10.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:c1
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 10
auto vlan20
iface vlan20
address 10.1.20.5/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.20.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:c1
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 20
auto vlan30
iface vlan30
address 10.1.30.5/24
address-virtual 00:00:5E:00:01:01 10.1.30.1/24
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:c1
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 30
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20 30=30
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-learning off
auto vlan220_l3
iface vlan220_l3
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 220
auto vlan297_l3
iface vlan297_l3
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 297
auto vxlan99
iface vxlan99
bridge-vlan-vni-map 220=4001 297=4002
bridge-vids 220 297
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports bond1 bond2 bond3 vxlan48
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:c1
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 10 20 30
bridge-pvid 1
auto br_l3vni
iface br_l3vni
bridge-ports vxlan99
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:c1
bridge-vlan-aware yes
cumulus@spine01:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.101/32
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp4
iface swp4
cumulus@spine02:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.102/32
auto mgmt
iface mgmt
address 127.0.0.1/8
address ::1/128
vrf-table auto
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
ip-forward off
ip6-forward off
vrf mgmt
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp4
iface swp4
cumulus@server01:~$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The OOB network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
# The data plane network interfaces
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth1
auto eth2
iface eth2 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth2
auto uplink
iface uplink inet static
address 10.1.10.101
netmask 255.255.255.0
mtu 9000
bond-slaves eth1 eth2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-miimon 100
bond-lacp-rate 1
bond-min-links 1
bond-xmit-hash-policy layer3+4
post-up ip route add 10.0.0.0/8 via 10.1.10.1
cumulus@server02:~$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The OOB network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
# The data plane network interfaces
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth1
auto eth2
iface eth2 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth2
auto uplink
iface uplink inet static
address 10.1.20.102
netmask 255.255.255.0
mtu 9000
bond-slaves eth1 eth2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-miimon 100
bond-lacp-rate 1
bond-min-links 1
bond-xmit-hash-policy layer3+4
post-up ip route add 10.0.0.0/8 via 10.1.20.1
cumulus@server03:~$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The OOB network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
# The data plane network interfaces
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth1
auto eth2
iface eth2 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth2
auto uplink
iface uplink inet static
address 10.1.30.103
netmask 255.255.255.0
mtu 9000
bond-slaves eth1 eth2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-miimon 100
bond-lacp-rate 1
bond-min-links 1
bond-xmit-hash-policy layer3+4
post-up ip route add 10.0.0.0/8 via 10.1.30.1
cumulus@server04:~$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The OOB network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
# The data plane network interfaces
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth1
auto eth2
iface eth2 inet manual
# Required for Vagrant
post-up ip link set promisc on dev eth2
auto uplink
iface uplink inet static
address 10.1.10.104
netmask 255.255.255.0
mtu 9000
bond-slaves eth1 eth2
bond-mode 802.3ad
bond-miimon 100
bond-lacp-rate 1
bond-min-links 1
bond-xmit-hash-policy layer3+4
post-up ip route add 10.0.0.0/8 via 10.1.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh mac-holdtime 1080
evpn mh neigh-holdtime 1080
evpn mh startup-delay 180
interface bond1
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 1
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
interface bond2
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 2
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
interface bond3
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 3
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
interface swp51
evpn mh uplink
interface swp52
evpn mh uplink
vrf BLUE
vni 4002
exit-vrf
vrf RED
vni 4001
exit-vrf
vrf default
exit-vrf
vrf mgmt
exit-vrf
router bgp 65101 vrf default
bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
neighbor underlay peer-group
neighbor underlay remote-as external
neighbor underlay timers 3 9
neighbor underlay timers connect 10
neighbor underlay advertisement-interval 0
no neighbor underlay capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp51 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp51 timers 3 9
neighbor swp51 timers connect 10
neighbor swp51 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp51 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp52 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp52 timers 3 9
neighbor swp52 timers connect 10
neighbor swp52 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp52 capability extended-nexthop
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise-all-vni
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65101 vrf default
router bgp 65101 vrf RED
bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65101 vrf RED
router bgp 65101 vrf BLUE
bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65101 vrf BLUE
...
cumulus@leaf02:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh mac-holdtime 1080
evpn mh neigh-holdtime 1080
evpn mh startup-delay 180
interface bond1
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 1
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
interface bond2
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 2
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
interface bond3
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 3
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
interface swp51
evpn mh uplink
interface swp52
evpn mh uplink
vrf BLUE
vni 4002
exit-vrf
vrf RED
vni 4001
exit-vrf
vrf default
exit-vrf
vrf mgmt
exit-vrf
router bgp 65102 vrf default
bgp router-id 10.10.10.2
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
neighbor underlay peer-group
neighbor underlay remote-as external
neighbor underlay timers 3 9
neighbor underlay timers connect 10
neighbor underlay advertisement-interval 0
no neighbor underlay capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp51 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp51 timers 3 9
neighbor swp51 timers connect 10
neighbor swp51 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp51 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp52 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp52 timers 3 9
neighbor swp52 timers connect 10
neighbor swp52 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp52 capability extended-nexthop
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise-all-vni
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65102 vrf default
router bgp 65102 vrf RED
bgp router-id 10.10.10.2
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65102 vrf RED
router bgp 65102 vrf BLUE
bgp router-id 10.10.10.2
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65102 vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf03:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh mac-holdtime 1080
evpn mh neigh-holdtime 1080
evpn mh startup-delay 180
interface bond1
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 1
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
interface bond2
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 2
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
interface bond3
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 3
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
interface swp51
evpn mh uplink
interface swp52
evpn mh uplink
vrf BLUE
vni 4002
exit-vrf
vrf RED
vni 4001
exit-vrf
vrf default
exit-vrf
vrf mgmt
exit-vrf
router bgp 65103 vrf default
bgp router-id 10.10.10.3
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
neighbor underlay peer-group
neighbor underlay remote-as external
neighbor underlay timers 3 9
neighbor underlay timers connect 10
neighbor underlay advertisement-interval 0
no neighbor underlay capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp51 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp51 timers 3 9
neighbor swp51 timers connect 10
neighbor swp51 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp51 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp52 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp52 timers 3 9
neighbor swp52 timers connect 10
neighbor swp52 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp52 capability extended-nexthop
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise-all-vni
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65103 vrf default
router bgp 65103 vrf RED
bgp router-id 10.10.10.3
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65103 vrf RED
router bgp 65103 vrf BLUE
bgp router-id 10.10.10.3
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65103 vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf03:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
evpn mh mac-holdtime 1080
evpn mh neigh-holdtime 1080
evpn mh startup-delay 180
interface bond1
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 1
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
interface bond2
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 2
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
interface bond3
evpn mh es-df-pref 50000
evpn mh es-id 3
evpn mh es-sys-mac 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
interface swp51
evpn mh uplink
interface swp52
evpn mh uplink
vrf BLUE
vni 4002
exit-vrf
vrf RED
vni 4001
exit-vrf
vrf default
exit-vrf
vrf mgmt
exit-vrf
router bgp 65104 vrf default
bgp router-id 10.10.10.4
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
neighbor underlay peer-group
neighbor underlay remote-as external
neighbor underlay timers 3 9
neighbor underlay timers connect 10
neighbor underlay advertisement-interval 0
no neighbor underlay capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp51 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp51 timers 3 9
neighbor swp51 timers connect 10
neighbor swp51 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp51 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp52 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp52 timers 3 9
neighbor swp52 timers connect 10
neighbor swp52 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp52 capability extended-nexthop
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise-all-vni
neighbor swp51 activate
neighbor swp52 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65104 vrf default
router bgp 65104 vrf RED
bgp router-id 10.10.10.4
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65104 vrf RED
router bgp 65104 vrf BLUE
bgp router-id 10.10.10.4
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65104 vrf BLUE
...
cumulus@spine01:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
vrf default
exit-vrf
vrf mgmt
exit-vrf
router bgp 65199 vrf default
bgp router-id 10.10.10.101
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
neighbor underlay peer-group
neighbor underlay remote-as external
neighbor underlay timers 3 9
neighbor underlay timers connect 10
neighbor underlay advertisement-interval 0
no neighbor underlay capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp1 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp1 timers 3 9
neighbor swp1 timers connect 10
neighbor swp1 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp1 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp2 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp2 timers 3 9
neighbor swp2 timers connect 10
neighbor swp2 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp2 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp3 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp3 timers 3 9
neighbor swp3 timers connect 10
neighbor swp3 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp3 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp4 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp4 timers 3 9
neighbor swp4 timers connect 10
neighbor swp4 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp4 capability extended-nexthop
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor swp1 activate
neighbor swp2 activate
neighbor swp3 activate
neighbor swp4 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor swp1 activate
neighbor swp2 activate
neighbor swp3 activate
neighbor swp4 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65199 vrf default
cumulus@spine02:~$ sudo cat /etc/frr/frr.conf
...
vrf default
exit-vrf
vrf mgmt
exit-vrf
router bgp 65199 vrf default
bgp router-id 10.10.10.102
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
neighbor underlay peer-group
neighbor underlay remote-as external
neighbor underlay timers 3 9
neighbor underlay timers connect 10
neighbor underlay advertisement-interval 0
no neighbor underlay capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp1 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp1 timers 3 9
neighbor swp1 timers connect 10
neighbor swp1 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp1 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp2 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp2 timers 3 9
neighbor swp2 timers connect 10
neighbor swp2 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp2 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp3 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp3 timers 3 9
neighbor swp3 timers connect 10
neighbor swp3 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp3 capability extended-nexthop
neighbor swp4 interface peer-group underlay
neighbor swp4 timers 3 9
neighbor swp4 timers connect 10
neighbor swp4 advertisement-interval 0
neighbor swp4 capability extended-nexthop
! Address families
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor swp1 activate
neighbor swp2 activate
neighbor swp3 activate
neighbor swp4 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor swp1 activate
neighbor swp2 activate
neighbor swp3 activate
neighbor swp4 activate
neighbor underlay activate
exit-address-family
! end of router bgp 65199 vrf default
This simulation starts with the EVPN-MH with Head End Replication configuration. The demo is pre-configured using NVUE commands.
- Run the vtysh
show evpn escommand to show the Ethernet segments across all VNIs. - Run the vtysh
show bgp l2vpn evpn route type eadcommand to show the type-1 EAD routes.
To further validate the configuration, run the commands shown in the troubleshooting section below.
When you run the nv set vrf RED evpn vni 4001 and the nv set vrf BLUE evpn vni 4002 commands, NVUE creates the following in the /etc/network/interfaces file:
- Creates a single VXLAN device (vxlan99)
- Assigns two VLANs automatically from the reserved VLAN range and adds
_l3(layer 3) at the end (for example vlan220_l3 and vlan297_l3) - Maps the VLANs to the VNIs (
bridge-vlan-vni-map 220=4001 297=4002) - Creates a layer 3 bridge called br_l3vni
- Reserves and assigns a dedicated hardware address for the layer 3 bridge from the pool of MAC addresses available on the switch
- Adds the VXLAN device to the br_l3vni bridge
- Assigns vlan220_l3 to vrf RED and vlan297_l3 to vrf BLUE
cumulus@leaf01:~$ sudo cat /etc/network/interfaces
...
auto vlan220_l3
iface vlan220_l3
vrf RED
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 220
auto vlan297_l3
iface vlan297_l3
vrf BLUE
vlan-raw-device br_l3vni
vlan-id 297
auto vxlan99
iface vxlan99
bridge-vlan-vni-map 220=4001 297=4002
bridge-vids 220 297
bridge-learning off
auto br_l3vni
iface br_l3vni
bridge-ports vxlan99
hwaddress 44:38:39:22:01:b1
bridge-vlan-aware yes
...