Cumulus Linux Configuration Guide for Ethernet Storage Fabrics
NVIDIA Spectrum switches with the Cumulus Linux network operating system allow you to create predictable, low latency, high throughput networks. The combination of best-in-class hardware and software enables you to deploy an efficient, redundant, and Ethernet Storage Fabrics (ESFs) optimized network with minimum effort. ESF includes complete, hybrid, or HCI storage fabrics and the storage backend for AI systems.
This configuration guide demonstrates a generic network configuration on NVIDIA Spectrum switches for ESF using the Cumulus Linux operating system with the NVIDIA User Experience - NVUE command line interface (CLI). NVIDIA also offers a portfolio of NVIDIA DGX POD reference architecture solutions with all leading partners.
You can use Cumulus Linux set to configure a redundant active-active layer 2 and layer 3 environment with Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation (MLAG) and Virtual Router Redundancy (VRR).
ESF environments with NVMe over Fabrics (NVMeOF) or GPUDirect technologies typically leverage RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) to speed up the intensive data movements between nodes by eliminating latency-extensive data copying, CPU or GPU interrupts, and context switching. A fully shared buffer architecture enables NVIDIA Spectrum switches to deliver a fair, predictable, line-rate throughput with ultra-low port-to-port latency for RoCE traffic. Most RoCE configurations include complex steps and manual configuration can be error prone. Cumulus Linux simplifies the RoCE configuration to a single command and automatically applies best practice settings for optimal performance.
In addition, NVIDIA Spectrum ASIC telemetry capabilities, including the unique What Just Happened (WJH) feature, provide real-time visibility into the network. You can look at flow latency events, buffer occupancy, and dropped packets to discover, diagnose, and resolve network problems. WJH monitoring supports all events and traffic types, including layer 1, layer 2, ACLs, layer 3, tunneling, buffers, and RoCE.
Network simulation is essential to avoid manual CLI, and copy and paste configuration errors. NVIDIA Air provides an online cloud-based network simulation platform where you can create a digital twin of your physical environment. You can build, simulate, and experience Cumulus Linux switches in AIR while testing your deployment configuration before applying it to production. Check out the NVIDIA Air user guide for more details.
There might be different specifications for each storage vendor deployment. You can always check out Cumulus Linux documentation to explore more details and match the configuration for your deployment.
Cumulus Linux documentation offers pre-built Try It demos for certain features like MLAG, VRR, VXLAN, and EVPN. These demos automatically start a network simulation in Air so you can practice configuration.
If your switches are still running NVIDIA Onyx, migrate to Cumulus Linux by following this guide to uninstall the Onyx image and install a new Cumulus Linux image. To ease the transition from ONYX to NVUE, you can upload the running configuration file from the Onyx switch with this NVUE Migration Tool.
Deployment Types
Storage vendors typically use layer 2 connectivity between storage arrays and the top-of-rack (ToR or leaf) switches when deploying ESF.
These are the three main network configurations:
- MLAG - Layer 2 ToR with routed (layer 3) uplinks to the spines.
- MLAG over MLAG (also called Back-to-Back MLAG) - Layer 2 ToR with switched (layer 2) uplinks to the spines. You can use this scenario for larger layer 2 domains but with a maximum of two spines. You configure MLAG in two levels, on the ToR and on the spines. Routing is on the spines.
- Active-Active VXLAN - An extended layer 2 domain over layer 3 networks using VXLAN and EVPN. Such deployments can use VXLAN layer 2 stretch or routing configurations.
MLAG is an active-active layer 2 redundancy protocol that allows a redundant ToR layer 2 network while doubling the bandwidth. However, it also enables you to leverage VRR, the active-active routing instances. With VRR, both ToR (or spine) switches route the storage traffic simultaneously and create a redundant, higher bandwidth layer 3 network.
Regardless of the ESF network design you chose, when it comes to ToR layer 2 redundancy, some vendors prefer to deploy active-active bonding (LACP/xor) on the storage Network Interface Cards (NICs) and some prefer to deploy active-backup (or alb). The examples below use the MLAG protocol for layer 2 or layer 3 redundancy (or both).
With RoCEv1, you have to set layer 2 fabric everywhere, so routing (VRR) is not required. For RoCEv2, if your network requires inter-subnet routing, you can deploy a layer 3 fabric with VRR gateways (and BGP with EVPN).
MLAG
This section shows you how to configure MLAG on Cumulus Linux using NVUE.
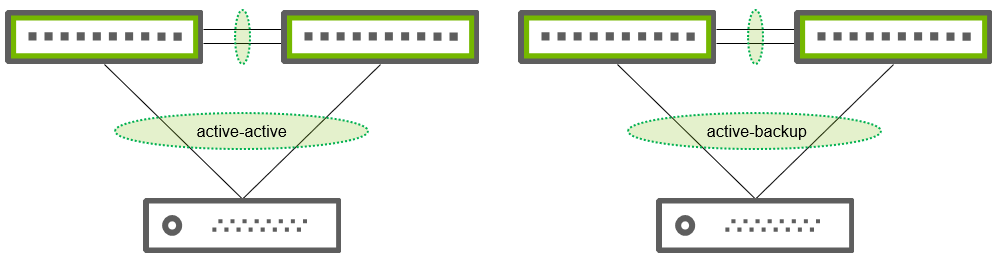
To achieve redundant top-of-rack deployment using MLAG, you must configure storage array NICs with active-active bonding. The examples below use the MLAG protocol set even for non-active-active bonds towards the ToR switches:
- To use VRR as a storage traffic default gateway to route to other subnets.
- In MLAG over MLAG (back-to-back MLAG) deployments, where the ToR uplinks are set as MLAG port.
Before you configure MLAG, make sure that both peers are running the same Cumulus Linux release. NVIDIA recommends that you run the latest Cumulus Linux release. To verify the Cumuls Linux release on the switch, run the cat /etc/lsb-release or nv show system command.
Inter-Chassis Bond (Peer Link)
MLAG requires a dedicated link (bond) between the peers. Cumulus Linux uses the reserved name peerlink for this bond with a unique VLAN layer 3 subinterface called peerlink.4094. The peer link maintains state information between the MLAG peers and serves as a traffic backup path in case of failures.
When planning for link failures, you need to set a peer link with enough bandwidth to meet your site strategy for handling failure scenarios. NVIDIA recommends that you determine how much bandwidth sends across the single-connected interfaces and set half of that bandwidth to the peer link.
By default, Cumulus Linux allows all VLANs on the peer link and adds them automatically when you create the peer link. Cumulus Linux also creates the peerlink.4094 subinterface automatically when you run the following commands. The interface IPv6 linklocal address provides layer 3 connectivity between the peers.
To create the peer link and peerlink.4094 interfaces:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member <interface-list>
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
Do not use 169.254.0.1 as the MLAG peer IP address. Cumulus Linux uses this address for BGP unnumbered interfaces.
MLAG Backup IP Address
MLAG uses the backup IP address to maintain the MLAG domain when the peer link goes down.
To set the MLAG backup IP address:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup [peer-address] vrf mgmt
Make sure that the MLAG backup IP address is different than the peerlink.4094 address and that it is reachable from the network. Use the switch loopback or management IP address.
MLAG System MAC Address
The MLAG system MAC address represents both peers as the same switch in various control protocols, such as Spanning Tree and LACP. Make sure to set an identical MLAG system MAC address on both peers.
To set the MLAG system MAC address:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address <address>
-
Use the MLAG MAC address from the reserved range of 44:38:39:ff:00:00-44:38:39:ff:ff:ff only. Always set a unique MAC address for different MLAG pairs.
-
If your ESF environment is based on an active-active VXLAN and EVPN fabric, you must also set a system global anycast MAC address on both peers:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set system global anycast-mac <address>
MLAG Ports
An MLAG port is a bond interface set on both MLAG peers and contains the interfaces that connect to the storage NIC as its members. You must specify each MLAG port with a unique MLAG ID (on both peers). Cumulus Linux uses LACP (802.3ad) bond mode by default but balance-xor mode is also an option.
MLAG port configuration depends on the bonding type on the storage array NICs. For example, when the NICs are set to active-active bonding mode (LACP/xor), you must configure the MLAG ports on the ToR switches connected to them. If the array NICs are set to active-backup (or alb) bonding, do not set the MLAG ports; the traffic goes only through a single switch until there is a link failure, or a different flow or application transmit.
To configure the MLAG port, create a bond interface with members and set an MLAG ID. Skip this step if you do not need MLAG ports.
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface <bond-name> bond member <interface-list>
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface <bond-name> bond mlag id <number>
As most ESF environments use jumbo MTU settings, the Cumulus Linux default MTU is 9216B for all physical and logical interfaces. To change the MTU:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface <interface-list> link mtu <mtu>
You can define the MLAG master and slave statically by setting the MLAG priority:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority <priority>
To postpone MLAG to be operational after reboot (to let the servers boot before the switches):
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay <seconds>
For more information about MLAG, see this documentation.
MLAG over MLAG (Back to Back MLAG)
Sometimes ESF environments require layer 2 connectivity for many hosts, where you need more than two ToR switches. In this case, the ESF environment scales into a leaf-spine topology to extend the layer 2 domain. There are two types of network deployments: MLAG over MLAG or extended layer 2 domains over a layer 3 fabric with VXLAN and EVPN.
With MLAG over MLAG, you also set MLAG on the spines and configure an MLAG port between the ToR and spines.
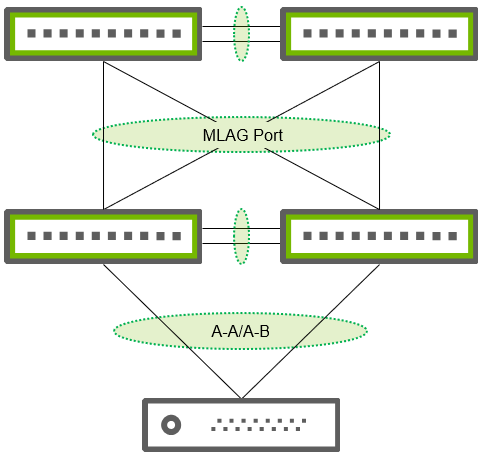
MLAG configuration on the spines is the same as on the ToR switches. The illustration above shows that all physical ports between the ToR and the spines are bonded into a single MLAG port. This bond must have the same MLAG ID on each MLAG peer (the ID can be different on the ToR and spines).
Bridge and VLANs
The Ethernet bridge enables layer 2 on Cumulus Linux switches by connecting the physical and logical interfaces into a single layer 2 domain. However, Cumulus Linux does not have a bridge by default and all physical ports are routed. Therefore, you must create a VLAN-aware bridge to enable layer 2 communication between the storage NICs and the ToR switches. The bridge implements all layer 2 technologies like STP, MAC address learning, VLANs, trunks, and so on.
After creating the bridge, you need to assign ports (swp/MLAG ports). Cumulus Linux adds the ports automatically into VLAN 1 as an untagged VLAN.
To create a bridge and assign ports to the bridge:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface <interface> bridge domain br_default
In most cases, you do not need to use the default VLAN1 on the switch. To add new VLANs to the bridge and set the port as access (untagged):
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan <vlan-list>
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface <interface> bridge domain br_default access <vlan-id>
If the storage array NICs use dot1q, set the ToR downlink as trunk ports. Each trunk port works with dot1q tags for specified VLANs and a native VLAN (untagged).
To set the port as a trunk with native VLAN:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface <interface> bridge domain br_default vlan <vlan-list>
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface <interface> bridge domain br_default untagged <vlan-id>
When deploying MLAG over MLAG, the configuration of the bridge and VLANs is the same for both MLAG layers (domains). If you use more than one VLAN on the storage NICs, use the same trunk configuration on the MLAG port between the ToR and spines.
MLAG Configuration Example
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.14 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.13 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.14 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.13 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
Routing Configuration
VRR serves as the gateway for storage traffic, either to route between VLANs on the ToR switches or route traffic between racks in the data center and external networks.
Depending on your network deployment type, you can configure VRR instances on the ToR switches or the spines (MLAG over MLAG). For each storage subnet (VLAN), you need to create a VRR instance. This virtual router instance works on top of a Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) and holds a virtual IP address that serves as the gateway for the subnet and the virtual MAC address to reply to ARP requests from the NIC.
VRR is an active-active routing instance, so both MLAG peers must have the same VRR instance configuration to reply to ARP requests and forward routed traffic simultaneously. VRR is different from the Virtual Routing Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) as the instances on both peers are independent of each other and work simultaneously instead of in active-standby mode.
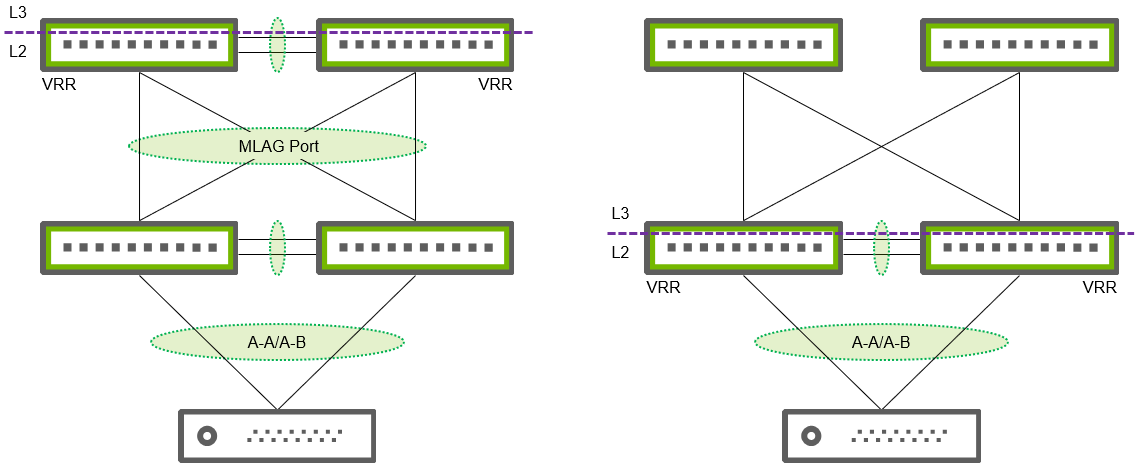
To set VRR, first create an SVI (VLAN interface) on each peer and set unique IP addresses within the same subnet (as the NIC subnet). Then, configure the VRR instance on top of each SVI. Both peers share the same virtual IP address and MAC address.
Create a layer 3 VLAN interface with the vlan keyword followed by the VLAN ID and set a unique IP address:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan<ID> ip address <address>
Add VRR addresses on top of the SVI and enable the virtual instance:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan<ID> ip vrr address <address>
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan<ID> ip vrr mac-address <address>
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan<ID> ip vrr state up
After you set VRR for the layer 2 domain (ToR and spine) MLAG peers, you need to configure layer 3 uplinks, either router ports or SVIs. Then, you can use static or dynamic routing to route traffic. The most common routing protocol in data centers is Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), particularly eBGP.
Cumulus Linux provides a unique and easy way to configure BGP using Auto BGP and BGP Unnumbered.
VRR Configuration Example
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.2/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.3/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond member swp1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1 bond mlag id 1
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.14 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.2/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.2/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.2/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.13 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.3/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.3/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.3/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.12 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp2-3
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.11 vrf mgmt
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond member swp4-swp5
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond2 bond mlag id 2
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 link mtu 9000
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface swp1,bond2 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.14 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag priority 1000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.2/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.2/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.2/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine01:mgmt:~$ nv config save
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface peerlink bond member swp3-4
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag peer-ip linklocal
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag backup 192.168.200.13 vrf mgmt
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag mac-address 44:38:39:BE:EF:BB
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set mlag init-delay 10
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond member swp1-2
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bond mlag id 3
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 link mtu 9000
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface bond3 bridge domain br_default vlan 10,20,30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip address 10.1.10.3/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip ip vrr address 10.1.10.1/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan10 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip address 10.1.20.3/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip ip vrr address 10.1.20.1/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan20 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip address 10.1.30.3/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip ip vrr address 10.1.30.1/24
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv set interface vlan30 ip vrr state up
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
cumulus@spine02:mgmt:~$ nv config save
Configuration Verification
You can verify the configuration with NVUE or Linux commands.
MLAG
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv show mlag
operational applied description
-------------- ----------------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
debug off Enable MLAG debugging
init-delay 10 The delay, in seconds, before bonds are brought up.
mac-address 44:38:39:be:ef:aa 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA Override anycast-mac and anycast-id
peer-ip fe80::4638:39ff:fe00:22 linklocal Peer Ip Address
priority 1000 1000 Mlag Priority
[backup] 192.168.200.12 192.168.200.12 Set of MLAG backups
backup-active True Mlag Backup Status
backup-reason Mlag Backup Reason
local-id 44:38:39:00:00:21 Mlag Local Unique Id
local-role primary Mlag Local Role
peer-alive True Mlag Peer Alive Status
peer-id 44:38:39:00:00:22 Mlag Peer Unique Id
peer-interface peerlink.4094 Mlag Peerlink Interface
peer-priority 32768 Mlag Peer Priority
peer-role secondary Mlag Peer Role
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv show mlag
operational applied description
-------------- ----------------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
debug off Enable MLAG debugging
init-delay 10 The delay, in seconds, before bonds are brought up.
mac-address 44:38:39:be:ef:aa 44:38:39:BE:EF:AA Override anycast-mac and anycast-id
peer-ip fe80::4638:39ff:fe00:21 linklocal Peer Ip Address
priority 32768 32768 Mlag Priority
[backup] 192.168.200.11 192.168.200.11 Set of MLAG backups
backup-active True Mlag Backup Status
backup-reason Mlag Backup Reason
local-id 44:38:39:00:00:22 Mlag Local Unique Id
local-role secondary Mlag Local Role
peer-alive True Mlag Peer Alive Status
peer-id 44:38:39:00:00:21 Mlag Peer Unique Id
peer-interface peerlink.4094 Mlag Peerlink Interface
peer-priority 1000 Mlag Peer Priority
peer-role primary Mlag Peer Role
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ clagctl
The peer is alive
Our Priority, ID, and Role: 1000 44:38:39:00:00:21 primary
Peer Priority, ID, and Role: 32768 44:38:39:00:00:22 secondary
Peer Interface and IP: peerlink.4094 fe80::4638:39ff:fe00:22 (linklocal)
Backup IP: 192.168.200.12 (active)
System MAC: 44:38:39:be:ef:aa
CLAG Interfaces
Our Interface Peer Interface CLAG Id Conflicts Proto-Down Reason
---------------- ---------------- ------- -------------------- -----------------
bond1 bond1 1 - -
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ clagctl
The peer is alive
Our Priority, ID, and Role: 32768 44:38:39:00:00:22 secondary
Peer Priority, ID, and Role: 1000 44:38:39:00:00:21 primary
Peer Interface and IP: peerlink.4094 fe80::4638:39ff:fe00:21 (linklocal)
Backup IP: 192.168.200.11 (active)
System MAC: 44:38:39:be:ef:aa
CLAG Interfaces
Our Interface Peer Interface CLAG Id Conflicts Proto-Down Reason
---------------- ---------------- ------- -------------------- -----------------
bond1 bond1 1 - -
Bridge and VLANs
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv show bridge domain br_default
operational applied description
------------- ----------- ---------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------
encap 802.1Q 802.1Q Interfaces added to this domain will, by default, use this encapsul...
mac-address auto Override global mac address
type vlan-aware vlan-aware Type of bridge domain.
untagged 1 Interfaces added to this domain will, by default, be trunk interfac...
multicast
snooping
enable on off Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
querier
enable off Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
stp
priority 32768 32768 stp priority. The priority value must be a number between 4096 and...
state up up The state of STP on the bridge
[vlan] 10 Set of vlans in the bridge domain. Only applicable when the domain...
[vlan] 20
[vlan] 30
[mdb] Set of mdb entries in the bridge domain
[router-port] 1 Set of multicast router ports
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv show bridge domain br_default
operational applied description
------------- ----------- ---------- ----------------------------------------------------------------------
encap 802.1Q 802.1Q Interfaces added to this domain will, by default, use this encapsul...
mac-address auto Override global mac address
type vlan-aware vlan-aware Type of bridge domain.
untagged 1 Interfaces added to this domain will, by default, be trunk interfac...
multicast
snooping
enable on off Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
querier
enable off Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
stp
priority 32768 32768 stp priority. The priority value must be a number between 4096 and...
state up up The state of STP on the bridge
[vlan] 10 Set of vlans in the bridge domain. Only applicable when the domain...
[vlan] 20
[vlan] 30
[mdb] Set of mdb entries in the bridge domain
[router-port] 1 Set of multicast router ports
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ bridge vlan show
port vlan ids
peerlink 1 PVID Egress Untagged
10
20
30
bond1 1 PVID Egress Untagged
10
20
30
br_default 10
20
30
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ bridge vlan show
port vlan ids
peerlink 1 PVID Egress Untagged
10
20
30
bond1 1 PVID Egress Untagged
10
20
30
br_default 10
20
30
Interfaces, SVI and VRR
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv show interface
Interface MTU Speed State Remote Host Remote Port Type Summary
--------------- ----- ----- ----- --------------- ----------------- -------- -----------------------------
+ bond1 9000 1G up bond
+ eth0 1500 1G up oob-mgmt-switch swp6 eth IP Address: 192.168.200.11/24
+ lo 65536 up loopback IP Address: 10.10.10.1/32
lo IP Address: 127.0.0.1/8
lo IP Address: ::1/128
+ peerlink 9216 2G up bond
+ peerlink.4094 9216 up sub
+ swp1 9000 1G up server01 44:38:39:00:00:12 swp
+ swp2 9216 1G up leaf02 swp2 swp
+ swp3 9216 1G up leaf02 swp3 swp
+ swp4 9216 1G up spine01 swp1 swp
+ swp5 9216 1G up spine02 swp1 swp
+ vlan10 9216 up svi IP Address: 10.1.10.2/24
+ vlan20 9216 up svi IP Address: 10.1.20.2/24
+ vlan30 9216 up svi IP Address: 10.1.30.2/24
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv show interface
Interface MTU Speed State Remote Host Remote Port Type Summary
--------------- ----- ----- ----- --------------- ----------------- -------- -----------------------------
+ bond1 9000 1G up bond
+ eth0 1500 1G up oob-mgmt-switch swp6 eth IP Address: 192.168.200.12/24
+ lo 65536 up loopback IP Address: 10.10.10.2/32
lo IP Address: 127.0.0.1/8
lo IP Address: ::1/128
+ peerlink 9216 2G up bond
+ peerlink.4094 9216 up sub
+ swp1 9000 1G up server01 44:38:39:00:00:16 swp
+ swp2 9216 1G up leaf01 swp2 swp
+ swp3 9216 1G up leaf01 swp3 swp
+ swp4 9216 1G up spine01 swp2 swp
+ swp5 9216 1G up spine02 swp2 swp
+ vlan10 9216 up svi IP Address: 10.1.10.3/24
+ vlan20 9216 up svi IP Address: 10.1.20.3/24
+ vlan30 9216 up svi IP Address: 10.1.30.3/24
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv show interface vlan10 ip vrr
operational applied description
----------- ----------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10 00:00:00:00:00:10 Override anycast-mac
mac-id none Override anycast-id
[address] 10.1.10.1/24 10.1.10.1/24 Virtual addresses with prefixes
state up up The state of the interface
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv show interface vlan20 ip vrr
operational applied description
----------- ----------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20 00:00:00:00:00:20 Override anycast-mac
mac-id none Override anycast-id
[address] 10.1.20.1/24 10.1.20.1/24 Virtual addresses with prefixes
state up up The state of the interface
cumulus@leaf01:mgmt:~$ nv show interface vlan30 ip vrr
operational applied description
----------- ----------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30 00:00:00:00:00:30 Override anycast-mac
mac-id none Override anycast-id
[address] 10.1.30.1/24 10.1.30.1/24 Virtual addresses with prefixes
state up up The state of the interface
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv show interface vlan10 ip vrr
operational applied description
----------- ----------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:10 00:00:00:00:00:10 Override anycast-mac
mac-id none Override anycast-id
[address] 10.1.10.1/24 10.1.10.1/24 Virtual addresses with prefixes
state up up The state of the interface
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv show interface vlan20 ip vrr
operational applied description
----------- ----------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:20 00:00:00:00:00:20 Override anycast-mac
mac-id none Override anycast-id
[address] 10.1.20.1/24 10.1.20.1/24 Virtual addresses with prefixes
state up up The state of the interface
cumulus@leaf02:mgmt:~$ nv show interface vlan30 ip vrr
operational applied description
----------- ----------------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------------------
enable on Turn the feature 'on' or 'off'. The default is 'off'.
mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:30 00:00:00:00:00:30 Override anycast-mac
mac-id none Override anycast-id
[address] 10.1.30.1/24 10.1.30.1/24 Virtual addresses with prefixes
state up up The state of the interface
Extended Layer 2 Domain over Layer 3 Fabric (VXLAN and EVPN)
If your ESF environment requires more than two spines in the layer 2 domain, or you need to tunnel layer 2 storage traffic over the layer 3 fabric, use VXLAN Active-Active mode mode with EVPN. In this deployment, you must use the BGP protocol to work with the EVPN control plane.
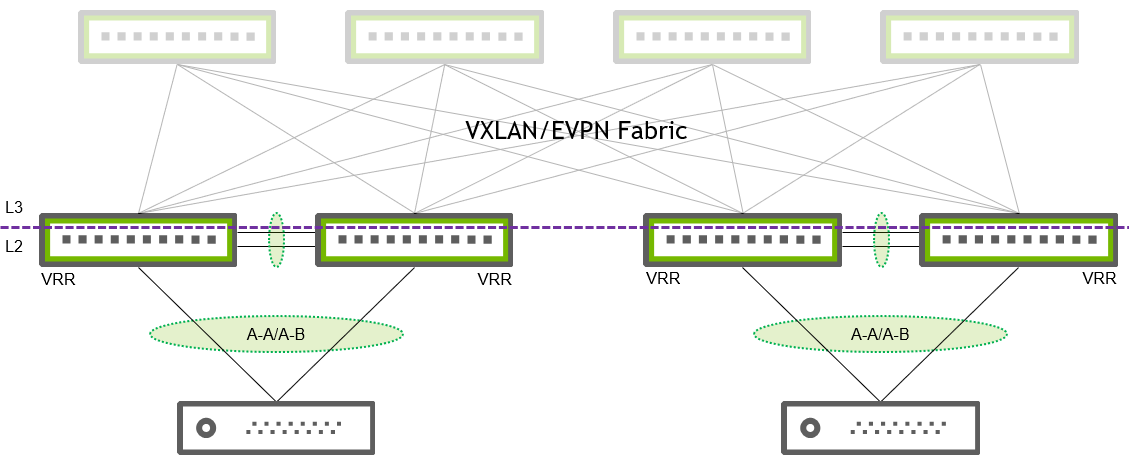
If your ESF environment only uses a single VLAN or the VLANs do not communicate, you need to set the layer 2 extension (Layer 2 stretch) functionality.
If you need to deploy EVPN inter-subnet routing in your ESF deployment, Cumulus Linux offers two options:
- Centralized routing, where a designated VTEP serves as the layer 3 gateway for the subnets and performs routing between them. The rest of the VTEPs just perform bridging.
- Distributed symmetric routing, where all VTEPs perform routing on ingress and egress.
When working with an EVPN network, you can leverage EVPN Multihoming (EVPN MH) to eliminate the need for MLAG in your environment. By removing MLAG from the ToRs, you can use a larger layer 2 redundancy group (more than two ToRs). EVPN multihoming uses a standard BGP-EVPN control plane and allows multi-vendor interoperability so that you can deploy multi-vendor ToRs.
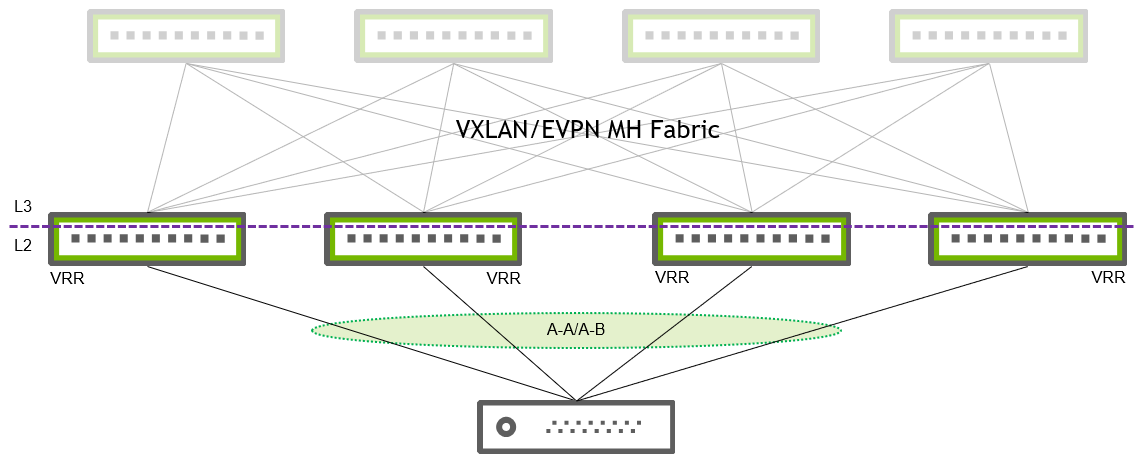
VXLAN and EVPN, and EVPN MH are rare configurations in ESF networks so this guide does not include a step-by-step configuration. You can find a few configuration examples here.
Check out the Network Virtualization and EVPN Multihoming documentation for more detailed information and configuration commands.
If you use an NSX-T environment, check out this Cumulus Linux Deployment Guide for VMware NSX-T.
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE)
When ESF runs RoCE traffic, you must configure all network elements in the traffic path to handle RoCE. Cumulus Linux provides a single RoCE command that automatically sets all RoCE best practice configuration on the switch. The command sets all the needed settings to achieve the best performance. This configuration includes buffer pool settings, traffic classification and priority mappings, PFC and ECN thresholds, and queuing and scheduling settings for regular, RoCE, and CNP packets.
To configure the switch to work with RoCE:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set qos roce
Cumulus Linux supports a single command configuration both for RoCEv1 and RoCEv2. The default RoCE mode is lossless with PFC and ECN. You can set lossy mode to use ECN only.
To configure RoCE lossy mode:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv set qos roce lossy
For more information on Cumulus Linux RoCE default best-practice configuration, refer to RDMA over Converged Ethernet - RoCE.
- The NVIDIA Spectrum ASIC with Cumulus Linux provides a line rate RoCE traffic on top of VXLAN and EVPN fabrics while keeping all QoS settings over the tunnels end-to-end without any latency impact.
- Make sure to configure RoCE on the NICs as well. For NIC RoCE configuration, refer to the MLNX_OFED documentation. In addition, NVIDIA ConnectX SmartNICs provides seamless RoCE NIC configuration using the zero-touch RoCE (ZTR) feature.
Configuration Management
Cumulus Linux has a declarative CLI with commit-confirm and configuration management capabilities. All the configuration commands take effect only after you apply them and remain persistent after you save them.
To apply the configuration as a running configuration:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv config apply
To save the configuration as a persistent startup configuration:
cumulus@switch:mgmt:~$ nv config save
After you save the configuration, NVUE creates a startup.yaml configuration file. Cumulus Linux uses this YAML file as the startup configuration on the switch.
NVUE has many useful configuration management options. Check out the configuration management commands section of NVUE documentation for more details.