Set up an apt Package Cache
Advantages and Uses of Locally Cached Packages
Air-gapped Networks
Package mirroring is handy when switches do not have a direct connection to the Internet to receive updates or install software. Instead of reaching out to the NVIDIA repository on the Internet, switches configured to use a local mirror can reach out to a locally trusted target that you configured already.
Granular Control of Software Versions
Package mirroring is also a way to lock down switches from updating packages, as they cannot receive newer package versions from those that exist on the mirror, so by controlling what is on the mirror you can control what packages switches can install.
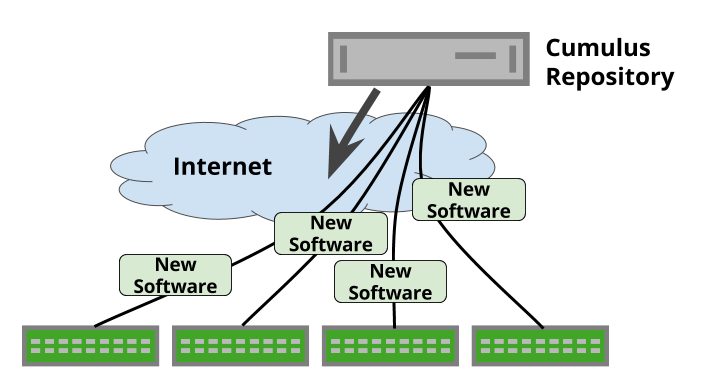
Standard package workflow: Packages downloaded directly from the NVIDIA repository by each switch.
Speed, Efficiency and Bandwidth Reduction
Switches configured to receive their packages from a local mirror get those packages from a local source, which generally means faster download times. The other benefit is package caching; if one switch downloads a package, the mirror caches that package so that all subsequent downloads occur directly from the mirror for added speed. Reducing external bandwidth requirements might be a concern depending on your scale and package needs.
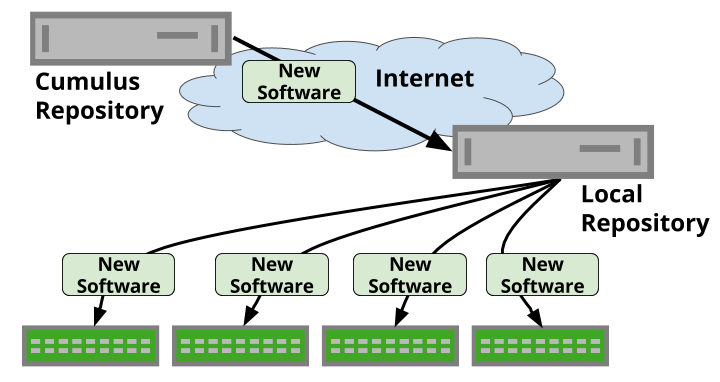
Tools for Mirroring Packages
In traditional Linux form, there are many package mirroring tools available for Debian.
The apt-mirror program can copy the entire NVIDIA repository, so you can point your local switches at the local copy of the repository. This approach works, but is a bit more heavyweight than you might want. For that reason, NVIDIA recommends using the apt-cacher-ng program.
apt-cacher-ng has been around for quite some time now and has many proponents. It replaces the original apt-cacher program as it is more robust.
apt-cacher-ng offers several benefits over other offerings:
- Small footprint:
apt-cacher-nguses fraction of the space of a full mirror, and the cache automatically clears old packages that are no longer requested. - Reduced WAN bandwidth consumption:
apt-cacher-ngdownloads each package only one time and caches it for subsequent requests from other switches. - Faster package downloads:
apt-cacher-ngreduces download time for all but the first request from a switch. - Easy client configuration: Change a single file. Instead of changing repository URLs to point to new repositories, you add a new proxy to the configuration.
- Easy installation: Single package install, with no additional configuration in most cases. Just install and go. You have no need to install an additional web server.
Install and Configure apt-cacher
Install apt-cacher-ng on a Debian/Ubuntu Server
Before you install apt-cacher-ng, you need to reference the Debian Jessie upstream repository. Create a file called debian.list in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory and add the following lines:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian jessie main
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian jessie main
After you save the file, apt-cacher-ng should be available:
cumulus@cumulus:mgmt-vrf:~$ sudo apt-cache policy apt-cacher-ng
apt-cacher-ng:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 0.8.0-3
Version table:
0.8.0-3 0
500 http://deb.debian.org/debian/ jessie/main amd64 Packages
Now you are ready to install the apt-cacher-ng package:
$ sudo apt-get update -y
$ sudo apt-get install apt-cacher-ng
Configure Switches to Use the Apt-Cacher as a Proxy
Create the file /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/90apt-proxy and add the following line in the file:
Acquire::http::Proxy "http://192.168.252.254:3142";
Remember to update the IP address to reflect the IP address of your server running apt-cacher-ng.
Other Helpful Tips
Do not Mix Packages from Different Distributions
NVIDIA strongly recommends you do not install packages from one Linux distribution onto another distribution. For example, do not install any Ubuntu packages on a Cumulus Linux switch, as Cumulus Linux is a Debian distro.
Freeze Package State
To freeze your package state, turn off the apt-cacher-ng daemon on the server. All the switches become frozen at their software revisions until the daemon starts again.
If you are using systemd on your mirror server, run:
$ sudo systemctl stop apt-cacher-ng
If you are not using systemd, run this command instead:
$ sudo service apt-cacher-ng stop
Clear Package Cache on Upgrades
It might make sense to clear the package cache after certain events, such as upgrading to a new version of Cumulus Linux or for whenever you want to serve a new version of an existing package.
To clear the package cache for a Cumulus Linux 3.x repository on Ubuntu 16.04, run the following command:
$ sudo rm -rfv /var/cache/apt-cacher-ng/repo3.cumulusnetworks.com/repo/dists/