Cumulus Linux Derivation of MAC Address for a Bridge
Cumulus Linux sets the MAC address for a bridge, and therefore layer 3 switch virtual interfaces (SVIs), differently depending on the version of Cumulus Linux you have deployed. Version 3.6.0 and later releases use the MAC address of the first port in the bridge-ports list. Earlier releases use alternate methods for determining the MAC address.
This article summarizes the various derivation methods and illustrates the results using an example bridge configuration. Additionally, it provides guidelines for choosing a derivation method for your network and instructions for modifying its default behavior if so desired.
Default Methods Used by Cumulus Linux
The following table lists the method used by each version of Cumulus Linux by default.
| Version | Method |
|---|---|
| 3.6.0 and later | First Port Interface Address |
| 3.5.3 | Lowest Port Interface Address |
| 3.5.0 through 3.5.2 | eth0 Interface Address |
| 3.4.3 and earlier | Lowest Port Interface Address |
Example Bridge Configuration
The following example switch configuration shows the differences between the methods for determining the MAC address for a bridge interface. This example shows a VLAN-aware bridge (for large scale, layer 2 environments using a single instance of spanning tree protocol — STP) configured with a management port of eth0, four switch ports (swp1-4), and an LACP bond interface (bond1), containing two switch ports (swp5-6). It also contains a single VLAN, 100, which has a layer 3 switch virtual interface (SVI).
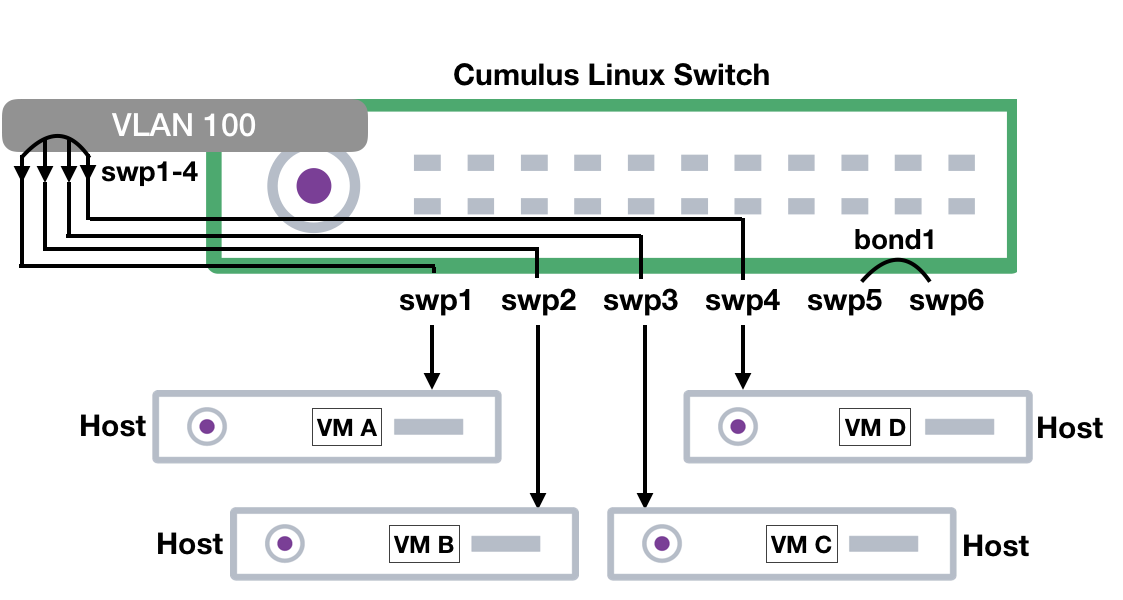
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto swp2
iface swp2
auto swp3
iface swp3
auto swp4
iface swp4
auto swp5
iface swp5
auto swp6
iface swp6
auto bond1
iface bond1
bond-slaves swp5 swp6
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports bond1 swp1 swp2 swp3 swp4
bridge-vids 100
bridge-vlan-aware yes
auto vlan100
iface vlan100
address 10.1.1.1/24
vlan-id 100
vlan-raw-device bridge
First Interface Address Method
This method assigns the MAC address of the first interface in its bridge-ports list to the bridge MAC address. In this example configuration, the first interface is bond1:
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports bond1 swp1 swp2 swp3 swp4
The interface bond1 (the bond master) obtains its MAC address from its bond slaves (swp5-6).
auto bond1
iface bond1
bond-slaves swp5 swp6
Using the configuration example, you can see the addresses of each of these interfaces by piping the ip link show command through grep. Note that the MAC address of the bond1 interface is the same as the address for switch ports swp5 and swp6 (the bond interface selects the MAC address of the first slave to use for all member links). The bridge then has the same address as bond1 (highlighted in purple).
cumulus@cumulus:~$ ip link show | grep -A1 -E "eth0|swp[1-6]:|bridge"
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:00:00:11:11:11 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: swp1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:d9:fc:77 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: swp2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:b0:c1:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: swp3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:eb:80:47 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
6: swp4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:1a:d4:43 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
7: swp5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,SLAVE,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bond1 state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
8: swp6: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,SLAVE,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bond1 state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
--
47: bond1: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,MASTER,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master bridge state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
48: bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
49: vlan100@bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
First Interface Address Usage Considerations
Using this method to assign the bridge’s MAC address can cause issues when you update the bridge-ports list. When the first MAC address of the first interface in bridge-ports changes, either through enslaving a new port or releasing the current first port, the bridge’s MAC address changes, thus changing its STP bridge address. This can result in STP reconverging and an outage for the bridge domain.
Cumulus Linux 3.6.0 and later use the First Interface Address method by default. When upgrading from an earlier version to 3.6.0 or later, it is likely that the bridge and SVI MAC addresses is going to change between versions. This can cause issues if an SVI is expecting a static lease from DHCP that it can use for in-band management as is common in an out-of-band network.
Lowest Interface Address Method
This method inspects every interface in the bridge-ports list and assigns the lowest MAC address for the bridge address. In the example configuration, the bridge-ports list contains five interfaces:
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports bond1 swp1 swp2 swp3 swp4
Using the configuration example, you can see the addresses of each of these interfaces by piping the ip link show command through grep. Comparing these addresses, you can see that swp2 interface has the lowest address. Note that this address is then the address used for the bridge (highlighted in purple).
cumulus@cumulus:~$ ip link show | grep -A1 -E "swp[1-6]:|bridge"
3: swp1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:d9:fc:77 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: swp2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:b0:c1:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: swp3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:eb:80:47 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
6: swp4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:1a:d4:43 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
7: swp5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,SLAVE,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bond1 state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
8: swp6: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,SLAVE,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bond1 state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
--
47: bond1: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,MASTER,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master bridge state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
48: bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 08:00:27:b0:c1:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
The output shown above is from a Cumulus VX deployment, where the interface MAC is randomly allocated from a range provided by the hypervisor. By contrast, a Cumulus Linux switch assigns MAC addresses linearly to interfaces based on the system MAC provided by the hardware vendor in the EEPROM. As such, this typically results in the lowest numbered interface on a switch having the lowest MAC address.
Lowest Interface Address Usage Considerations
Using this method to assign the bridge’s MAC address can cause issues when you update the bridge-ports list. If the lowest MAC address changes, either through enslaving a new port or releasing the current lowest interface, the bridge’s MAC address is going to change, thus changing its STP bridge address. This can result in STP reconverging and an outage for the bridge domain.
Cumulus Linux 3.5.3 and 3.4.3 and earlier use the Lowest Interface Address method by default.
eth0 Interface Address Method
This method assigns the address of the eth0 interface to the bridge MAC address. Using the configuration example, you can see the addresses of each of these interfaces by piping the ip link show command through grep. Note the matching address for the bridge and eth0 (highlighted here).
cumulus@cumulus:~$ ip link show | grep -A1 -E "eth0|bridge"
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:00:00:11:11:11 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
28: bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 00:00:00:11:11:11 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
29: vlan100@bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 00:00:00:11:11:11 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
eth0 Usage Considerations
Using this method to assign the bridge’s MAC address can cause issues when the eth0 interface of the switch becomes part of a VLAN the switch is bridging. In the event the switch sees a packet with the source MAC of its own bridge address, which is the same as its eth0 address, it drops the packet rather than bridges it.
Cumulus Linux 3.5.0 through 3.5.2 use the eth0 Interface Address method by default.
Static Address Method
This method requires the administrator to manually assign a static address for the bridge rather than using a dynamically assigned one, the way the other methods do.
Static Address Usage Considerations
You must assign an address that is unique throughout the entire network.
None of the Cumulus Linux versions use this method by default.
Change Default MAC Address Derivation Method
You can reconfigure Cumulus Linux versions 3.6.0 and later to use any MAC address derivation method. To reconfigure Cumulus Linux versions 3.5.3 and earlier, you must use the static MAC address method.
Choose a Derivation Method
Choosing the right derivation method for your network depends on the configuration of your interfaces. Use the following table to help you determine what is best for your network:
| Derivation Method | When to Use | When Not to Use | Cumulus Linux Default |
|---|---|---|---|
First Interface Address |
|
|
3.6.0 and later |
Lowest Interface Address |
|
|
3.5.3, 3.4.3 and earlier |
eth0 Address |
|
|
3.5.0 - 3.5.2 |
Static MAC Address |
|
|
Never |
Modify the Derivation Method
If you wish to modify the default derivation method, follow the instructions for your configuration choice:
Use Lowest Interface Address Method
To change to this method:
-
Install an
ifupdown2policy file. -
Reload the interface.
-
Update the bridge ports to force the address change.
cumulus@cumulus:~$ cat /etc/network/ifupdown2/policy.d/bridgemac.json { "bridge": { "module_globals": { "bridge_set_static_mac_from_port": "no" } } } cumulus@cumulus:~$ sudo ifreload -a cumulus@cumulus:~$ ip link set dev bridge address 00:11:22:33:44:55This might cause an STP reconvergence event.
You can verify the configuration change using the ip link show command piped through grep to see the addresses:
cumulus@cumulus:~$ ip link show | grep -A1 -E "swp[1-6]:|bridge"
3: swp1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:d9:fc:77 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: swp2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:b0:c1:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: swp3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:eb:80:47 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
6: swp4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bridge state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:1a:d4:43 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
7: swp5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,SLAVE,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bond1 state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
8: swp6: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,SLAVE,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master bond1 state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
--
47: bond1: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,MASTER,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master bridge state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 08:00:27:4a:25:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
48: bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 08:00:27:b0:c1:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Use eth0 Address Method
To change to this method:
-
Install an
ifupdown2policy file. -
Reload the interface.
In this case, the MAC address changes immediately.
cumulus@cumulus:~$ cat /etc/network/ifupdown2/policy.d/bridgemac.json { "bridge": { "module_globals": { "bridge_mac_iface": ["eth0", "eth1"] } } } cumulus@cumulus:~$ sudo ifreload -a
You can verify the configuration change using the ip link show command piped through grep to see the addresses:
cumulus@cumulus:~$ ip link show | grep -A1 -E "eth0|bridge"
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:11:22:33:44:55 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
42: bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 00:11:22:33:44:55 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Use Static MAC Address
To change to this method, you specify an address in the configuration file, under the bridge’s stanza.
The MAC address allocated to the bridge must be unique across the entire network.
cumulus@cumulus:~$ cd /etc/network/
cumulus@cumulus:~$ vi interfaces
...
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-ports swp1 swp2 swp3 swp4 bond1
bridge-vids 100
bridge-vlan-aware yes
hwaddress 00:11:22:33:44:55
...
You can verify the configuration change using the ip link show command.
cumulus@cumulus:~$ ip link show bridge
42: bridge: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 00:11:22:33:44:55 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff