ECMP
Equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) is a routing strategy whereby packets are forwarded along multiple paths of equal cost. Load sharing occurs automatically for IPv4 and IPv6 routes with multiple installed next hops. The hardware or the routing protocol configuration determines the maximum number of routes for which load sharing occurs.
Refer to Cumulus Linux and ECMP for more information about ECMP.
ECMP monitoring is supported on NVIDIA Spectrum switches running Cumulus Linux.
ECMP Commands
Monitor ECMP routing data with the following commands. See the command line reference for additional options, definitions, and examples.
netq show ecmp
netq show ecmp-hash-config
View ECMP Resource Utilization in the UI
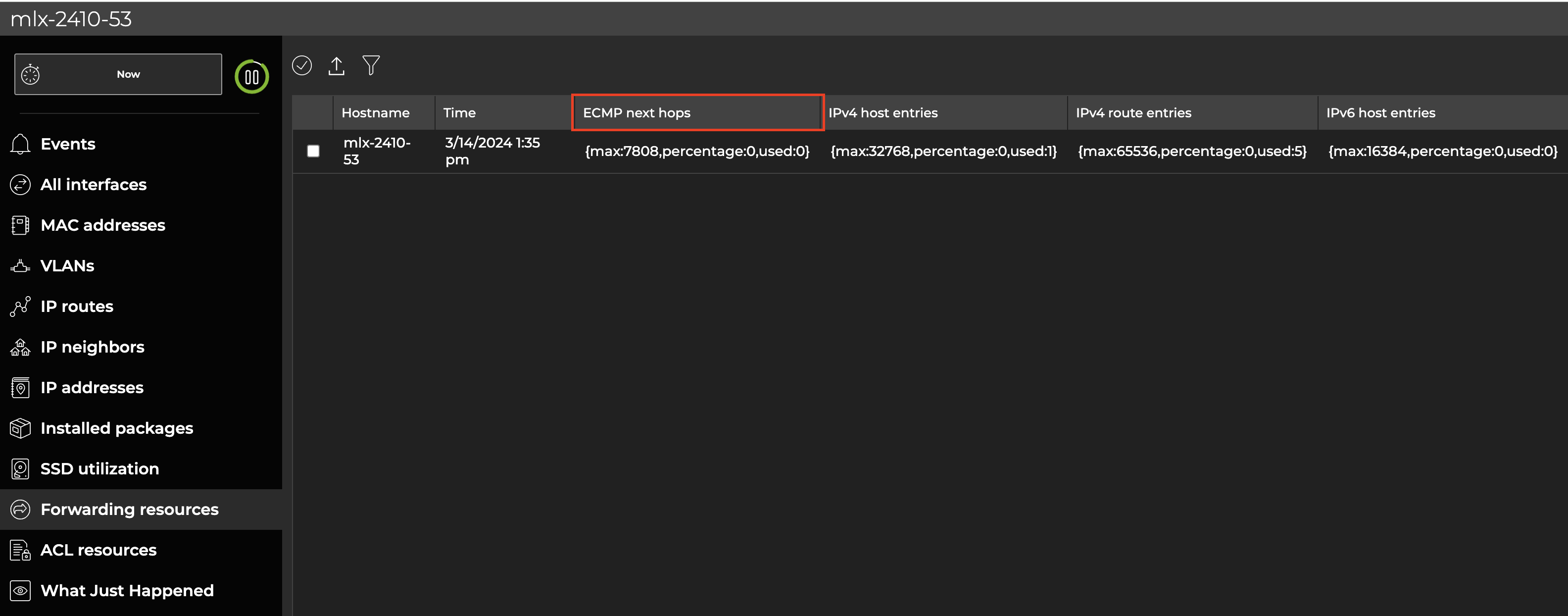
You can view resource utilization for ECMP next hops in the full-screen switch card. Search for the device’s hostname in the global search field or from the header select Add card > Device card. Select a switch from the list. When the card opens on the dashboard, expand it to the largest size.
Select Forwarding resources from the side menu. The ECMP next hops column displays the maximum number of hops seen in the forwarding table, the number used, and the percentage of this usage compared to the maximum number.
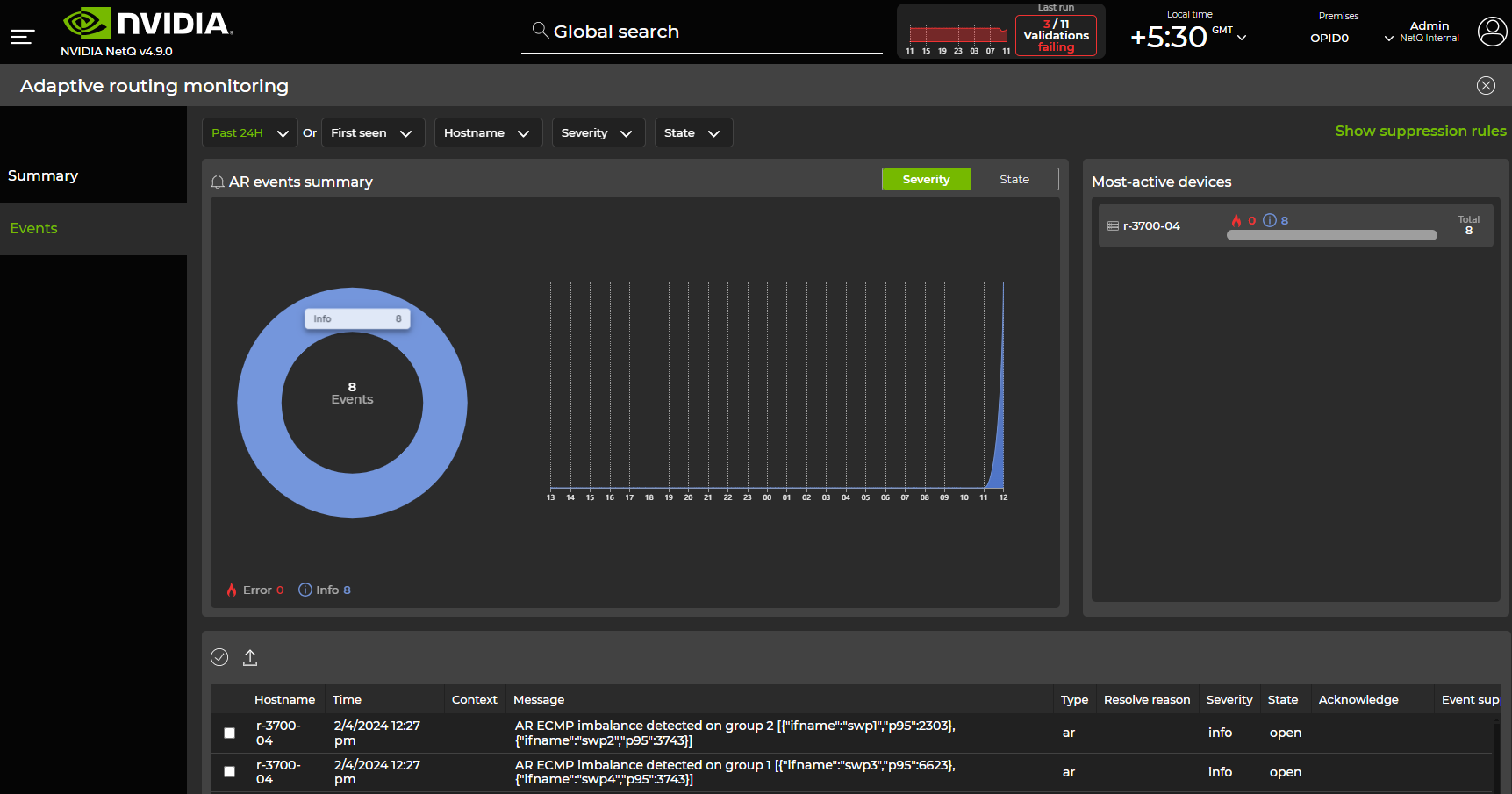
Adaptive Routing
Adaptive routing is a load balancing feature that improves network utilization for eligible IP packets by selecting forwarding paths dynamically based on the state of the switch, such as queue occupancy and port utilization. You can use the adaptive routing dashboard to view switches with adaptive routing capabilities, events related to adaptive routing, RoCE settings, and egress queue lengths in the form of histograms.
Requirements
- Adaptive routing monitoring is supported on Spectrum-4 switches. It requires a switch fabric running Cumulus Linux 5.5.0 or later.
- To display adaptive routing data, you must configure adaptive routing on the switch; it can be either enabled or disabled. Switches without an adaptive routing configuration will not appear in the UI or CLI.
- RoCE lossless mode must be enabled to display adaptive routing data. Switches with RoCE lossy mode enabled will appear in the UI and CLI, but will not display adaptive routing data.
- To view a switch’s histogram data and adaptive routing imbalance events, you must enable
ASIC monitoring on the switch. If you stop the
asic-monitorservice, NetQ will report values of 0 for all histogram metrics (P95, standard deviation, mean, and maximum queue lengths).
Adaptive Routing Commands
Monitor adaptive routing with the netq show adaptive-routing config commands. The output of these commands display adaptive routing information either globally on the switch or at the interface level.
netq show adaptive-routing config global
netq show adaptive-routing config interface
Access the Adaptive Routing Dashboard
From the header or Menu, select Spectrum-X, then Adaptive routing.
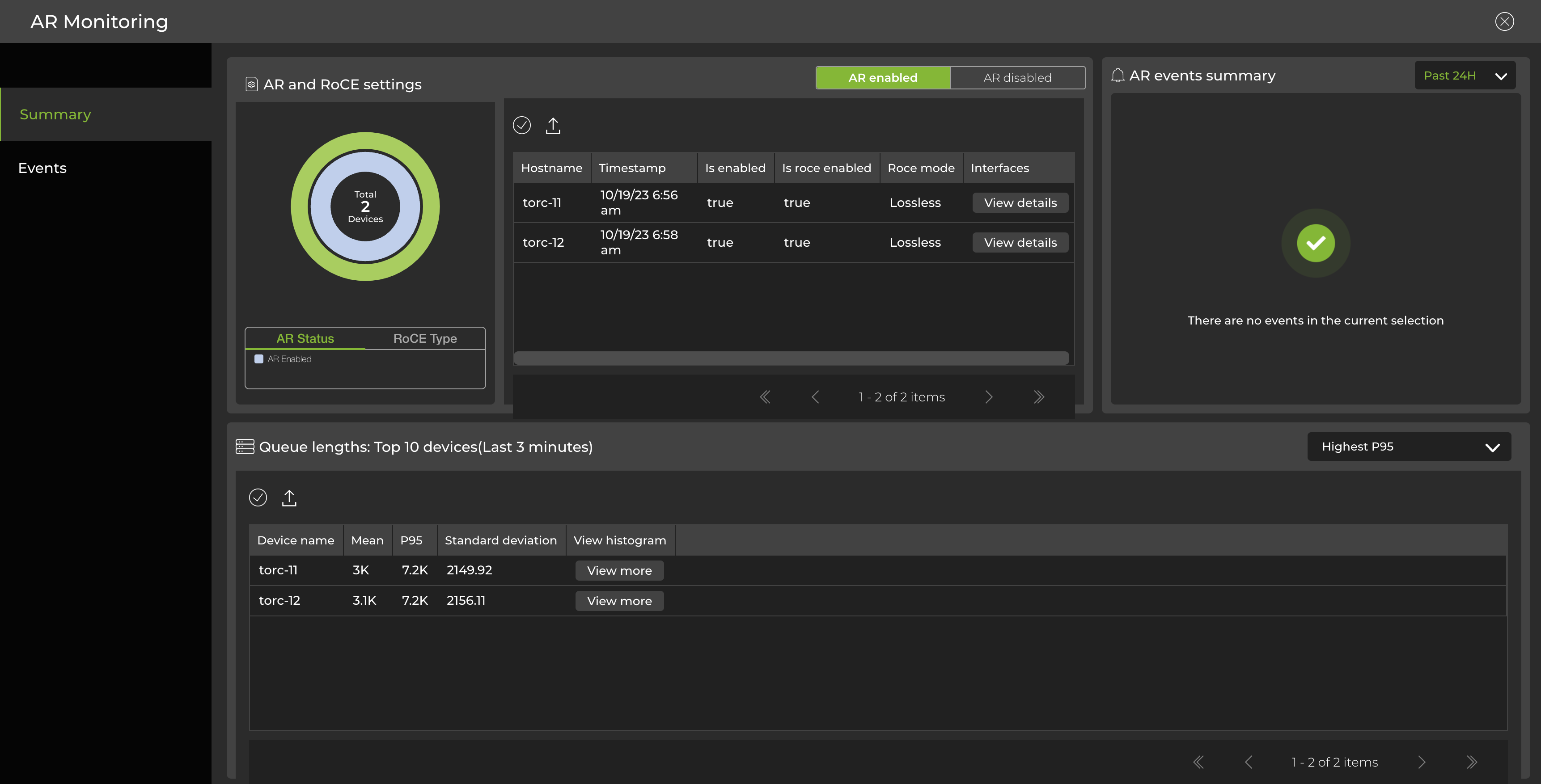
The adaptive routing dashboard displays:
- Devices with adaptive routing configured (enabled or disabled) and their RoCE modes (lossy or lossless).
- A list of interfaces on the switch and their configurations.
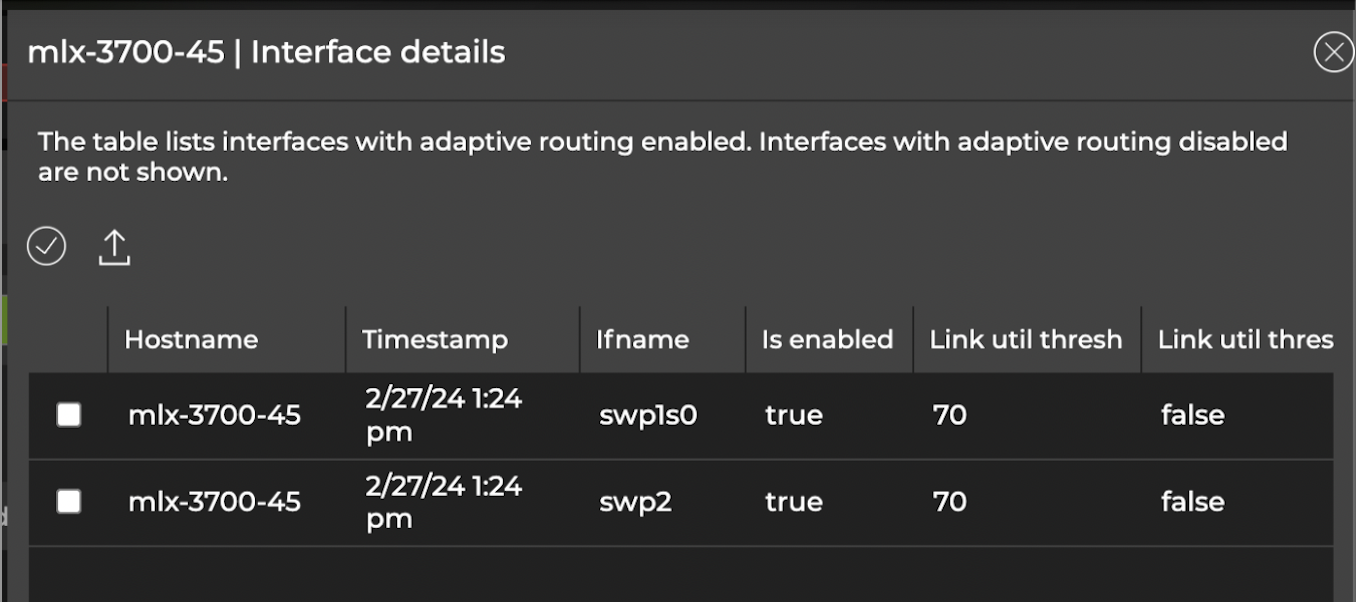
In the Interfaces column, select View details to view interfaces with adaptive routing configured:
The Events tab displays a summary of adaptive routing events, including ECMP traffic imbalances. The table displays up to 10 switches, which can be sorted by highest P95 value, highest standard deviation, or ports with the widest deviation from the P95 value (aggregated over the past 3 minutes). From this panel, you can select View more in the View histogram column to display queue lengths in the form of histograms for any listed switch.