Set Up Your Virtual Machine for an On-premises HA Server Cluster
Follow these steps to set up and configure your VM on a cluster of servers in an on-premises deployment. First configure the VM on the master node, and then configure the VM on each worker node. NVIDIA recommends installing the virtual machines on different physical servers to increase redundancy in the event of a hardware failure.
System Requirements
Verify that each node in your cluster—the master node and two worker nodes—meets the VM requirements.
| Resource | Minimum Requirements |
|---|---|
| Processor | 16 virtual CPUs |
| Memory | 64 GB RAM |
| Local disk storage | 500 GB SSD with minimum disk IOPS of 1000 for a standard 4kb block size (Note: This must be an SSD; other storage options can lead to system instability and are not supported.) |
| Network interface speed | 1 Gb NIC |
| Hypervisor | KVM/QCOW (QEMU Copy on Write) image for servers running Ubuntu; VMware ESXi™ 6.5 or later (OVA image) for servers running Cumulus Linux or Ubuntu |
Port Requirements
Confirm that the required ports are open for communications.
| Port or Protocol Number | Protocol | Component Access |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | IP Protocol | Calico networking (IP-in-IP Protocol) |
| 22 | TCP | SSH |
| 80 | TCP | nginx |
| 179 | TCP | Calico networking (BGP) |
| 443 | TCP | NetQ UI |
| 2379 | TCP | etcd datastore |
| 4789 | UDP | Calico networking (VxLAN) |
| 5000 | TCP | Docker registry |
| 6443 | TCP | kube-apiserver |
| 30001 | TCP | DPU communication |
| 31980 | TCP | NetQ Agent communication |
| 31982 | TCP | NetQ Agent SSL communication |
| 32708 | TCP | API Gateway |
Additionally, for internal cluster communication, you must open these ports:
| Port or Protocol Number | Protocol | Component Access |
|---|---|---|
| 8080 | TCP | Admin API |
| 5000 | TCP | Docker registry |
| 6443 | TCP | Kubernetes API server |
| 10250 | TCP | kubelet health probe |
| 2379 | TCP | etcd |
| 2380 | TCP | etcd |
| 7072 | TCP | Kafka JMX monitoring |
| 9092 | TCP | Kafka client |
| 7071 | TCP | Cassandra JMX monitoring |
| 7000 | TCP | Cassandra cluster communication |
| 9042 | TCP | Cassandra client |
| 7073 | TCP | Zookeeper JMX monitoring |
| 2888 | TCP | Zookeeper cluster communication |
| 3888 | TCP | Zookeeper cluster communication |
| 2181 | TCP | Zookeeper client |
| 36443 | TCP | Kubernetes control plane |
Installation and Configuration
-
Download the NetQ image.
a. Log in to your NVIDIA Application Hub account.
b. Select NVIDIA Licensing Portal.
c. Select Software Downloads from the menu.
d. Click Product Family and select NetQ.
e. For deployments using KVM, download the NetQ SW 4.12 KVM image. For deployments using VMware, download the NetQ SW 4.12 VMware image
f. If prompted, read the license agreement and proceed with the download.
NVIDIA employees can download NetQ directly from the NVIDIA Licensing Portal.
- Open your hypervisor and configure your VM. You can use the following examples for reference or use your own hypervisor instructions.
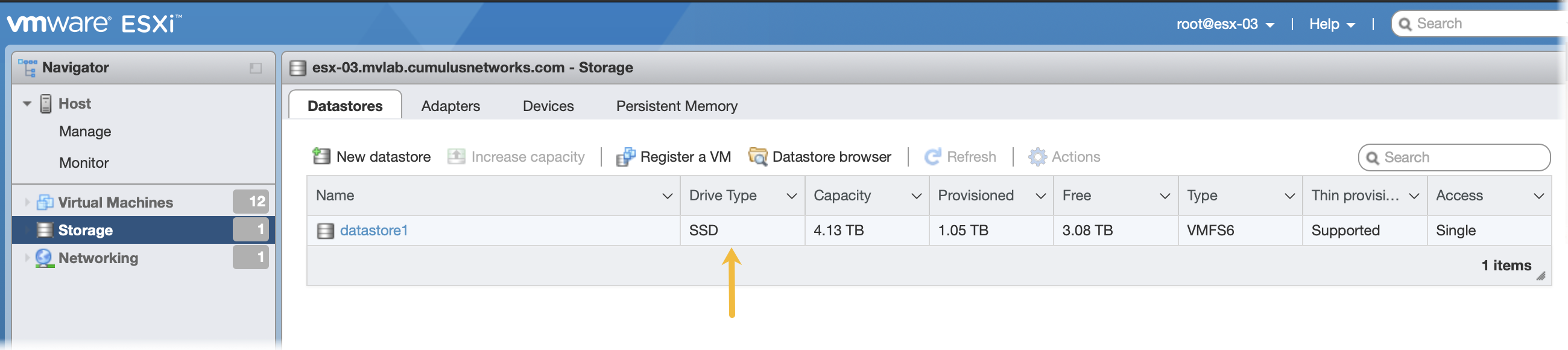
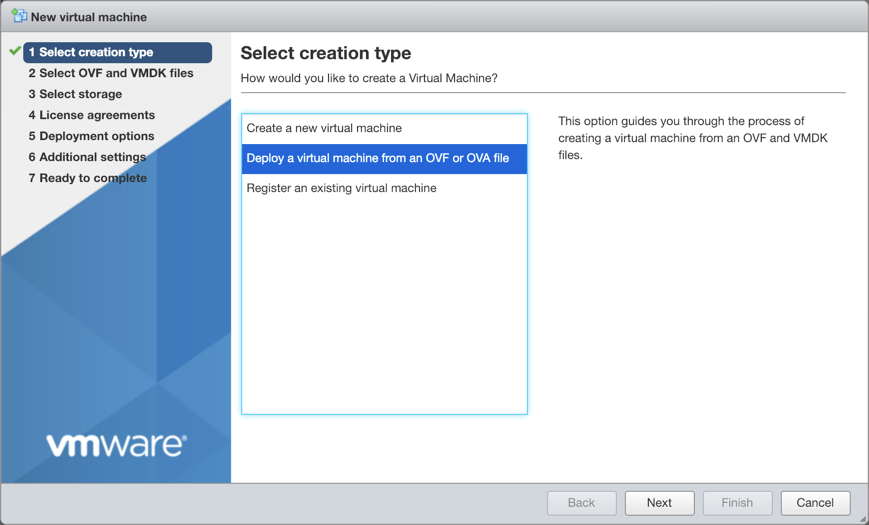
This example shows the VM setup process for a system with Libvirt and KVM/QEMU installed. Confirm that the SHA256 checksum matches the one posted on the NVIDIA Application Hub to ensure the image download has not been corrupted. Tip: Copy, instead of moving, the original QCOW2 image that was downloaded to avoid re-downloading it again later should you need to perform this process again. For a Direct VM, where the VM uses a MACVLAN interface to sit on the host interface for its connectivity: Replace the disk path value with the location where the QCOW2 image is to reside. Replace network model value (eth0 in the above example) with the name of the interface where the VM is connected to the external network. Or, for a Bridged VM, where the VM attaches to a bridge which has already been setup to allow for external access: Replace network bridge value (br0 in the above example) with the name of the (pre-existing) bridge interface where the VM is connected to the external network. Make note of the name used during install as this is needed in a later step. Enter the address of the hardware in your browser. Log in to VMware using credentials with root access. Click Storage in the Navigator to verify you have an SSD installed. Click Create/Register VM at the top of the right pane. Select Deploy a virtual machine from an OVF or OVA file, and click Next. Provide a name for the VM, for example NetQ. Tip: Make note of the name used during install as this is needed in a later step. Drag the NetQ image file you downloaded from the NVIDIA Application Hub to the installation wizard, then click Next. Select the storage type and data store for the image, then click Next.
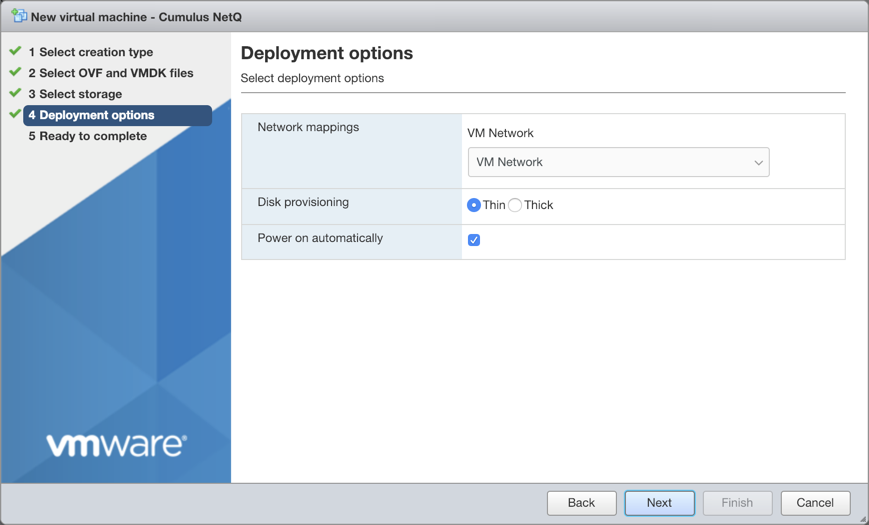
Accept the default deployment options or modify them according to your network needs. Click Next when you are finished. Review the configuration summary. Click Back to change any of the settings, or click Finish to continue with the creation of the VM. The progress of the request is shown in the Recent Tasks window at the bottom of the application. This may take some time. After the VM is deployed, the wizard displays the full hardware and configuration details.KVM Example Configuration
$ sha256sum ./Downloads/netq-4.12.0-ubuntu-20.04-ts-qemu.qcow2
$ a0d9a4f9ce8925b7dfb90a5a44616cadbf3fc667013abae07cd774555c08ff6f ./Downloads/netq-4.12.0-ubuntu-20.04-ts-qemu.qcow2$ sudo mkdir /vms
$ sudo cp ./Downloads/netq-4.12.0-ubuntu-20.04-ts-qemu.qcow2 /vms/ts.qcow2$ virt-install --name=netq_ts --vcpus=16 --memory=65536 --os-type=linux --os-variant=generic --disk path=/vms/ts.qcow2,format=qcow2,bus=virtio,cache=none --network=type=direct,source=eth0,model=virtio --import --noautoconsole
$ virt-install --name=netq_ts --vcpus=16 --memory=65536 --os-type=linux --os-variant=generic \ --disk path=/vms/ts.qcow2,format=qcow2,bus=virtio,cache=none --network=bridge=br0,model=virtio --import --noautoconsole
$ virsh console netq_ts
VMware Example Configuration
This example shows the VM setup process using an OVA file with VMware ESXi.

- Log in to the VM and change the password.
Use the default credentials to log in the first time:
- Username: cumulus
- Password: cumulus
$ ssh cumulus@<ipaddr>
Warning: Permanently added '<ipaddr>' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
cumulus@<ipaddr>'s password:
You are required to change your password immediately (root enforced)
System information as of Thu Dec 3 21:35:42 UTC 2020
System load: 0.09 Processes: 120
Usage of /: 8.1% of 61.86GB Users logged in: 0
Memory usage: 5% IP address for eth0: <ipaddr>
Swap usage: 0%
WARNING: Your password has expired.
You must change your password now and login again!
Changing password for cumulus.
(current) UNIX password: cumulus
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
Connection to <ipaddr> closed.
Log in again with your new password.
$ ssh cumulus@<ipaddr>
Warning: Permanently added '<ipaddr>' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
cumulus@<ipaddr>'s password:
System information as of Thu Dec 3 21:35:59 UTC 2020
System load: 0.07 Processes: 121
Usage of /: 8.1% of 61.86GB Users logged in: 0
Memory usage: 5% IP address for eth0: <ipaddr>
Swap usage: 0%
Last login: Thu Dec 3 21:35:43 2020 from <local-ipaddr>
cumulus@ubuntu:~$
- Verify that the master node is ready for installation. Fix any errors before installing the NetQ software.
cumulus@hostname:~$ sudo opta-check
- Change the hostname for the VM from the default value.
The default hostname for the NetQ virtual machines is ubuntu. Change the hostname to fit your naming conventions while meeting Internet and Kubernetes naming standards.
Kubernetes requires hostnames to be composed of a sequence of labels concatenated with dots. For example, “en.wikipedia.org” is a hostname. Each label must be from 1 to 63 characters long. The entire hostname, including the delimiting dots, has a maximum of 253 ASCII characters.
The Internet standards (RFCs) for protocols specify that labels may contain only the ASCII letters a through z (in lower case), the digits 0 through 9, and the hyphen-minus character ('-').
Use the following command:
cumulus@hostname:~$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname NEW_HOSTNAME
Add the same NEW_HOSTNAME value to /etc/hosts on your VM for the localhost entry. For example:
127.0.0.1 localhost NEW_HOSTNAME
-
Open your hypervisor and set up the VM in the same manner as for the master node.
Make a note of the private IP address you assign to the worker node. You will need it to complete the installation.
-
Verify that the worker node is ready for installation. Fix any errors indicated before installing the NetQ software.
cumulus@hostname:~$ sudo opta-check
-
Repeat steps 6 and 7 for each additional worker node in your cluster.
-
Install and activate the NetQ software using the CLI.
Run the following command on your master node to initialize the cluster. Copy the output of the command to use on your worker nodes:
cumulus@<hostname>:~$ netq install cluster master-init
Please run the following command on all worker nodes:
netq install cluster worker-init c3NoLXJzYSBBQUFBQjNOemFDMXljMkVBQUFBREFRQUJBQUFCQVFDM2NjTTZPdVM3dQN9MWTU1a
-
Run the
netq install cluster worker-init <ssh-key>command on each of your worker nodes. -
Run the following commands on your master node, using the IP addresses of your worker nodes and the HA cluster virtual IP address (VIP):
The HA cluster virtual IP must be:
netq install command.cumulus@<hostname>:~$ netq install cluster full interface eth0 bundle /mnt/installables/NetQ-4.12.0.tgz workers <worker-1-ip> <worker-2-ip> cluster-vip <vip-ip>
NetQ uses the 10.244.0.0/16 (pod-ip-range) and 10.96.0.0/16 (service-ip-range) networks for internal communication by default. If you are using these networks, you must override each range by specifying new subnets for these parameters in the install command:
cumulus@hostname:~$ netq install cluster full interface eth0 bundle /mnt/installables/NetQ-4.12.0.tgz workers <worker-1-ip> <worker-2-ip> pod-ip-range <pod-ip-range> service-ip-range <service-ip-range>
You can specify the IP address of the server instead of the interface name using the ip-addr <ip-address> argument:
cumulus@hostname:~$ netq install cluster full ip-addr <ip-address> bundle /mnt/installables/NetQ-4.12.0.tgz workers <worker-1-ip> <worker-2-ip>
If you change the server IP address or hostname after installing NetQ, you must reset the server with the netq bootstrap reset keep-db command and rerun the install command.
If this step fails for any reason, run netq bootstrap reset and then try again.
Verify Installation Status
To view the status of the installation, use the netq show status [verbose] command. The following example shows a successful on-premises installation:
State: Active
NetQ Live State: Active
Installation Status: FINISHED
Version: 4.12.0
Installer Version: 4.12.0
Installation Type: Cluster
Activation Key: EhVuZXRxLWVuZHBvaW50LWdhdGV3YXkYsagDIixPSUJCOHBPWUFnWXI2dGlGY2hTRzExR2E5aSt6ZnpjOUvpVVTaDdpZEhFPQ==
Master SSH Public Key: c3NoLXJzYSBBQUFBQjNOemFDMXljMkVBQUFBREFRQUJBQUFCZ1FDNW9iVXB6RkczNkRC
Is Cloud: False
Kubernetes Cluster Nodes Status:
IP Address Hostname Role NodeStatus Virtual IP
------------ ----------- ------ ------------ ------------
10.213.7.52 10.213.7.52 Worker Ready 10.213.7.53
10.213.7.51 10.213.7.51 Worker Ready 10.213.7.53
10.213.7.49 10.213.7.49 Master Ready 10.213.7.53
In Summary, Live state of the NetQ is... Active
Run the netq show opta-health command to verify that all applications are operating properly. Allow at least 15 minutes for all applications to come up and report their status.
cumulus@hostname:~$ netq show opta-health
Application Status Namespace Restarts Timestamp
----------------------------------------------------- -------- ------------- ---------- ------------------------
cassandra-rc-0-w7h4z READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
cp-schema-registry-deploy-6bf5cbc8cc-vwcsx READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
kafka-broker-rc-0-p9r2l READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
kafka-connect-deploy-7799bcb7b4-xdm5l READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
netq-api-gateway-deploy-55996ff7c8-w4hrs READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
netq-app-address-deploy-66776ccc67-phpqk READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
netq-app-admin-oob-mgmt-server READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
netq-app-bgp-deploy-7dd4c9d45b-j9bfr READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
netq-app-clagsession-deploy-69564895b4-qhcpr READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
netq-app-configdiff-deploy-ff54c4cc4-7rz66 READY default 0 Fri Apr 10 16:08:38 2020
...
If any of the applications or services display a DOWN status after 30 minutes, open a support ticket and attach the output of the opta-support command.