Configure and Monitor What Just Happened Metrics
The What Just Happened (WJH) feature, available on Mellanox switches, streams detailed and contextual telemetry data for analysis. This provides real-time visibility into problems in the network, such as hardware packet drops due to buffer congestion, incorrect routing, and ACL or layer 1 problems. You must have Cumulus Linux 4.0.0 or later and NetQ 2.4.0 or later to take advantage of this feature.
If your switches are sourced from a vendor other than Mellanox, this view is blank as no data is collected.
When WJH capabilities are combined with Cumulus NetQ, you have the ability to hone in on losses, anywhere in the fabric, from a single management console. You can:
- View any current or historic drop information, including the reason for the drop
- Identify problematic flows or endpoints, and pin-point exactly where communication is failing in the network
By default, Cumulus Linux 4.0.0 provides the NetQ 2.3.1 Agent and CLI. If you installed Cumulus Linux 4.0.0 on your Mellanox switch, you need to upgrade the NetQ Agent and optionally the CLI to release 2.4.0 or later (preferably the latest release).
cumulus@:~$ sudo apt-get update cumulus@ :~$ sudo apt-get install -y netq-agent cumulus@ :~$ netq config restart agent cumulus@ :~$ sudo apt-get install -y netq-apps cumulus@ :~$ netq config restart cli
Configure the WJH Feature
WJH is enabled by default on Mellanox switches and no configuration is required in Cumulus Linux 4.0.0; however, you must enable the NetQ Agent to collect the data in NetQ 2.4.0 or later.
To enable WJH in NetQ:
-
Configure the NetQ Agent on the Mellanox switch.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq config add agent wjh -
Restart the NetQ Agent to start collecting the WJH data.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq config restart agent
When you are finished viewing the WJH metrics, you might want to stop the NetQ Agent from collecting WJH data to reduce network traffic. Use netq config del agent wjh followed by netq config restart agent to disable the WJH feature on the given switch.
Using wjh_dump.py on a Mellanox platform that is running Cumulus Linux 4.0 and the NetQ 2.4.0 agent causes the NetQ WJH client to stop receiving packet drop call backs. To prevent this issue, run wjh_dump.py on a different system than the one where the NetQ Agent has WJH enabled, or disable wjh_dump.py and restart the NetQ Agent (run netq config restart agent).
Configure Latency and Congestion Thresholds
WJH latency and congestion metrics depend on threshold settings to trigger the events. Packet latency is measured as the time spent inside a single system (switch). Congestion is measured as a percentage of buffer occupancy on the switch. When WJH triggers events when the high and low thresholds are crossed.
To configure these thresholds, run:
netq config add agent wjh-threshold (latency|congestion) <text-tc-list> <text-port-list> <text-th-hi> <text-th-lo>
You can specify multiple traffic classes and multiple ports by separating the classes or ports by a comma (no spaces).
This example creates latency thresholds for Class 3 traffic on port swp1 where the upper threshold is 10 and the lower threshold is 1.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq config add agent wjh-threshold latency 3 swp1 10 1
This example creates congestion thresholds for Class 4 traffic on port swp1 where the upper threshold is 200 and the lower threshold is 10.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq config add agent wjh-threshold congestion 4 swp1 200 10
View What Just Happened Metrics
You can view the WJH metrics from the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI.
-
Click
(main menu).
-
Click What Just Happened under the Network column.
This view displays events based on conditions detected in the data plane. The most recent 1000 events from the last 24 hours are presented for each drop category.
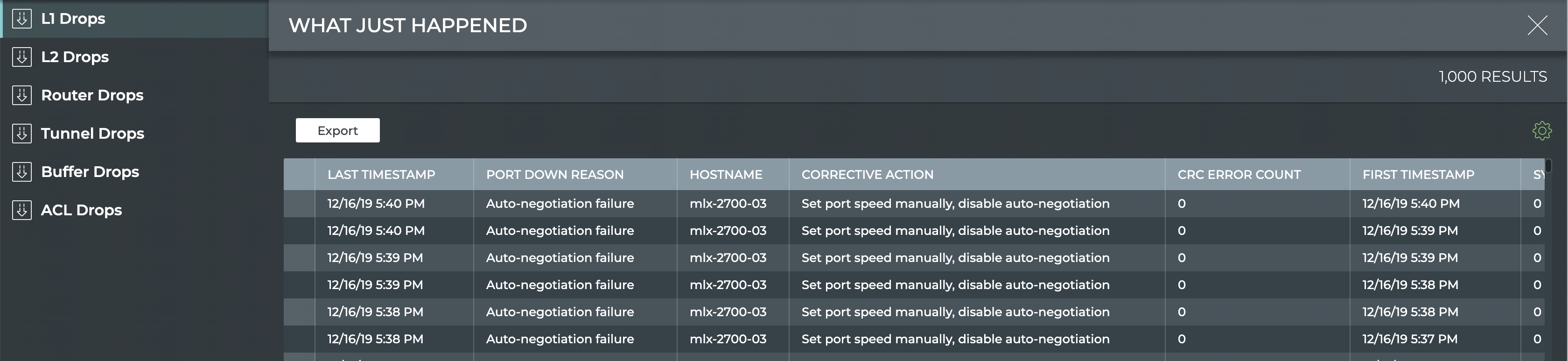
- By default the layer 1 drops are shown. Click one of the other drop categories to view those drops for all devices.
Run one of the following commands:
netq [<hostname>] show wjh-drop <text-drop-type> [ingress-port <text-ingress-port>] [severity <text-severity>] [reason <text-reason>] [src-ip <text-src-ip>] [dst-ip <text-dst-ip>] [proto <text-proto>] [src-port <text-src-port>] [dst-port <text-dst-port>] [src-mac <text-src-mac>] [dst-mac <text-dst-mac>] [egress-port <text-egress-port>] [traffic-class <text-traffic-class>] [rule-id-acl <text-rule-id-acl>] [between <text-time> and <text-endtime>] [around <text-time>] [json]
netq [<hostname>] show wjh-drop [ingress-port <text-ingress-port>] [severity <text-severity>] [details] [between <text-time> and <text-endtime>] [around <text-time>] [json]
Use the various options to restrict the output accordingly.
This example uses the first form of the command to show drops on switch leaf03 for the past week.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq leaf03 show wjh-drop between now and 7d
Matching wjh records:
Drop type Aggregate Count
------------------ ------------------------------
L1 560
Buffer 224
Router 144
L2 0
ACL 0
Tunnel 0
This example uses the second form of the command to show drops on switch leaf03 for the past week including the drop reasons.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq leaf03 show wjh-drop details between now and 7d
Matching wjh records:
Drop type Aggregate Count Reason
------------------ ------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------
L1 556 None
Buffer 196 WRED
Router 144 Blackhole route
Buffer 14 Packet Latency Threshold Crossed
Buffer 14 Port TC Congestion Threshold
L1 4 Oper down
This example shows the drops seen at layer 2 across the network.
cumulus@mlx-2700-03:mgmt:~$ netq show wjh-drop l2
Matching wjh records:
Hostname Ingress Port Reason Agg Count Src Ip Dst Ip Proto Src Port Dst Port Src Mac Dst Mac First Timestamp Last Timestamp
----------------- ------------------------ --------------------------------------------- ------------------ ---------------- ---------------- ------ ---------------- ---------------- ------------------ ------------------ ------------------------------ ----------------------------
mlx-2700-03 swp1s2 Port loopback filter 10 27.0.0.19 27.0.0.22 0 0 0 00:02:00:00:00:73 0c:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff Mon Dec 16 11:54:15 2019 Mon Dec 16 11:54:15 2019
mlx-2700-03 swp1s2 Source MAC equals destination MAC 10 27.0.0.19 27.0.0.22 0 0 0 00:02:00:00:00:73 00:02:00:00:00:73 Mon Dec 16 11:53:17 2019 Mon Dec 16 11:53:17 2019
mlx-2700-03 swp1s2 Source MAC equals destination MAC 10 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 0 0 00:02:00:00:00:73 00:02:00:00:00:73 Mon Dec 16 11:40:44 2019 Mon Dec 16 11:40:44 2019
The following two examples include the severity of a drop event (error, warning or notice) for ACLs and routers.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show wjh-drop acl
Matching wjh records:
Hostname Ingress Port Reason Severity Agg Count Src Ip Dst Ip Proto Src Port Dst Port Src Mac Dst Mac Acl Rule Id Acl Bind Point Acl Name Acl Rule First Timestamp Last Timestamp
----------------- ------------------------ --------------------------------------------- ---------------- ------------------ ---------------- ---------------- ------ ---------------- ---------------- ------------------ ------------------ ---------------------- ---------------------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------------ ----------------------------
leaf01 swp2 Ingress router ACL Error 49 55.0.0.1 55.0.0.2 17 8492 21423 00:32:10:45:76:89 00:ab:05:d4:1b:13 0x0 0 Tue Oct 6 15:29:13 2020 Tue Oct 6 15:29:39 2020
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show wjh-drop router
Matching wjh records:
Hostname Ingress Port Reason Severity Agg Count Src Ip Dst Ip Proto Src Port Dst Port Src Mac Dst Mac First Timestamp Last Timestamp
----------------- ------------------------ --------------------------------------------- ---------------- ------------------ ---------------- ---------------- ------ ---------------- ---------------- ------------------ ------------------ ------------------------------ ----------------------------
leaf01 swp1 Blackhole route Notice 36 46.0.1.2 47.0.2.3 6 1235 43523 00:01:02:03:04:05 00:06:07:08:09:0a Tue Oct 6 15:29:13 2020 Tue Oct 6 15:29:47 2020
This table lists all of the supported metrics and provides a brief description of each.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | What Just Happened. |
| Closes full screen card and returns to workbench. | |
| Results | Number of results found for the selected tab. |
| L1 Drops tab | Displays the reason why a port is in the down state. By default, the listing is sorted by Last Timestamp. The tab provides the following additional data about each drop event:
|
| L2 Drops tab | Displays the reason for a link to be down. By default, the listing is sorted by Last Timestamp. The tab provides the following additional data about each drop event:
|
| Router Drops tab | Displays the reason why the server is unable to route a packet. By default, the listing is sorted by Last Timestamp. The tab provides the following additional data about each drop event:
|
| Tunnel Drops tab | Displays the reason for a tunnel to be down. By default, the listing is sorted by Last Timestamp. The tab provides the following additional data about each drop event:
|
| Buffer Drops tab | Displays the reason for the server buffer to be drop packets. By default, the listing is sorted by Last Timestamp. The tab provides the following additional data about each drop event:
|
| ACL Drops tab | Displays the reason for an ACL to drop packets. By default, the listing is sorted by Last Timestamp. The tab provides the following additional data about each drop event:
|
| Table Actions | Select, export, or filter the list. Refer to Table Settings. |