Configure Notifications
To take advantage of the numerous event messages generated and processed by NetQ, you must integrate with third-party event notification applications. You can integrate NetQ with Syslog, PagerDuty, Slack, and Email. You may integrate with one or more of these applications simultaneously.
In an on-premises deployment, the NetQ On-premises Appliance or VM receives the raw data stream from the NetQ Agents, processes the data, stores, and delivers events to the Notification function. Notification then filters and sends messages to any configured notification applications. In a cloud deployment, the NetQ Cloud Appliance or VM passes the raw data stream on to the NetQ Cloud service for processing and delivery.
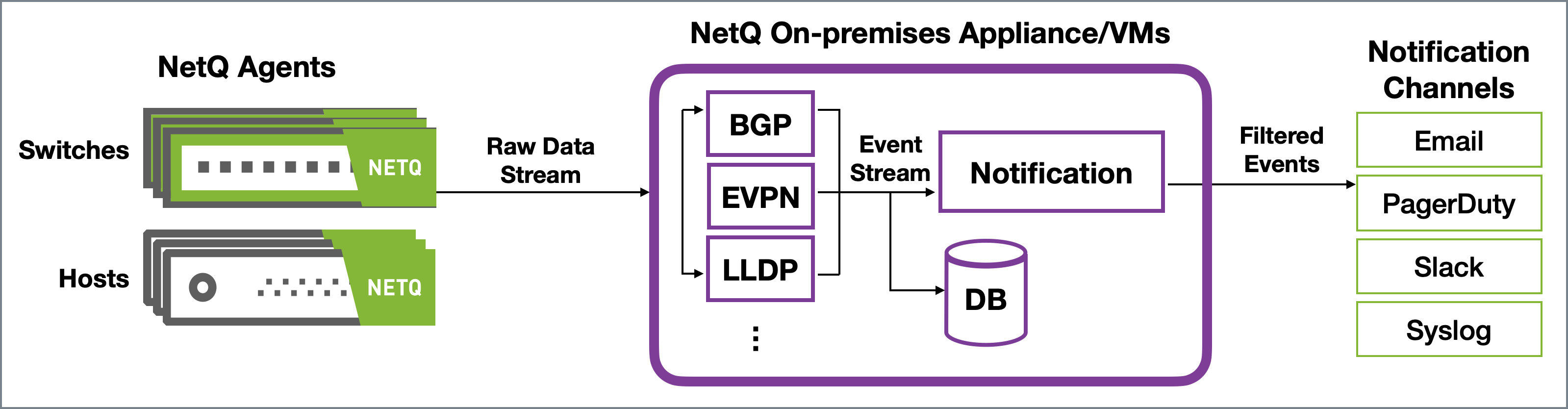
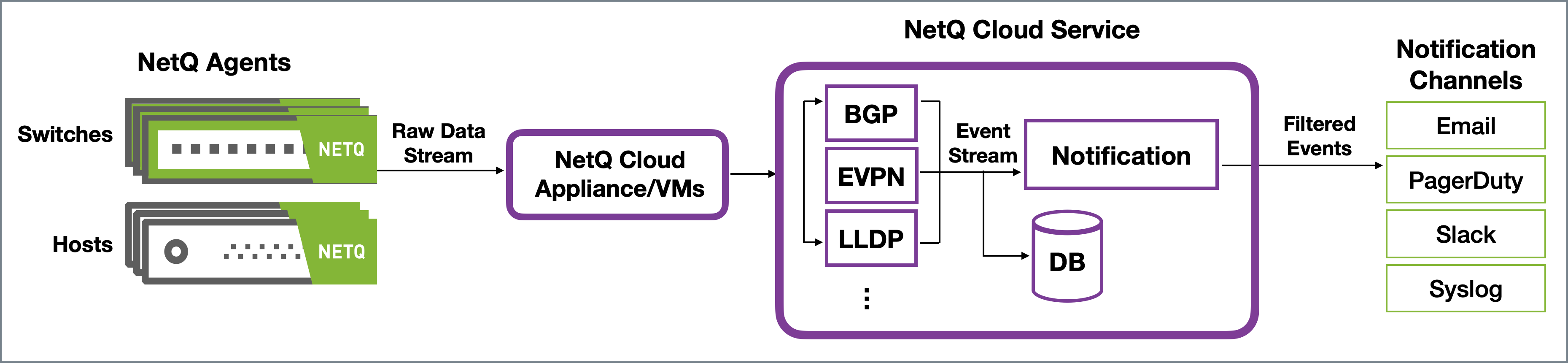
You may choose to implement a proxy server (that sits between the NetQ Appliance or VM and the integration channels) that receives, processes and distributes the notifications rather than having them sent directly to the integration channel. If you use such a proxy, you must configure NetQ with the proxy information.
Notifications are generated for the following types of events:
| Category | Events |
|---|---|
| Network Protocol Validations |
|
| Interfaces |
|
| Services |
|
| Traces |
|
| Sensors |
|
| System Software |
|
| System Hardware |
|
* This type of event can only be viewed in the CLI with this release.
Event filters are based on rules you create. You must have at least one rule per filter. A select set of events can be triggered by a user-configured threshold.
Refer to the System Event Messages Reference for descriptions and examples of these events.
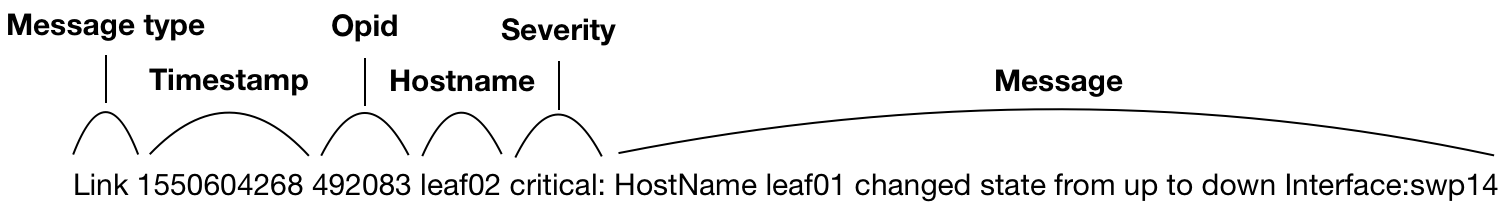
Event Message Format
Messages have the following structure:
<message-type><timestamp><opid><hostname><severity><message>
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| message type | Category of event; agent, bgp, clag, clsupport, configdiff, evpn, license, link, lldp, mtu, node, ntp, ospf, packageinfo, ptm, resource, runningconfigdiff, sensor, services, ssdutil, tca, trace, version, vlan or vxlan |
| timestamp | Date and time event occurred |
| opid | Identifier of the service or process that generated the event |
| hostname | Hostname of network device where event occurred |
| severity | Severity level in which the given event is classified; debug, error, info, warning, or critical |
| message | Text description of event |
For example:
You can integrate notification channels using the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI.
- Channels card: specify channels
- Threshold Crossing Rules card: specify rules and filters, assign existing channels
-
netq notification (channel|rule|filter)command: specify channels, rules, and filters
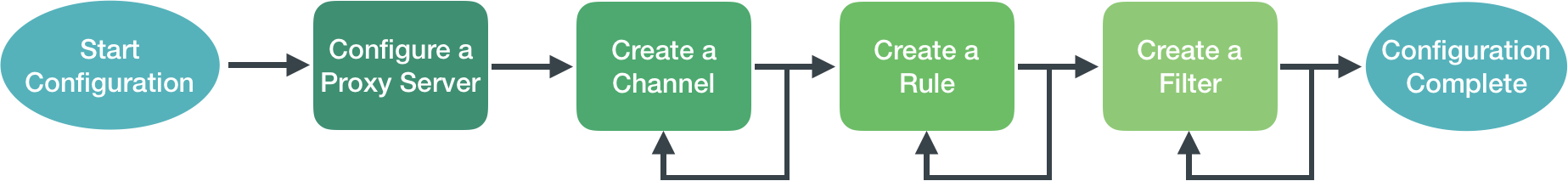
To set up the integrations, you must configure NetQ with at least one channel, one rule, and one filter. To refine what messages you want to view and where to send them, you can add additional rules and filters and set thresholds on supported event types. You can also configure a proxy server to receive, process, and forward the messages. This is accomplished using the NetQ UI and NetQ CLI in the following order:
Configure Basic NetQ Event Notifications
The simplest configuration you can create is one that sends all events generated by all interfaces to a single notification application. This is described here. For more granular configurations and examples, refer to Configure Advanced NetQ Event Notifications.
A notification configuration must contain one channel, one rule, and one filter. Creation of the configuration follows this same path:
- Add a channel.
- Add a rule that accepts a selected set events.
- Add a filter that associates this rule with the newly created channel.
Create a Channel
The first step is to create a PagerDuty, Slack, syslog, or Email channel to receive the notifications.
You can use the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI to create a Slack channel.
- Click
, and then click Channels in the Notifications column.
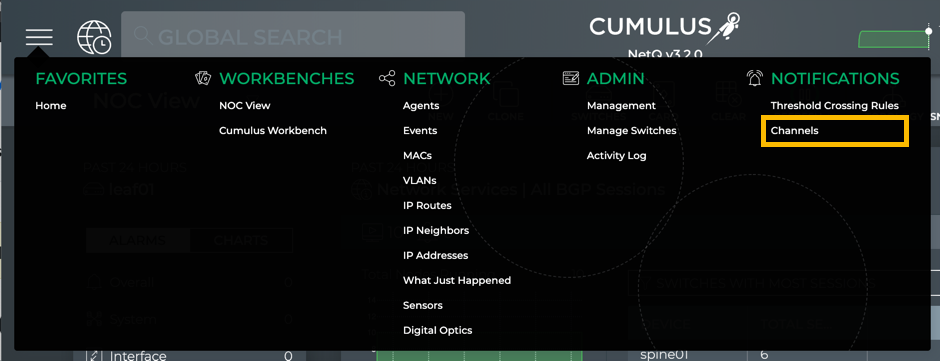
- The Slack tab is displayed by default.

-
Add a channel.
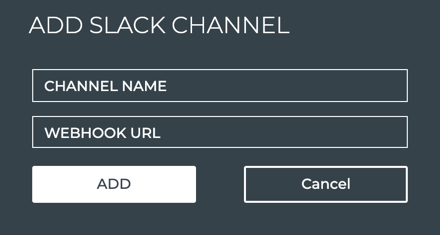
- When no channels have been specified, click Add Slack Channel.
- When at least one channel has been specified, click
above the table.
-
Provide a unique name for the channel. Note that spaces are not allowed. Use dashes or camelCase instead.
-
Create an incoming webhook as described in the documentation for your version of Slack. Then copy and paste it here.
-
Click Add.
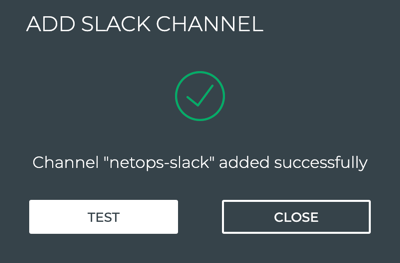
-
To verify the channel configuration, click Test.

- To return to your workbench, click
in the top right corner of the card.
To create and verify the specification of a Slack channel, run:
netq add notification channel slack <text-channel-name> webhook <text-webhook-url> [severity info|severity warning|severity error|severity debug] [tag <text-slack-tag>]
netq show notification channel [json]
This example shows the creation of a slk-netq-events channel and verifies the configuration.
-
Create an incoming webhook as described in the documentation for your version of Slack.
-
Create the channel.
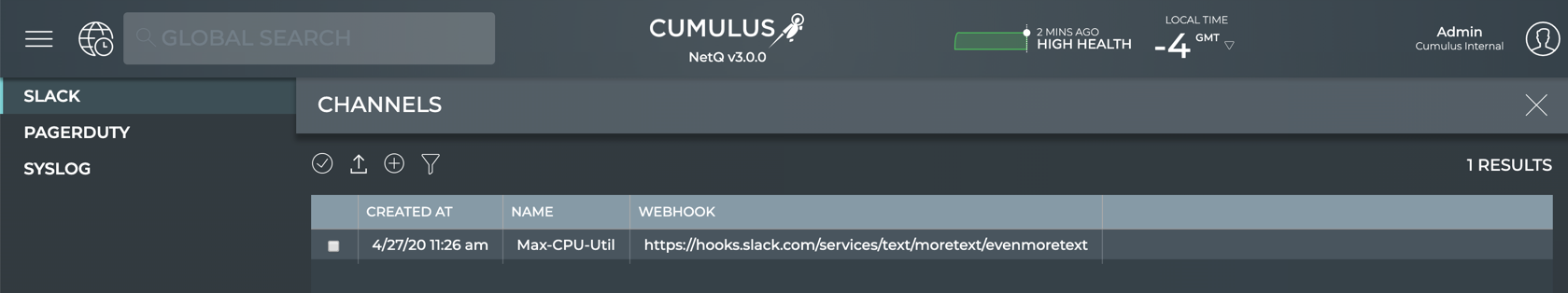
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel slack slk-netq-events webhook https://hooks.slack.com/services/text/moretext/evenmoretext Successfully added/updated channel slk-netq-events -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- -------- ---------------------- slk-netq-events slack info webhook:https://hooks.s lack.com/services/text/ moretext/evenmoretext
You can use the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI to create a PagerDuty channel.
- Click
, and then click Channels in the Notifications column.

- Click PagerDuty.

-
Add a channel.
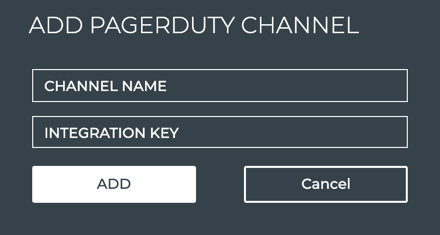
- When no channels have been specified, click Add PagerDuty Channel.
- When at least one channel has been specified, click
above the table.
-
Provide a unique name for the channel. Note that spaces are not allowed. Use dashes or camelCase instead.
-
Obtain and enter an integration key (also called a service key or routing key).
-
Click Add.
-
Verify it is correctly configured.
- To return to your workbench, click
in the top right corner of the card.
To create and verify the specification of a PagerDuty channel, run:
netq add notification channel pagerduty <text-channel-name> integration-key <text-integration-key> [severity info|severity warning|severity error|severity debug]
netq show notification channel [json]
This example shows the creation of a pd-netq-events channel and verifies the configuration.
-
Obtain an integration key as described in this PagerDuty support page.
-
Create the channel.
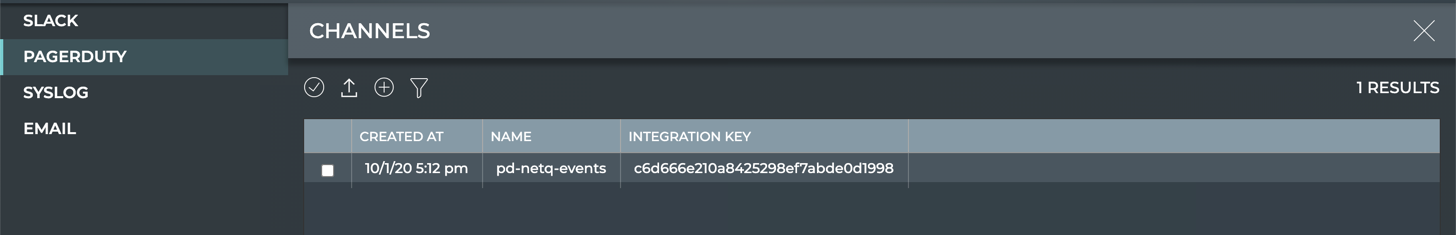
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel pagerduty pd-netq-events integration-key c6d666e210a8425298ef7abde0d1998 Successfully added/updated channel pd-netq-events -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------ pd-netq-events pagerduty info integration-key: c6d666e 210a8425298ef7abde0d1998
You can use the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI to create a Slack channel.
- Click
, and then click Channels in the Notifications column.

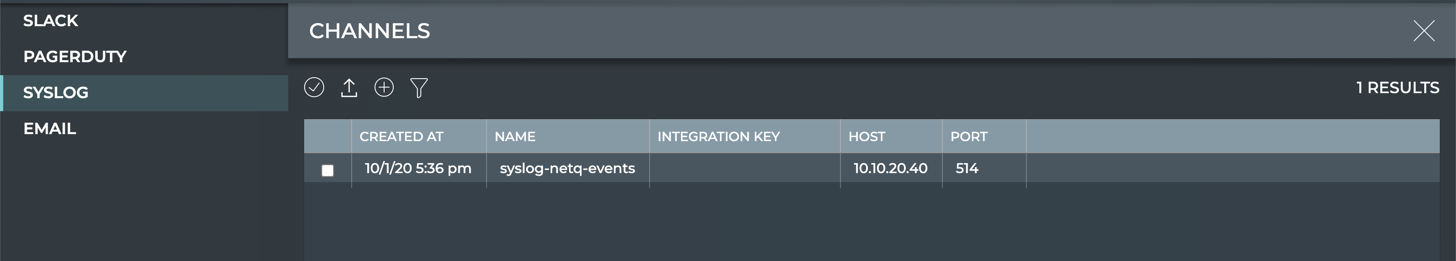
- Click Syslog.
-
Add a channel.
- When no channels have been specified, click Add Syslog Channel.
- When at least one channel has been specified, click
above the table.
-
Provide a unique name for the channel. Note that spaces are not allowed. Use dashes or camelCase instead.
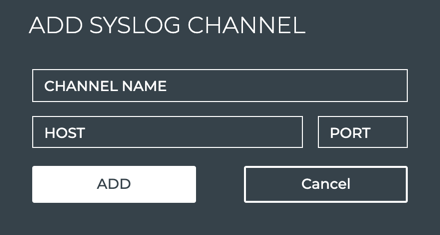
-
Enter the IP address and port of the Syslog server.
-
Click Add.
-
To verify the channel configuration, click Test.
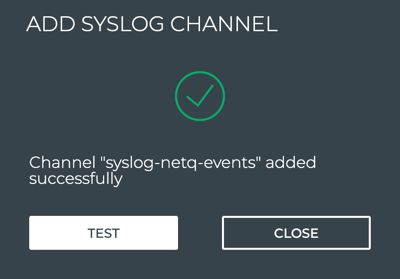
- To return to your workbench, click
in the top right corner of the card.
To create and verify the specification of a syslog channel, run:
netq add notification channel syslog <text-channel-name> hostname <text-syslog-hostname> port <text-syslog-port> [severity info | severity warning | severity error | severity debug]
netq show notification channel [json]
This example shows the creation of a syslog-netq-events channel and verifies the configuration.
-
Obtain the syslog server hostname (or IP address) and port.
-
Create the channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel syslog syslog-netq-events hostname syslog-server port 514 Successfully added/updated channel syslog-netq-events -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- -------- ---------------------- syslog-netq-eve syslog info host:syslog-server nts port: 514
You can use the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI to create an Email channel.
- Click
, and then click Channels in the Notifications column.

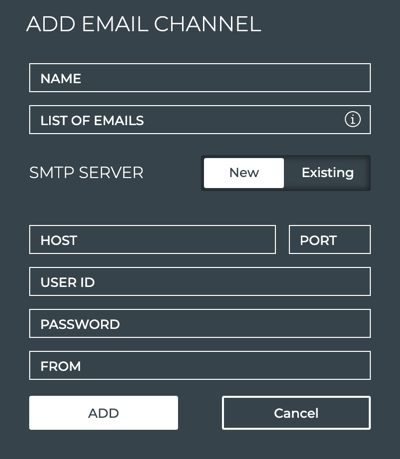
- Click Email.

-
Add a channel.
- When no channels have been specified, click Add Email Channel.
- When at least one channel has been specified, click
above the table.
-
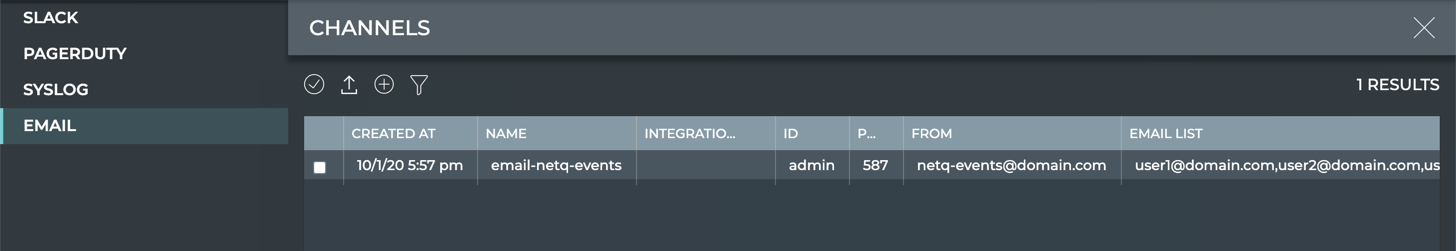
Provide a unique name for the channel. Note that spaces are not allowed. Use dashes or camelCase instead.
-
Enter a list of emails for the persons who you want to receive the notifications from this channel.
Enter the emails separated by commas, and no spaces. For example:
user1@domain.com,user2@domain.com,user3@domain.com. -
The first time you configure an Email channel, you must also specify the SMTP server information:
- Host: hostname or IP address of the SMTP server
- Port: port of the SMTP server; typically 587
- User ID/Password: your administrative credentials
- From: email address that indicates who sent the event messages
After the first time, any additional email channels you create can use this configuration, by clicking Existing.
-
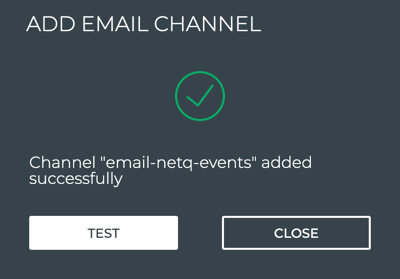
Click Add.
-
To verify the channel configuration, click Test.
- To return to your workbench, click
in the top right corner of the card.
To create and verify the specification of an Email channel, run:
netq add notification channel email <text-channel-name> to <text-email-toids> [smtpserver <text-email-hostname>] [smtpport <text-email-port>] [login <text-email-id>] [password <text-email-password>] [severity info | severity warning | severity error | severity debug]
netq add notification channel email <text-channel-name> to <text-email-toids>
netq show notification channel [json]
The configuration is different depending on whether you are using the on-premises or cloud version of NetQ. No SMTP configuration is required for cloud deployments as the NetQ cloud service uses the NetQ SMTP server to push email notifications.
For an on-premises deployment:
-
Set up an SMTP server. The server can be internal or public.
-
Create a user account (login and password) on the SMTP server. Notifications are sent to this address.
-
Create the notification channel using this form of the CLI command:
netq add notification channel email <text-channel-name> to <text-email-toids> [smtpserver <text-email-hostname>] [smtpport <text-email-port>] [login <text-email-id>] [password <text-email-password>] [severity info | severity warning | severity error | severity debug]
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel email onprem-email to netq-notifications@domain.com smtpserver smtp.domain.com smtpport 587 login smtphostlogin@domain.com password MyPassword123
Successfully added/updated channel onprem-email
-
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------ onprem-email email info password: MyPassword123, port: 587, isEncrypted: True, host: smtp.domain.com, from: smtphostlogin@doma in.com, id: smtphostlogin@domain .com, to: netq-notifications@d omain.com
For a cloud deployment:
-
Create the notification channel using this form of the CLI command:
netq add notification channel email <text-channel-name> to <text-email-toids>
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel email cloud-email to netq-cloud-notifications@domain.com
Successfully added/updated channel cloud-email
-
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------ cloud-email email info password: TEiO98BOwlekUP TrFev2/Q==, port: 587, isEncrypted: True, host: netqsmtp.domain.com, from: netqsmtphostlogin@doma in.com, id: smtphostlogin@domain .com, to: netq-notifications@d omain.com
Create a Rule
The second step is to create and verify a rule that accepts a set of events. Rules for system events are created using the NetQ CLI.
To create and verify the specification of a rule, run:
netq add notification rule <text-rule-name> key <text-rule-key> value <text-rule-value>
netq show notification rule [json]
Refer to Configure Notifications for a list of available keys and values.
This example creates a rule named all-interfaces, using the key ifname and the value ALL to indicate that all events from all interfaces should be sent to any channel with this rule.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule all-interfaces key ifname value ALL
Successfully added/updated rule all-ifs
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
all-interfaces ifname ALL
Refer to Advanced Configuration to create rules based on thresholds.
Create a Filter
The final step is to create a filter to tie the rule to the channel. Filters are created for system events using the NetQ CLI.
To create and verify a filter, run:
netq add notification filter <text-filter-name> rule <text-rule-name-anchor> channel <text-channel-name-anchor>
netq show notification filter [json]
These examples use the channels created in the Configure Notifications topic and the rule created in the Configure Notifications topic.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter notify-all-ifs rule all-interfaces channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter notify-all-ifs
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
notify-all-ifs 1 info pd-netq-events all-interfaces
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter notify-all-ifs rule all-interfaces channel slk-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter notify-all-ifs
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
notify-all-ifs 1 info slk-netq-events all-interfaces
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter notify-all-ifs rule all-interfaces channel syslog-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter notify-all-ifs
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
notify-all-ifs 1 info syslog-netq-events all-ifs
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter notify-all-ifs rule all-interfaces channel onprem-email
Successfully added/updated filter notify-all-ifs
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
notify-all-ifs 1 info onprem-email all-ifs
NetQ is now configured to send all interface events to your selected channel.
Refer to Advanced Configuration to create filters for threshold-based events.
Configure Advanced NetQ Event Notifications
If you want to create more granular notifications based on such items as selected devices, characteristics of devices, or protocols, or you want to use a proxy server, you need more than the basic notification configuration. Details for creating these more complex notification configurations are included here.
Configure a Proxy Server
To send notification messages through a proxy server instead of directly to a notification channel, you configure NetQ with the hostname and optionally a port of a proxy server. If no port is specified, NetQ defaults to port 80. Only one proxy server is currently supported. To simplify deployment, configure your proxy server before configuring channels, rules, or filters.
To configure and verify the proxy server, run:
netq add notification proxy <text-proxy-hostname> [port <text-proxy-port>]
netq show notification proxy
This example configures and verifies the proxy4 server on port 80 to act as a proxy for event notifications.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification proxy proxy4
Successfully configured notifier proxy proxy4:80
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification proxy
Matching config_notify records:
Proxy URL Slack Enabled PagerDuty Enabled
------------------ -------------------------- ----------------------------------
proxy4:80 yes yes
Create Channels
Create one or more PagerDuty, Slack, syslog, or Email channels to receive the notifications.
NetQ sends notifications to PagerDuty as PagerDuty events.
For example:
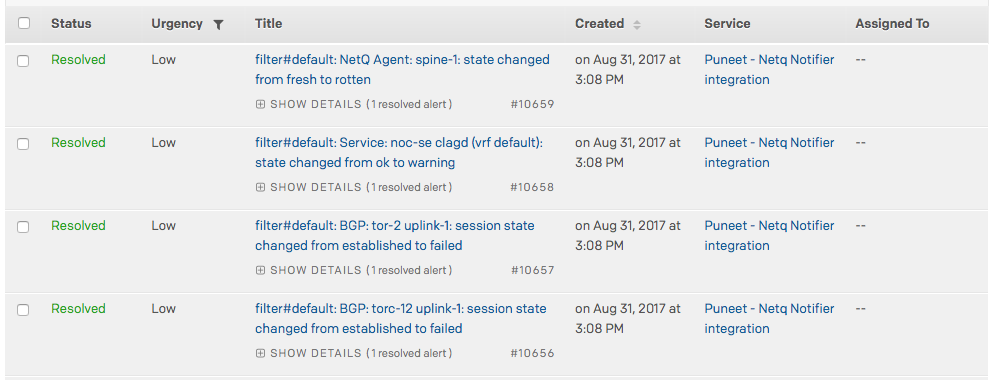
To create and verify the specification of a PagerDuty channel, run:
netq add notification channel pagerduty <text-channel-name> integration-key <text-integration-key> [severity info|severity warning|severity error|severity debug]
netq show notification channel [json]
where:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| <text-channel-name> | User-specified PagerDuty channel name |
| integration-key <text-integration-key> | The integration key is also called the service_key or routing_key. The default is an empty string (""). |
| severity <level> | (Optional) The log level to set, which can be one of info, warning, error, critical or debug. The severity defaults to info if unspecified. |
This example shows the creation of a pd-netq-events channel and verifies the configuration.
-
Obtain an integration key as described in this PagerDuty support page.
-
Create the channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel pagerduty pd-netq-events integration-key c6d666e210a8425298ef7abde0d1998 Successfully added/updated channel pd-netq-events -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------ pd-netq-events pagerduty info integration-key: c6d666e 210a8425298ef7abde0d1998
NetQ Notifier sends notifications to Slack as incoming webhooks for a Slack channel you configure.
For example:
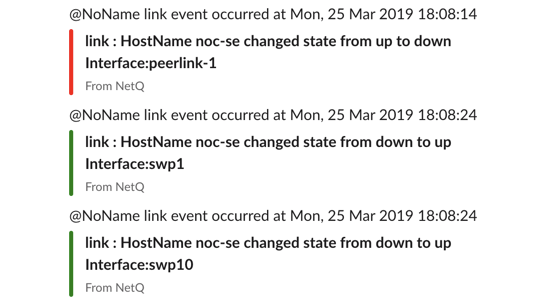
To create and verify the specification of a Slack channel, run:
netq add notification channel slack <text-channel-name> webhook <text-webhook-url> [severity info|severity warning|severity error|severity debug] [tag <text-slack-tag>]
netq show notification channel [json]
where:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| <text-channel-name> | User-specified Slack channel name |
| webhook <text-webhook-url> | WebHook URL for the desired channel. For example: https://hooks.slack.com/services/text/moretext/evenmoretext |
| severity <level> | The log level to set, which can be one of error, warning, info, or debug. The severity defaults to info. |
| tag <text-slack-tag> | Optional tag appended to the Slack notification to highlight particular channels or people. The tag value must be preceded by the @ sign. For example, @netq-info. |
This example shows the creation of a slk-netq-events channel and verifies the configuration.
-
Create an incoming webhook as described in the documentation for your version of Slack.
-
Create the channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel slack slk-netq-events webhook https://hooks.slack.com/services/text/moretext/evenmoretext severity warning tag @netq-ops Successfully added/updated channel slk-netq-events -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------ slk-netq-events slack warning tag: @netq-ops, webhook: https://hooks.s lack.com/services/text/m oretext/evenmoretext
To create and verify the specification of a syslog channel, run:
netq add notification channel syslog <text-channel-name> hostname <text-syslog-hostname> port <text-syslog-port> [severity info | severity warning | severity error | severity debug]
netq show notification channel [json]
where:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| <text-channel-name> | User-specified syslog channel name |
| hostname <text-syslog-hostname> | Hostname or IP address of the syslog server to receive notifications |
| port <text-syslog-port> | Port on the syslog server to receive notifications |
| severity <level> | The log level to set, which can be one of error, warning, info, or debug. The severity defaults to info. |
This example shows the creation of a syslog-netq-events channel and verifies the configuration.
-
Obtain the syslog server hostname (or IP address) and port.
-
Create the channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel syslog syslog-netq-events hostname syslog-server port 514 severity error Successfully added/updated channel syslog-netq-events -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- -------- ---------------------- syslog-netq-eve syslog error host:syslog-server nts port: 514
The configuration is different depending on whether you are using the on-premises or cloud version of NetQ.
To create an Email notification channel for an on-premises deployment, run:
netq add notification channel email <text-channel-name> to <text-email-toids> [smtpserver <text-email-hostname>] [smtpport <text-email-port>] [login <text-email-id>] [password <text-email-password>] [severity info | severity warning | severity error | severity debug]
This example creates an email channel named onprem-email that uses the smtpserver on port 587 to send messages to those persons with access to the smtphostlogin account.
-
Set up an SMTP server. The server can be internal or public.
-
Create a user account (login and password) on the SMTP server. Notifications are sent to this address.
-
Create the notification channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel email onprem-email to netq-notifications@domain.com smtpserver smtp.domain.com smtpport 587 login smtphostlogin@domain.com password MyPassword123 severity warning Successfully added/updated channel onprem-email -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------ onprem-email email warning password: MyPassword123, port: 587, isEncrypted: True, host: smtp.domain.com, from: smtphostlogin@doma in.com, id: smtphostlogin@domain .com, to: netq-notifications@d omain.com
In cloud deployments as the NetQ cloud service uses the NetQ SMTP server to push email notifications.
To create an Email notification channel for a cloud deployment, run:
netq add notification channel email <text-channel-name> to <text-email-toids> [severity info | severity warning | severity error | severity debug]
netq show notification channel [json]
This example creates an email channel named cloud-email that uses the NetQ SMTP server to send messages to those persons with access to the netq-cloud-notifications account.
-
Create the channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel email cloud-email to netq-cloud-notifications@domain.com severity error Successfully added/updated channel cloud-email -
Verify the configuration.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel Matching config_notify records: Name Type Severity Channel Info --------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------ cloud-email email error password: TEiO98BOwlekUP TrFev2/Q==, port: 587, isEncrypted: True, host: netqsmtp.domain.com, from: netqsmtphostlogin@doma in.com, id: smtphostlogin@domain .com, to: netq-notifications@d omain.com
Create Rules
Each rule is comprised of a single key-value pair. The key-value pair indicates what messages to include or drop from event information sent to a notification channel. You can create more than one rule for a single filter. Creating multiple rules for a given filter can provide a very defined filter. For example, you can specify rules around hostnames or interface names, enabling you to filter messages specific to those hosts or interfaces. You should have already defined channels (as described earlier).
There is a fixed set of valid rule keys. Values are entered as regular expressions and vary according to your deployment.
Rule Keys and Values
| Service | Rule Key | Description | Example Rule Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| BGP | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | bgp |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf11, exit01, spine-4 | |
| peer | User-defined, text-based name for a peer switch or host | server4, leaf-3, exit02, spine06 | |
| desc | Text description | ||
| vrf | Name of VRF interface | mgmt, default | |
| old_state | Previous state of the BGP service | Established, Failed | |
| new_state | Current state of the BGP service | Established, Failed | |
| old_last_reset_time | Previous time that BGP service was reset | Apr3, 2019, 4:17 pm | |
| new_last_reset_time | Most recent time that BGP service was reset | Apr8, 2019, 11:38 am | |
| ConfigDiff | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | configdiff |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf11, exit01, spine-4 | |
| vni | Virtual Network Instance identifier | 12, 23 | |
| old_state | Previous state of the configuration file | created, modified | |
| new_state | Current state of the configuration file | created, modified | |
| EVPN | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | evpn |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf-9, exit01, spine04 | |
| vni | Virtual Network Instance identifier | 12, 23 | |
| old_in_kernel_state | Previous VNI state, in kernel or not | true, false | |
| new_in_kernel_state | Current VNI state, in kernel or not | true, false | |
| old_adv_all_vni_state | Previous VNI advertising state, advertising all or not | true, false | |
| new_adv_all_vni_state | Current VNI advertising state, advertising all or not | true, false | LCM | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | clag |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf-9, exit01, spine04 | |
| old_conflicted_bonds | Previous pair of interfaces in a conflicted bond | swp7 swp8, swp3 swp4 | |
| new_conflicted_bonds | Current pair of interfaces in a conflicted bond | swp11 swp12, swp23 swp24 | |
| old_state_protodownbond | Previous state of the bond | protodown, up | |
| new_state_protodownbond | Current state of the bond | protodown, up | |
| Link | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | link |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf-6, exit01, spine7 | |
| ifname | Software interface name | eth0, swp53 | |
| LLDP | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | lldp |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf41, exit01, spine-5, tor-36 | |
| ifname | Software interface name | eth1, swp12 | |
| old_peer_ifname | Previous software interface name | eth1, swp12, swp27 | |
| new_peer_ifname | Current software interface name | eth1, swp12, swp27 | |
| old_peer_hostname | Previous user-defined, text-based name for a peer switch or host | server02, leaf41, exit01, spine-5, tor-36 | |
| new_peer_hostname | Current user-defined, text-based name for a peer switch or host | server02, leaf41, exit01, spine-5, tor-36 | MLAG (CLAG) | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | clag |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf-9, exit01, spine04 | |
| old_conflicted_bonds | Previous pair of interfaces in a conflicted bond | swp7 swp8, swp3 swp4 | |
| new_conflicted_bonds | Current pair of interfaces in a conflicted bond | swp11 swp12, swp23 swp24 | |
| old_state_protodownbond | Previous state of the bond | protodown, up | |
| new_state_protodownbond | Current state of the bond | protodown, up | |
| Node | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | node |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf41, exit01, spine-5, tor-36 | |
| ntp_state | Current state of NTP service | in sync, not sync | |
| db_state | Current state of DB | Add, Update, Del, Dead | |
| NTP | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | ntp |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf-9, exit01, spine04 | |
| old_state | Previous state of service | in sync, not sync | |
| new_state | Current state of service | in sync, not sync | |
| Port | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | port |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf13, exit01, spine-8, tor-36 | |
| ifname | Interface name | eth0, swp14 | |
| old_speed | Previous speed rating of port | 10 G, 25 G, 40 G, unknown | |
| old_transreceiver | Previous transceiver | 40G Base-CR4, 25G Base-CR | |
| old_vendor_name | Previous vendor name of installed port module | Amphenol, OEM, Mellanox, Fiberstore, Finisar | |
| old_serial_number | Previous serial number of installed port module | MT1507VS05177, AVE1823402U, PTN1VH2 | |
| old_supported_fec | Previous forward error correction (FEC) support status | none, Base R, RS | |
| old_advertised_fec | Previous FEC advertising state | true, false, not reported | |
| old_fec | Previous FEC capability | none | |
| old_autoneg | Previous activation state of auto-negotiation | on, off | |
| new_speed | Current speed rating of port | 10 G, 25 G, 40 G | |
| new_transreceiver | Current transceiver | 40G Base-CR4, 25G Base-CR | |
| new_vendor_name | Current vendor name of installed port module | Amphenol, OEM, Mellanox, Fiberstore, Finisar | |
| new_part_number | Current part number of installed port module | SFP-H10GB-CU1M, MC3309130-001, 603020003 | |
| new_serial_number | Current serial number of installed port module | MT1507VS05177, AVE1823402U, PTN1VH2 | |
| new_supported_fec | Current FEC support status | none, Base R, RS | |
| new_advertised_fec | Current FEC advertising state | true, false | |
| new_fec | Current FEC capability | none | |
| new_autoneg | Current activation state of auto-negotiation | on, off | |
| Sensors | sensor | Network protocol or service identifier | Fan: fan1, fan-2 Power Supply Unit: psu1, psu2 Temperature: psu1temp1, temp2 |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf-26, exit01, spine2-4 | |
| old_state | Previous state of a fan, power supply unit, or thermal sensor | Fan: ok, absent, bad PSU: ok, absent, bad Temp: ok, busted, bad, critical |
|
| new_state | Current state of a fan, power supply unit, or thermal sensor | Fan: ok, absent, bad PSU: ok, absent, bad Temp: ok, busted, bad, critical |
|
| old_s_state | Previous state of a fan or power supply unit. | Fan: up, down PSU: up, down |
|
| new_s_state | Current state of a fan or power supply unit. | Fan: up, down PSU: up, down |
|
| new_s_max | Current maximum temperature threshold value | Temp: 110 | |
| new_s_crit | Current critical high temperature threshold value | Temp: 85 | |
| new_s_lcrit | Current critical low temperature threshold value | Temp: -25 | |
| new_s_min | Current minimum temperature threshold value | Temp: -50 | |
| Services | message_type | Network protocol or service identifier | services |
| hostname | User-defined, text-based name for a switch or host | server02, leaf03, exit01, spine-8 | |
| name | Name of service | clagd, lldpd, ssh, ntp, netqd, netq-agent | |
| old_pid | Previous process or service identifier | 12323, 52941 | |
| new_pid | Current process or service identifier | 12323, 52941 | |
| old_status | Previous status of service | up, down | |
| new_status | Current status of service | up, down |
Rule names are case sensitive, and no wildcards are permitted. Rule names may contain spaces, but must be enclosed with single quotes in commands. It is easier to use dashes in place of spaces or mixed case for better readability. For example, use bgpSessionChanges or BGP-session-changes or BGPsessions, instead of 'BGP Session Changes'. Use Tab completion to view the command options syntax.
Example Rules
Create a BGP Rule Based on Hostname:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule bgpHostname key hostname value spine-01
Successfully added/updated rule bgpHostname
Create a Rule Based on a Configuration File State Change:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule sysconf key configdiff value updated
Successfully added/updated rule sysconf
Create an EVPN Rule Based on a VNI:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule evpnVni key vni value 42
Successfully added/updated rule evpnVni
Create an Interface Rule Based on FEC Support:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule fecSupport key new_supported_fec value supported
Successfully added/updated rule fecSupport
Create a Service Rule Based on a Status Change:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule svcStatus key new_status value down
Successfully added/updated rule svcStatus
Create a Sensor Rule Based on a Threshold:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule overTemp key new_s_crit value 24
Successfully added/updated rule overTemp
Create an Interface Rule Based on Port:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule swp52 key port value swp52
Successfully added/updated rule swp52
View the Rule Configurations
Use the netq show notification command to view the rules on your
platform.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
evpnVni vni 42
fecSupport new_supported_fe supported
c
overTemp new_s_crit 24
svcStatus new_status down
swp52 port swp52
sysconf configdiff updated
Create Filters
You can limit or direct event messages using filters. Filters are created based on rules you define; like those in the previous section. Each filter contains one or more rules. When a message matches the rule, it is sent to the indicated destination. Before you can create filters, you need to have already defined the rules and configured channels (as described earlier).
As filters are created, they are added to the bottom of a filter list. By default, filters are processed in the order they appear in this list (from top to bottom) until a match is found. This means that each event message is first evaluated by the first filter listed, and if it matches then it is processed, ignoring all other filters, and the system moves on to the next event message received. If the event does not match the first filter, it is tested against the second filter, and if it matches then it is processed and the system moves on to the next event received. And so forth. Events that do not match any filter are ignored.
You may need to change the order of filters in the list to ensure you capture the events you want and drop the events you do not want. This is possible using the before or after keywords to ensure one rule is processed before or after another.
This diagram shows an example with four defined filters with sample output results.
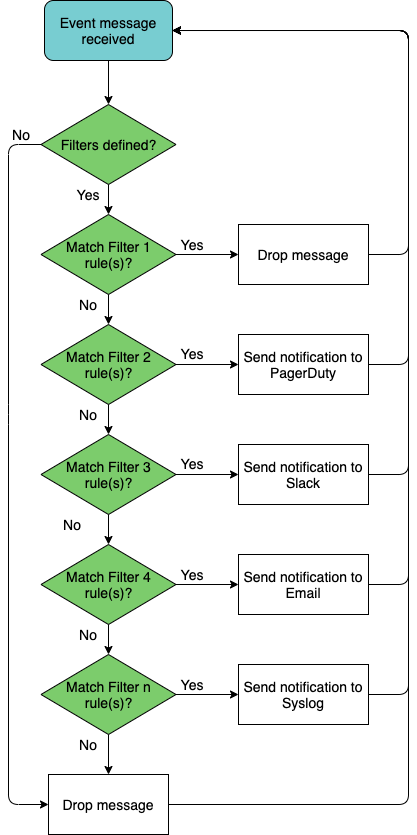
Filter names may contain spaces, but must be enclosed with single quotes in commands. It is easier to use dashes in place of spaces or mixed case for better readability. For example, use bgpSessionChanges or BGP-session-changes or BGPsessions, instead of 'BGP Session Changes'. Filter names are also case sensitive.
Example Filters
Create a filter for BGP Events on a Particular Device:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter bgpSpine rule bgpHostname channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter bgpSpine
Create a Filter for a Given VNI in Your EVPN Overlay:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter vni42 severity warning rule evpnVni channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter vni42
Create a Filter for when a Configuration File has been Updated:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter configChange severity info rule sysconf channel slk-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter configChange
Create a Filter to Monitor Ports with FEC Support:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter newFEC rule fecSupport channel slk-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter newFEC
Create a Filter to Monitor for Services that Change to a Down State:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter svcDown severity error rule svcStatus channel slk-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter svcDown
Create a Filter to Monitor Overheating Platforms:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter critTemp severity error rule overTemp channel onprem-email
Successfully added/updated filter critTemp
Create a Filter to Drop Messages from a Given Interface, and match against this filter before any other filters. To create a drop style filter, do not specify a channel. To put the filter first, use the before option.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter swp52Drop severity error rule swp52 before bgpSpine
Successfully added/updated filter swp52Drop
View the Filter Configurations
Use the netq show notification command to view the filters on your
platform.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
swp52Drop 1 error NetqDefaultChann swp52
el
bgpSpine 2 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
vni42 3 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
configChange 4 info slk-netq-events sysconf
newFEC 5 info slk-netq-events fecSupport
svcDown 6 critical slk-netq-events svcStatus
critTemp 7 critical onprem-email overTemp
Reorder Filters
When you look at the results of the netq show notification filter command above, you might notice that although you have the drop-based filter first (no point in looking at something you are going to drop anyway, so that is good), but the critical severity events are processed last, per the current definitions. If you wanted to process those before
lesser severity events, you can reorder the list using the before and after options.
For example, to put the two critical severity event filters just below the drop filter:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter critTemp after swp52Drop
Successfully added/updated filter critTemp
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter svcDown before bgpSpine
Successfully added/updated filter svcDown
You do not need to reenter all the severity, channel, and rule information for existing rules if you only want to change their processing order.
Run the netq show notification command again to verify the changes:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
swp52Drop 1 error NetqDefaultChann swp52
el
critTemp 2 critical onprem-email overTemp
svcDown 3 critical slk-netq-events svcStatus
bgpSpine 4 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
vni42 5 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
configChange 6 info slk-netq-events sysconf
newFEC 7 info slk-netq-events fecSupport
Suppress Events
Cumulus NetQ can generate many network events. You can configure whether to suppress any events from appearing in NetQ output. By default, all events are delivered.
You can suppress an event until a certain period of time; otherwise, the event is suppressed for 2 years. Providing an end time eliminates the generation of messages for a short period of time, which is useful when you are testing a new network configuration and the switch may be generating many messages.
You can suppress events for the following types of messages:
- agent: NetQ Agent messages
- bgp: BGP-related messages
- btrfsinfo: Messages related to the BTRFS file system in Cumulus Linux
- clag: MLAG-related messages
- clsupport: Messages generated when creating the
cl-support script - configdiff: Messages related to the difference between two configurations
- evpn: EVPN-related messages
- link: Messages related to links, including state and interface name
- ntp: NTP-related messages
- ospf: OSPF-related messages
- sensor: Messages related to various sensors
- services: Service-related information, including whether a service is active or inactive
- ssdutil: Messages related to the storage on the switch
Add an Event Suppression Configuration
When you add a new configuration, you can specify a scope, which limits the suppression in the following order:
- Hostname.
- Severity.
- Message type-specific filters. For example, the target VNI for EVPN messages, or the interface name for a link message.
NetQ has a predefined set of filter conditions. To see these conditions, run netq show events-config show-filter-conditions:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show events-config show-filter-conditions
Matching config_events records:
Message Name Filter Condition Name Filter Condition Hierarchy Filter Condition Description
------------------------ ------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------------
evpn vni 3 Target VNI
evpn severity 2 Severity critical/info
evpn hostname 1 Target Hostname
clsupport fileAbsName 3 Target File Absolute Name
clsupport severity 2 Severity critical/info
clsupport hostname 1 Target Hostname
link new_state 4 up / down
link ifname 3 Target Ifname
link severity 2 Severity critical/info
link hostname 1 Target Hostname
ospf ifname 3 Target Ifname
ospf severity 2 Severity critical/info
ospf hostname 1 Target Hostname
sensor new_s_state 4 New Sensor State Eg. ok
sensor sensor 3 Target Sensor Name Eg. Fan, Temp
sensor severity 2 Severity critical/info
sensor hostname 1 Target Hostname
configdiff old_state 5 Old State
configdiff new_state 4 New State
configdiff type 3 File Name
configdiff severity 2 Severity critical/info
configdiff hostname 1 Target Hostname
ssdutil info 3 low health / significant health drop
ssdutil severity 2 Severity critical/info
ssdutil hostname 1 Target Hostname
agent db_state 3 Database State
agent severity 2 Severity critical/info
agent hostname 1 Target Hostname
ntp new_state 3 yes / no
ntp severity 2 Severity critical/info
ntp hostname 1 Target Hostname
bgp vrf 4 Target VRF
bgp peer 3 Target Peer
bgp severity 2 Severity critical/info
bgp hostname 1 Target Hostname
services new_status 4 active / inactive
services name 3 Target Service Name Eg.netqd, mstpd, zebra
services severity 2 Severity critical/info
services hostname 1 Target Hostname
btrfsinfo info 3 high btrfs allocation space / data storage efficiency
btrfsinfo severity 2 Severity critical/info
btrfsinfo hostname 1 Target Hostname
clag severity 2 Severity critical/info
clag hostname 1 Target Hostname
For example, to create a configuration called mybtrfs that suppresses OSPF-related events on leaf01 for the next 10 minutes, run:
netq add events-config events_config_name mybtrfs message_type ospf scope '[{"scope_name":"hostname","scope_value":"leaf01"},{"scope_name":"severity","scope_value":"*"}]' suppress_until 600
Remove an Event Suppression Configuration
To remove an event suppression configuration, run netq del events-config events_config_id <text-events-config-id-anchor>.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq del events-config events_config_id eventsconfig_10
Successfully deleted Events Config eventsconfig_10
Show Event Suppression Configurations
You can view all event suppression configurations, or you can filter by a specific configuration or message type.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show events-config events_config_id eventsconfig_1
Matching config_events records:
Events Config ID Events Config Name Message Type Scope Active Suppress Until
-------------------- -------------------- -------------------- ------------------------------------------------------------ ------ --------------------
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c agent {"db_state":"*","hostname":"spine02","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine02
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c bgp {"vrf":"*","peer":"*","hostname":"spine04","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c btrfsinfo {"hostname":"spine04","info":"*","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c clag {"hostname":"spine04","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c clsupport {"fileAbsName":"*","hostname":"spine04","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c configdiff {"new_state":"*","old_state":"*","type":"*","hostname":"spin True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 e04","severity":"*"} 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c evpn {"hostname":"spine04","vni":"*","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c link {"ifname":"*","new_state":"*","hostname":"spine04","severity True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 ":"*"} 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c ntp {"new_state":"*","hostname":"spine04","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c ospf {"ifname":"*","hostname":"spine04","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c sensor {"sensor":"*","new_s_state":"*","hostname":"spine04","severi True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 ty":"*"} 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c services {"new_status":"*","name":"*","hostname":"spine04","severity" True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 :"*"} 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_1 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c ssdutil {"hostname":"spine04","info":"*","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:20
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
spine04
eventsconfig_10 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c btrfsinfo {"hostname":"fw2","info":"*","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:22
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
fw2
eventsconfig_10 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c clag {"hostname":"fw2","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:22
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
fw2
eventsconfig_10 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c clsupport {"fileAbsName":"*","hostname":"fw2","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:22
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
fw2
eventsconfig_10 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c link {"ifname":"*","new_state":"*","hostname":"fw2","severity":"* True Tue Jul 7 16:16:22
21b3effd79796e585c35 "} 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
fw2
eventsconfig_10 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c ospf {"ifname":"*","hostname":"fw2","severity":"*"} True Tue Jul 7 16:16:22
21b3effd79796e585c35 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
fw2
eventsconfig_10 job_cl_upgrade_2d89c sensor {"sensor":"*","new_s_state":"*","hostname":"fw2","severity": True Tue Jul 7 16:16:22
21b3effd79796e585c35 "*"} 2020
096d5fc6cef32b463e37
cca88d8ee862ae104d5_
fw2
If you are filtering for a message type, you must include the show-filter-conditions keyword to show the conditions associated with that message type and the hierarchy in which they’re processed.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show events-config message_type evpn show-filter-conditions
Matching config_events records:
Message Name Filter Condition Name Filter Condition Hierarchy Filter Condition Description
------------------------ ------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------------
evpn vni 3 Target VNI
evpn severity 2 Severity critical/info
evpn hostname 1 Target Hostname
Examples of Advanced Notification Configurations
Putting all of these channel, rule, and filter definitions together you create a complete notification configuration. The following are example notification configurations are created using the three-step process outlined above.
Create a Notification for BGP Events from a Selected Switch
In this example, we created a notification integration with a PagerDuty channel called pd-netq-events. We then created a rule bgpHostname and a filter called 4bgpSpine for any notifications from spine-01. The result is that any info severity event messages from Spine-01 are filtered to the pd-netq-events channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel pagerduty pd-netq-events integration-key 1234567890
Successfully added/updated channel pd-netq-events
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule bgpHostname key node value spine-01
Successfully added/updated rule bgpHostname
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter bgpSpine rule bgpHostname channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter bgpSpine
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel
Matching config_notify records:
Name Type Severity Channel Info
--------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------
pd-netq-events pagerduty info integration-key: 1234567
890
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
bgpSpine 1 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
Create a Notification for Warnings on a Given EVPN VNI
In this example, we created a notification integration with a PagerDuty channel called pd-netq-events. We then created a rule evpnVni and a filter called 3vni42 for any warnings messages from VNI 42 on the EVPN overlay network. The result is that any warning severity event messages from VNI 42 are filtered to the pd-netq-events channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel pagerduty pd-netq-events integration-key 1234567890
Successfully added/updated channel pd-netq-events
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule evpnVni key vni value 42
Successfully added/updated rule evpnVni
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter vni42 rule evpnVni channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter vni42
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel
Matching config_notify records:
Name Type Severity Channel Info
--------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------
pd-netq-events pagerduty info integration-key: 1234567
890
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
evpnVni vni 42
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
bgpSpine 1 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
vni42 2 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
Create a Notification for Configuration File Changes
In this example, we created a notification integration with a Slack channel called slk-netq-events. We then created a rule sysconf and a filter called configChange for any configuration file update messages. The result is that any configuration update messages are filtered to the slk-netq-events channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel slack slk-netq-events webhook https://hooks.slack.com/services/text/moretext/evenmoretext
Successfully added/updated channel slk-netq-events
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule sysconf key configdiff value updated
Successfully added/updated rule sysconf
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter configChange severity info rule sysconf channel slk-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter configChange
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel
Matching config_notify records:
Name Type Severity Channel Info
--------------- ---------------- -------- ----------------------
slk-netq-events slack info webhook:https://hooks.s
lack.com/services/text/
moretext/evenmoretext
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
evpnVni vni 42
sysconf configdiff updated
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
bgpSpine 1 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
vni42 2 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
configChange 3 info slk-netq-events sysconf
Create a Notification for When a Service Goes Down
In this example, we created a notification integration with a Slack channel called slk-netq-events. We then created a rule svcStatus and a filter called svcDown for any services state messages indicating a service is no longer operational. The result is that any service down messages are filtered to the slk-netq-events channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel slack slk-netq-events webhook https://hooks.slack.com/services/text/moretext/evenmoretext
Successfully added/updated channel slk-netq-events
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule svcStatus key new_status value down
Successfully added/updated rule svcStatus
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter svcDown severity error rule svcStatus channel slk-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter svcDown
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel
Matching config_notify records:
Name Type Severity Channel Info
--------------- ---------------- -------- ----------------------
slk-netq-events slack info webhook:https://hooks.s
lack.com/services/text/
moretext/evenmoretext
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
evpnVni vni 42
svcStatus new_status down
sysconf configdiff updated
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
bgpSpine 1 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
vni42 2 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
configChange 3 info slk-netq-events sysconf
svcDown 4 critical slk-netq-events svcStatus
Create a Filter to Drop Notifications from a Given Interface
In this example, we created a notification integration with a Slack channel called slk-netq-events. We then created a rule swp52 and a filter called swp52Drop that drops all notifications for events from interface swp52.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel slack slk-netq-events webhook https://hooks.slack.com/services/text/moretext/evenmoretext
Successfully added/updated channel slk-netq-events
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule swp52 key port value swp52
Successfully added/updated rule swp52
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter swp52Drop severity error rule swp52 before bgpSpine
Successfully added/updated filter swp52Drop
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel
Matching config_notify records:
Name Type Severity Channel Info
--------------- ---------------- -------- ----------------------
slk-netq-events slack info webhook:https://hooks.s
lack.com/services/text/
moretext/evenmoretext
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
evpnVni vni 42
svcStatus new_status down
swp52 port swp52
sysconf configdiff updated
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
swp52Drop 1 error NetqDefaultChann swp52
el
bgpSpine 2 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
vni42 3 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
configChange 4 info slk-netq-events sysconf
svcDown 5 critical slk-netq-events svcStatus
Create a Notification for a Given Device that has a Tendency to Overheat (using multiple rules)
In this example, we created a notification when switch leaf04 has passed over the high temperature threshold. Two rules were needed to create this notification, one to identify the specific device and one to identify the temperature trigger. We sent the message to the pd-netq-events channel.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification channel pagerduty pd-netq-events integration-key 1234567890
Successfully added/updated channel pd-netq-events
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule switchLeaf04 key hostname value leaf04
Successfully added/updated rule switchLeaf04
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification rule overTemp key new_s_crit value 24
Successfully added/updated rule overTemp
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter critTemp rule switchLeaf04 channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter critTemp
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add notification filter critTemp severity critical rule overTemp channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated filter critTemp
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel
Matching config_notify records:
Name Type Severity Channel Info
--------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------
pd-netq-events pagerduty info integration-key: 1234567
890
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
evpnVni vni 42
overTemp new_s_crit 24
svcStatus new_status down
switchLeaf04 hostname leaf04
swp52 port swp52
sysconf configdiff updated
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
swp52Drop 1 error NetqDefaultChann swp52
el
bgpSpine 2 info pd-netq-events bgpHostnam
e
vni42 3 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
configChange 4 info slk-netq-events sysconf
svcDown 5 critical slk-netq-events svcStatus
critTemp 6 critical pd-netq-events switchLeaf
04
overTemp
View Notification Configurations in JSON Format
You can view configured integrations using the netq show notification commands. To view the channels, filters, and rules, run the three flavors of the command. Include the json option to display JSON-formatted output.
For example:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel json
{
"config_notify":[
{
"type":"slack",
"name":"slk-netq-events",
"channelInfo":"webhook:https://hooks.slack.com/services/text/moretext/evenmoretext",
"severity":"info"
},
{
"type":"pagerduty",
"name":"pd-netq-events",
"channelInfo":"integration-key: 1234567890",
"severity":"info"
}
],
"truncatedResult":false
}
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule json
{
"config_notify":[
{
"ruleKey":"hostname",
"ruleValue":"spine-01",
"name":"bgpHostname"
},
{
"ruleKey":"vni",
"ruleValue":42,
"name":"evpnVni"
},
{
"ruleKey":"new_supported_fec",
"ruleValue":"supported",
"name":"fecSupport"
},
{
"ruleKey":"new_s_crit",
"ruleValue":24,
"name":"overTemp"
},
{
"ruleKey":"new_status",
"ruleValue":"down",
"name":"svcStatus"
},
{
"ruleKey":"configdiff",
"ruleValue":"updated",
"name":"sysconf"
}
],
"truncatedResult":false
}
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter json
{
"config_notify":[
{
"channels":"pd-netq-events",
"rules":"overTemp",
"name":"1critTemp",
"severity":"critical"
},
{
"channels":"pd-netq-events",
"rules":"evpnVni",
"name":"3vni42",
"severity":"warning"
},
{
"channels":"pd-netq-events",
"rules":"bgpHostname",
"name":"4bgpSpine",
"severity":"info"
},
{
"channels":"slk-netq-events",
"rules":"sysconf",
"name":"configChange",
"severity":"info"
},
{
"channels":"slk-netq-events",
"rules":"fecSupport",
"name":"newFEC",
"severity":"info"
},
{
"channels":"slk-netq-events",
"rules":"svcStatus",
"name":"svcDown",
"severity":"critical"
}
],
"truncatedResult":false
}
Manage NetQ Event Notification Integrations
You might need to modify event notification configurations at some point in the lifecycle of your deployment. You can add and remove channels, rules, filters, and a proxy at any time.
For integrations with threshold-based event notifications, refer to Configure Notifications.
Remove an Event Notification Channel
If you retire selected channels from a given notification appliacation, you might want to remove them from NetQ as well. You can remove channels using the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI.
To remove notification channels:
- Click
, and then click Channels in the Notifications column.
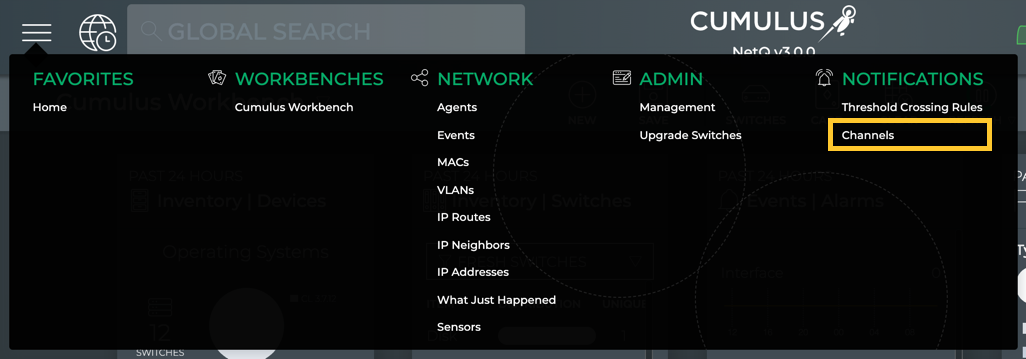
-
Click the tab for the type of channel you want to remove (Slack, PagerDuty, Syslog, Email).
-
Select one or more channels.
-
Click
.
To remove notification channels, run:
netq config del notification channel <text-channel-name-anchor>
This example removes a Slack integration and verifies it is no longer in the configuration:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq del notification channel slk-netq-events
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification channel
Matching config_notify records:
Name Type Severity Channel Info
--------------- ---------------- ---------------- ------------------------
pd-netq-events pagerduty info integration-key: 1234567
890
Delete an Event Notification Rule
You may find after some experience with a given rule that you want to edit or remove the rule to better meet your needs. You can remove rules using the NetQ CLI.
To remove notification rules, run:
netq config del notification rule <text-rule-name-anchor>
This example removes a rule named swp52 and verifies it is no longer in the configuration:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq del notification rule swp52
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification rule
Matching config_notify records:
Name Rule Key Rule Value
--------------- ---------------- --------------------
bgpHostname hostname spine-01
evpnVni vni 42
overTemp new_s_crit 24
svcStatus new_status down
switchLeaf04 hostname leaf04
sysconf configdiff updated
Delete an Event Notification Filter
You may find after some experience with a given filter that you want to edit or remove the filter to better meet your current needs. You can remove filters using the NetQ CLI.
To remove notification filters, run:
netq del notification filter <text-filter-name-anchor>
This example removes a filter named bgpSpine and verifies it is no longer in the configuration:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq del notification filter bgpSpine
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show notification filter
Matching config_notify records:
Name Order Severity Channels Rules
--------------- ---------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------
swp52Drop 1 error NetqDefaultChann swp52
el
vni42 2 warning pd-netq-events evpnVni
configChange 3 info slk-netq-events sysconf
svcDown 4 critical slk-netq-events svcStatus
critTemp 5 critical pd-netq-events switchLeaf
04
overTemp
Delete an Event Notification Proxy
You can remove the proxy server by running the netq del notification proxy command. This changes the NetQ behavior to send events directly to the notification channels.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq del notification proxy
Successfully overwrote notifier proxy to null
Configure Threshold-based Event Notifications
NetQ supports a set of events that are triggered by crossing a user-defined threshold, called TCA events. These events allow detection and prevention of network failures for selected interface, utilization, sensor, forwarding, ACL and digital optics events.
A notification configuration must contain one rule. Each rule must contain a scope and a threshold. Optionally, you can specify an associated channel. Note: If a rule is not associated with a channel, the event information is only reachable from the database. If you want to deliver events to one or more notification channels (Email, syslog, Slack, or PagerDuty), create them by following the instructions in Create a Channel, and then return here to define your rule.
Supported Events
The following events are supported:
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V4_FILTER_UPPER | Number of ingress ACL filters for IPv4 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V4_FILTER_UPPER | Number of egress ACL filters for IPv4 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V4_MANGLE_UPPER | Number of ingress ACL mangles for IPv4 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V4_MANGLE_UPPER | Number of egress ACL mangles for IPv4 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V6_FILTER_UPPER | Number of ingress ACL filters for IPv6 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V6_FILTER_UPPER | Number of egress ACL filters for IPv6 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V6_MANGLE_UPPER | Number of ingress ACL mangles for IPv6 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V6_MANGLE_UPPER | Number of egress ACL mangles for IPv6 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_8021x_FILTER_UPPER | Number of ingress ACL 802.1 filters on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_L4_PORT_CHECKERS_UPPER | Number of ACL port range checkers on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_REGIONS_UPPER | Number of ACL regions on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_MIRROR_UPPER | Number of ingress ACL mirrors on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_18B_RULES_UPPER | Number of ACL 18B rules on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_32B_RULES_UPPER | Number of ACL 32B rules on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_54B_RULES_UPPER | Number of ACL 54B rules on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_PBR_V4_FILTER_UPPER | Number of ingress policy-based routing (PBR) filters for IPv4 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_PBR_V6_FILTER_UPPER | Number of ingress policy-based routing (PBR) filters for IPv6 addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
Some of the event IDs have changed. If you have TCA rules configured for digital optics for a previous release, verify that they are using the correct event IDs. You might need to remove and recreate some of the events.
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALARM_UPPER | Transceiver Input power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host interface is greater than the maximum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALARM_LOWER | Transceiver Input power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is less than minimum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_WARNING_UPPER | Transceiver Input power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is greater than specified warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_WARNING_LOWER | Transceiver Input power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is less than minimum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_ALARM_UPPER | Laser bias current (mA) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is greater than maximum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS__CURRENT_ALARM_LOWER | Laser bias current (mA) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is less than minimum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_WARNING_UPPER | Laser bias current (mA) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is greater than maximum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS__CURRENT_WARNING_LOWER | Laser bias current (mA) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is less than minimum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_ALARM_UPPER | Laser output power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is greater than maximum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_ALARM_LOWER | Laser output power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is less than minimum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_WARNING_UPPER | Laser output power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is greater than maximum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_WARNING_LOWER | Laser output power (mW) for the digital optical module on a given switch or host is less than minimum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_ALARM_UPPER | Digital optical module temperature (°C) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_ALARM_LOWER | Digital optical module temperature (°C) on a given switch or host is less than minimum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_WARNING_UPPER | Digital optical module temperature (°C) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_WARNING_LOWER | Digital optical module temperature (°C) on a given switch or host is less than minimum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_ALARM_UPPER | Transceiver voltage (V) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_ALARM_LOWER | Transceiver voltage (V) on a given switch or host is less than minimum alarm threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_WARNING_UPPER | Transceiver voltage (V) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum warning threshold |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_WARNING_LOWER | Transceiver voltage (V) on a given switch or host is less than minimum warning threshold |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_TCAM_TOTAL_ROUTE_ENTRIES_UPPER | Number of routes on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_TOTAL_MCAST_ROUTES_UPPER | Number of multicast routes on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_MAC_ENTRIES_UPPER | Number of MAC addresses on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV4_ROUTE_UPPER | Number of IPv4 routes on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV4_HOST_UPPER | Number of IPv4 hosts on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV6_ROUTE_UPPER | Number of IPv6 hosts on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV6_HOST_UPPER | Number of IPv6 hosts on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TCAM_ECMP_NEXTHOPS_UPPER | Number of equal cost multi-path (ECMP) next hop entries on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_HW_IF_OVERSIZE_ERRORS | Number of times a frame is longer than maximum size (1518 Bytes) |
| TCA_HW_IF_UNDERSIZE_ERRORS | Number of times a frame is shorter than minimum size (64 Bytes) |
| TCA_HW_IF_ALIGNMENT_ERRORS | Number of times a frame has an uneven byte count and a CRC error |
| TCA_HW_IF_JABBER_ERRORS | Number of times a frame is longer than maximum size (1518 bytes) and has a CRC error |
| TCA_HW_IF_SYMBOL_ERRORS | Number of times undefined or invalid symbols have been detected |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_RXBROADCAST_UPPER | rx_broadcast bytes per second on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_RXBYTES_UPPER | rx_bytes per second on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_RXMULTICAST_UPPER | rx_multicast per second on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TXBROADCAST_UPPER | tx_broadcast bytes per second on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TXBYTES_UPPER | tx_bytes per second on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_TXMULTICAST_UPPER | tx_multicast bytes per second on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_LINK | Number of link flaps is greater than the maximum threshold |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER | CPU utilization (%) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER | Disk utilization (%) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_MEMORY_UTILIZATION_UPPER | Memory utilization (%) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_SENSOR_FAN_UPPER | Switch sensor reported fan speed on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_SENSOR_POWER_UPPER | Switch sensor reported power (Watts) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER | Switch sensor reported temperature (°C) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
| TCA_SENSOR_VOLTAGE_UPPER | Switch sensor reported voltage (Volts) on a given switch or host is greater than maximum threshold |
Define a Scope
A scope is used to filter the events generated by a given rule. Scope values are set on a per TCA rule basis. All rules can be filtered on Hostname. Some rules can also be filtered by other parameters.
Select Filter Parameters
You can filter rules based on the following filter parameters.
| Event ID | Scope Parameters |
|---|---|
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V4_FILTER_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V4_FILTER_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V4_MANGLE_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V4_MANGLE_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V6_FILTER_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V6_FILTER_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_V6_MANGLE_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_EG_ACL_V6_MANGLE_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_8021x_FILTER_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_L4_PORT_CHECKERS_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_REGIONS_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_ACL_MIRROR_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_18B_RULES_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_32B_RULES_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_ACL_54B_RULES_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_PBR_V4_FILTER_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IN_PBR_V6_FILTER_UPPER | Hostname |
| Event ID | Scope Parameters |
|---|---|
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALARM_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALARM_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_WARNING_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_WARNING_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_ALARM_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_ALARM_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_WARNING_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_WARNING_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_ALARM_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_ALARM_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_WARNING_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_OUTPUT_POWER_WARNING_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_ALARM_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_ALARM_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_WARNING_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_TEMPERATURE_WARNING_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_ALARM_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_ALARM_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_WARNING_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_WARNING_LOWER | Hostname, Interface |
| Event ID | Scope Parameters |
|---|---|
| TCA_TCAM_TOTAL_ROUTE_ENTRIES_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_TOTAL_MCAST_ROUTES_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_MAC_ENTRIES_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_ECMP_NEXTHOPS_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV4_ROUTE_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV4_HOST_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV6_ROUTE_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_TCAM_IPV6_HOST_UPPER | Hostname |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_HW_IF_OVERSIZE_ERRORS | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_HW_IF_UNDERSIZE_ERRORS | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_HW_IF_ALIGNMENT_ERRORS | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_HW_IF_JABBER_ERRORS | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_HW_IF_SYMBOL_ERRORS | Hostname, Interface |
| Event ID | Scope Parameters |
|---|---|
| TCA_RXBROADCAST_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_RXBYTES_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_RXMULTICAST_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_TXBROADCAST_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_TXBYTES_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| TCA_TXMULTICAST_UPPER | Hostname, Interface |
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| TCA_LINK | Hostname, Interface |
| Event ID | Scope Parameters |
|---|---|
| TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER | Hostname |
| TCA_MEMORY_UTILIZATION_UPPER | Hostname |
| Event ID | Scope Parameters |
|---|---|
| TCA_SENSOR_FAN_UPPER | Hostname, Sensor Name |
| TCA_SENSOR_POWER_UPPER | Hostname, Sensor Name |
| TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER | Hostname, Sensor Name |
| TCA_SENSOR_VOLTAGE_UPPER | Hostname, Sensor Name |
Specify the Scope
Scopes are defined and displayed as regular expressions. The definition and display is slightly different between the NetQ UI and the NetQ CLI, but the results are the same.
Scopes are displayed in TCA rule cards using the following format.
| Scope | Display in Card | Result |
|---|---|---|
| All devices | hostname = * | Show events for all devices |
| All interfaces | ifname = * | Show events for all devices and all interfaces |
| All sensors | s_name = * | Show events for all devices and all sensors |
| Particular device | hostname = leaf01 | Show events for leaf01 switch |
| Particular interface | ifname = swp14 | Show events for swp14 interface |
| Particular sensor | s_name = fan2 | Show events for the fan2 fan |
| Set of devices | hostname ^ leaf | Show events for switches having names starting with leaf |
| Set of interfaces | ifname ^ swp | Show events for interfaces having names starting with swp |
| Set of sensors | s_name ^ fan | Show events for sensors having names starting with fan |
When a rule is filtered by more than one parameter, each is displayed on the card. Leaving a value blank for a parameter defaults to all; all hostnames, interfaces, sensors, forwarding resources, ACL resources, and so forth.
Scopes are defined with regular expressions, as follows. When two paramaters are used, they are separated by a comma, but no space. When as asterisk (*) is used alone, it must be entered inside either single or double quotes. Single quotes are used here.
| Scope Value | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| <hostname> | leaf01 | Deliver events for the specified device |
| <partial-hostname>* | leaf* | Deliver events for devices with hostnames starting with specified text (leaf) |
| '*' | '*' | Deliver events for all devices |
| Scope Value | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| <hostname>,<interface> | leaf01,swp9 | Deliver events for the specified interface (swp9) on the specified device (leaf01) |
| <hostname>,'*' | leaf01,'*' | Deliver events for all interfaces on the specified device (leaf01) |
| '*',<interface> | '*',swp9 | Deliver events for the specified interface (swp9) on all devices |
| '*','*' | '*','*' | Deliver events for all devices and all interfaces |
| <partial-hostname>*,<interface> | leaf*,swp9 | Deliver events for the specified interface (swp9) on all devices with hostnames starting with the specified text (leaf) |
| <hostname>,<partial-interface>* | leaf01,swp* | Deliver events for all interface with names starting with the specified text (swp) on the specified device (leaf01) |
| Scope Value | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| <hostname>,<sensorname> | leaf01,fan1 | Deliver events for the specified sensor (fan1) on the specified device (leaf01) |
| '*',<sensorname> | '*',fan1 | Deliver events for the specified sensor (fan1) for all devices |
| <hostname>,'*' | leaf01,'*' | Deliver events for all sensors on the specified device (leaf01) |
| <partial-hostname>*,<interface> | leaf*,fan1 | Deliver events for the specified sensor (fan1) on all devices with hostnames starting with the specified text (leaf) |
| <hostname>,<partial-sensorname>* | leaf01,fan* | Deliver events for all sensors with names starting with the specified text (fan) on the specified device (leaf01) |
| '*','*' | '*','*' | Deliver events for all sensors on all devices |
Create a TCA Rule
Now that you know which events are supported and how to set the scope, you can create a basic rule to deliver one of the TCA events to a notification channel. This can be done using either the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI.
To create a TCA rule:
- Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Click
to add a rule.
The Create TCA Rule dialog opens. Four steps create the rule.
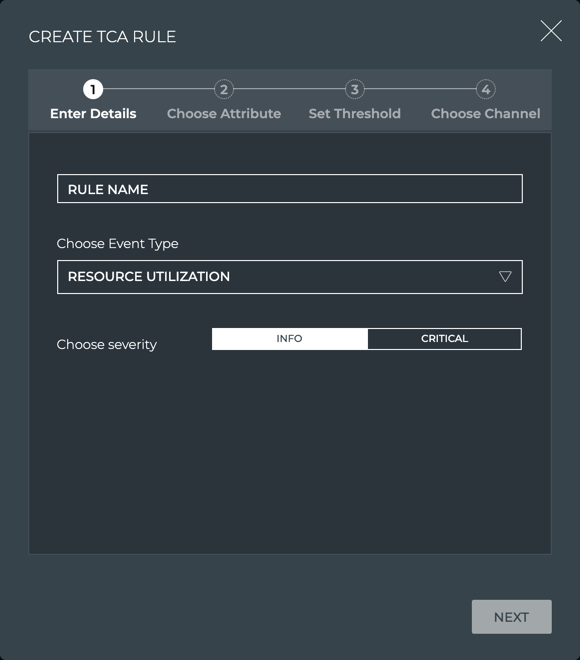
You can move forward and backward until you are satisfied with your rule definition.
- On the Enter Details step, enter a name for your rule, choose your TCA event type, and assign a severity.
The rule name has a maximum of 20 characters (including spaces).
-
Click Next.
-
On the Choose Attribute step, select the attribute to measure against.
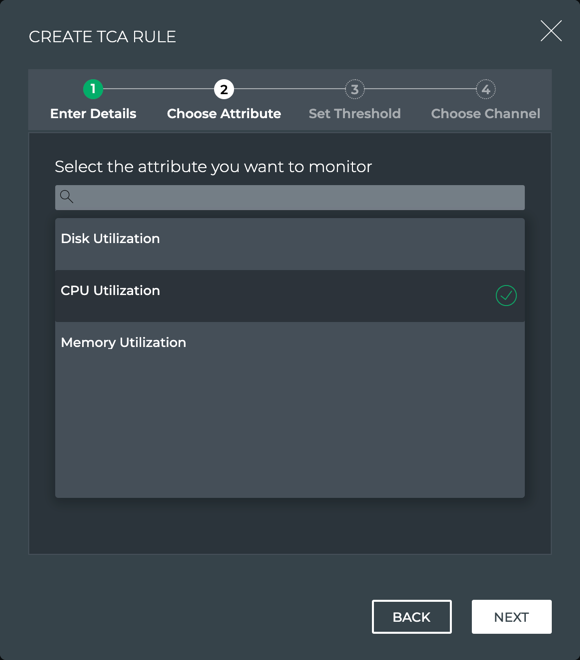
The attributes presented depend on the event type chosen in the Enter Details step. This example shows the attributes available when Resource Utilization was selected.
-
Click Next.
-
On the Set Threshold step, enter a threshold value.
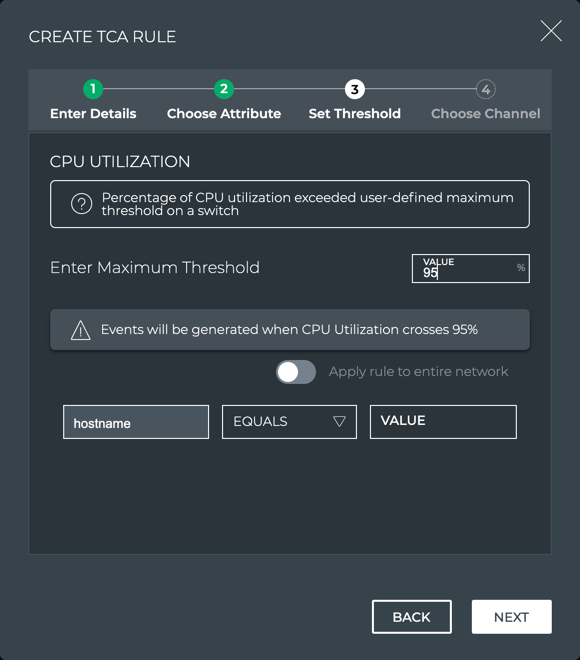


-
Define the scope of the rule.
-
If you want to restrict the rule to a particular device, and enter values for one or more of the available parameters.
-
If you want the rule to apply to all devices, click the scope toggle.
-
-
Click Next.
-
Optionally, select a notification channel where you want the events to be sent.
Only previously created channels are available for selection. If no channel is available or selected, the notifications can only be retrieved from the database. You can add a channel at a later time and then add it to the rule. Refer to Create a Channel and Modify TCA Rules.
-
Click Finish.
This example shows four rules. The rule on the left triggers an alarm event when the laser bias current exceeds the upper threshold set by the vendor on all interfaces of all leaf switches. The rule second to the left triggers an alarm event when the temperature on the temp1 sensor exceeds 32 °C on the all leaf switch. The rule second to the right triggers an alarm event when any device exceeds the maximum CPU utilization of 93%. The rule on the right triggers an informational event when switch leaf01 exceeds the maximum CPU utilization of 87%. Note that the cards indicate all rules are currently Active.
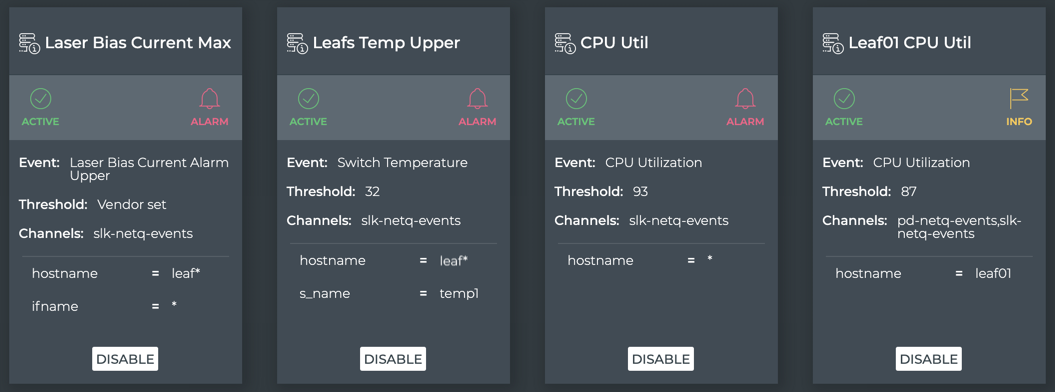
The simplest configuration you can create is one that sends a TCA event generated by all devices and all interfaces to a single notification application. Use the netq add tca command to configure the event. Its syntax is:
netq add tca [event_id <text-event-id-anchor>] [scope <text-scope-anchor>] [tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor>] [severity info | severity critical] [is_active true | is_active false] [suppress_until <text-suppress-ts>] [threshold_type user_set | threshold_type vendor_set] [threshold <text-threshold-value>] [channel <text-channel-name-anchor> | channel drop <text-drop-channel-name>]
Note that the event ID is case sensitive and must be in all uppercase.
For example, this rule tells NetQ to deliver an event notification to the tca_slack_ifstats pre-configured Slack channel when the CPU utilization exceeds 95% of its capacity on any monitored switch:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER scope '*' channel tca_slack_ifstats threshold 95
This rule tells NetQ to deliver an event notification to the tca_pd_ifstats PagerDuty channel when the number of transmit bytes per second (Bps) on the leaf12 switch exceeds 20,000 Bps on any interface:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_TXBYTES_UPPER scope leaf12,'*' channel tca_pd_ifstats threshold 20000
This rule tells NetQ to deliver an event notification to the syslog-netq syslog channel when the temperature on sensor temp1 on the leaf12 switch exceeds 32 degrees Celcius:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER scope leaf12,temp1 channel syslog-netq threshold 32
For a Slack channel, the event messages should be similar to this:
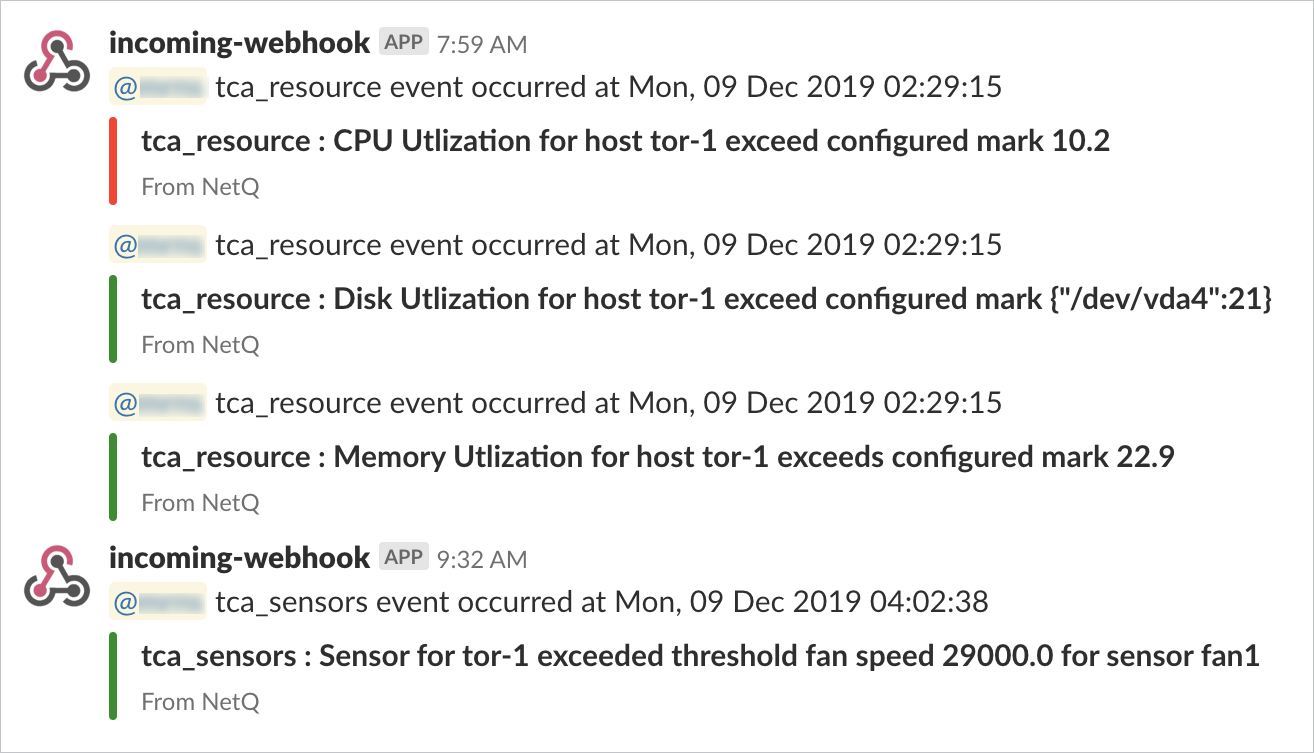
Set the Severity of a Threshold-based Event
In addition to defining a scope for TCA rule, you can also set a severity of either info or critical. To add a severity to a rule, use the severity option.
For example, if you want to add a critical severity to the CPU utilization rule you created earlier:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER scope '*' severity critical channel tca_slack_resources threshold 95
Or if an event is important, but not critical. Set the severity to info:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_TXBYTES_UPPER scope leaf12,'*' severity info channel tca_pd_ifstats threshold 20000
Set the Threshold for Digital Optics Events
Digital optics have the additional option of applying user- or vendor-defined thresholds, using the threshold_type and threshold options.
This example shows how to send an alarm event on channel ch1 when the upper threshold for module voltage exceeds the vendor-defined thresholds for interface swp31 on the mlx-2700-04 switch.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_ALARM_UPPER scope 'mlx-2700-04,swp31' severity critical is_active true threshold_type vendor_set channel ch1
Successfully added/updated tca
This example shows how to send an alarm event on channel ch1 when the upper threshold for module voltage exceeds the user-defined threshold of 3V for interface swp31 on the mlx-2700-04 switch.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_DOM_MODULE_VOLTAGE_ALARM_UPPER scope 'mlx-2700-04,swp31' severity critical is_active true threshold_type user_set threshold 3 channel ch1
Successfully added/updated tca
View the TCA Rules
Use the netq show tca command to view all of the created rules.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show tca
Matching config_tca records:
TCA Name Event Name Scope Severity Channel/s Active Threshold Unit Threshold Type Suppress Until
---------------------------- -------------------- -------------------------- -------- ------------------ ------ ------------------ -------- -------------- ----------------------------
TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_ {"hostname":"leaf01"} info pd-netq-events,slk True 87 % user_set Fri Oct 9 15:39:35 2020
UPPER -netq-events
TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_2 TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_ {"hostname":"*"} critical slk-netq-events True 93 % user_set Fri Oct 9 15:39:56 2020
UPPER
TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_ALARM_U TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT {"hostname":"leaf*","ifnam critical slk-netq-events True 0 mA vendor_set Fri Oct 9 16:02:37 2020
PPER_1 _ALARM_UPPER e":"*"}
TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALARM_UPPER TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALA {"hostname":"*","ifname":" info slk-netq-events True 0 mW vendor_set Fri Oct 9 15:25:26 2020
_1 RM_UPPER *"}
TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATU {"hostname":"leaf","s_name critical slk-netq-events True 32 degreeC user_set Fri Oct 9 15:40:18 2020
_1 RE_UPPER ":"temp1"}
TCA_TCAM_IPV4_ROUTE_UPPER_1 TCA_TCAM_IPV4_ROUTE_ {"hostname":"*"} critical pd-netq-events True 20000 % user_set Fri Oct 9 16:13:39 2020
UPPER
Create Multiple Rules for a TCA Event
You are likely to want more than one rule around a particular event. For example, you might want to:
- Monitor the same event but for a different interface, sensor, or device
- Send the event notification to more than one channel
- Change the threshold for a particular device that you are troubleshooting
And so forth.
In the NetQ UI you create multiple rules by adding mulitple rule cards. Refer to Create a TCA Rule.
In the NetQ CLI, you can also add multiple rules. This example shows the creation of three additional rules for the max temperature sensor.
netq add tca event_id TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER scope leaf*,temp1 channel syslog-netq threshold 32
netq add tca event_id TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER scope '*',temp1 channel tca_sensors,tca_pd_sensors threshold 32
netq add tca event_id TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER scope leaf03,temp1 channel syslog-netq threshold 29
Now you have four rules created (the original one, plus these three new ones) all based on the TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER event. To identify the various rules, NetQ automatically generates a TCA name for each rule. As each rule is created, an _# is added to the event name. The TCA Name for the first rule created is then TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER_1, the second rule created for this event is TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER_2, and so forth.
Manage Threshold-based Event Notifications
Once you have created a bunch of rules, you might want to modify them; view a list of the rules, disable a rule, delete a rule, and so forth.
View TCA Rules
You can view all of the threshold-crossing event rules you have created in the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI.
-
Click
.
-
Select Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
A card is displayed for every rule.
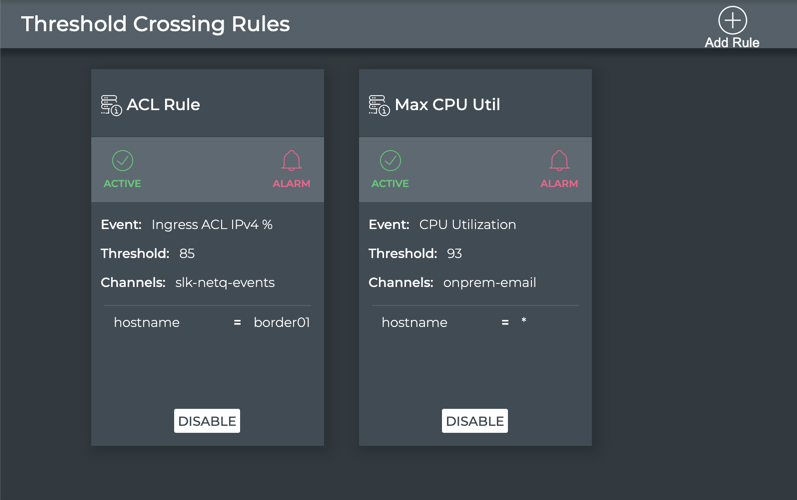
To view TCA rules, run:
netq show tca [tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor>] [json]
This example displays all TCA rules:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show tca
Matching config_tca records:
TCA Name Event Name Scope Severity Channel/s Active Threshold Unit Threshold Type Suppress Until
---------------------------- -------------------- -------------------------- -------- ------------------ ------ ------------------ -------- -------------- ----------------------------
TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_ {"hostname":"leaf01"} info pd-netq-events,slk True 87 % user_set Fri Oct 9 15:39:35 2020
UPPER -netq-events
TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_2 TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_ {"hostname":"*"} critical slk-netq-events True 93 % user_set Fri Oct 9 15:39:56 2020
UPPER
TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT_ALARM_U TCA_DOM_BIAS_CURRENT {"hostname":"leaf*","ifnam critical slk-netq-events True 0 mA vendor_set Fri Oct 9 16:02:37 2020
PPER_1 _ALARM_UPPER e":"*"}
TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALARM_UPPER TCA_DOM_RX_POWER_ALA {"hostname":"*","ifname":" info slk-netq-events True 0 mW vendor_set Fri Oct 9 15:25:26 2020
_1 RM_UPPER *"}
TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATURE_UPPER TCA_SENSOR_TEMPERATU {"hostname":"leaf","s_name critical slk-netq-events True 32 degreeC user_set Fri Oct 9 15:40:18 2020
_1 RE_UPPER ":"temp1"}
TCA_TCAM_IPV4_ROUTE_UPPER_1 TCA_TCAM_IPV4_ROUTE_ {"hostname":"*"} critical pd-netq-events True 20000 % user_set Fri Oct 9 16:13:39 2020
UPPER
This example display a specific TCA rule:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show tca tca_id TCA_TXMULTICAST_UPPER_1
Matching config_tca records:
TCA Name Event Name Scope Severity Channel/s Active Threshold Suppress Until
---------------------------- -------------------- -------------------------- ---------------- ------------------ ------ ------------------ ----------------------------
TCA_TXMULTICAST_UPPER_1 TCA_TXMULTICAST_UPPE {"ifname":"swp3","hostname info tca-tx-bytes-slack True 0 Sun Dec 8 16:40:14 2269
R ":"leaf01"}
Change the Threshold on a TCA Rule
To modify the threshold:
-
Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Locate the rule you want to modify and hover over the card.
-
Click
.
- Enter a new threshold value.
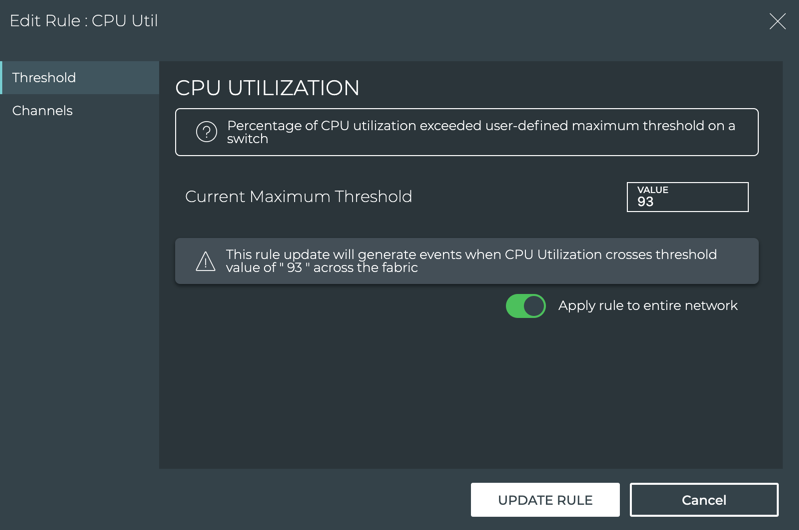
- Click Update Rule.
To modify the threshold, run:
netq add tca tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor> threshold <text-threshold-value>
This example changes the threshold for the rule TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 to a value of 96 percent. This overwrites the existing threshold value.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca tca_id TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 threshold 96
Change the Scope of a TCA Rule
To modify the scope:
-
Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Locate the rule you want to modify and hover over the card.
-
Click
.

- Change the scope, applying the rule to all devices or broadening or narrowing the scope. Refer to Specify the Scope for details.


- Click Update Rule.
To modify the scope, run:
netq add tca event_id <text-event-id-anchor> scope <text-scope-anchor> threshold <text-threshold-value>
This example changes the scope for the rule TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER to apply only to switches beginning with a hostname of leaf. You must also provide a threshold value. In this case we have used a value of 95 percent. Note that this overwrites the existing scope and threshold values.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca event_id TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER scope hostname^leaf threshold 95
Successfully added/updated tca
cumulus@switch:~$ netq show tca
Matching config_tca records:
TCA Name Event Name Scope Severity Channel/s Active Threshold Suppress Until
---------------------------- -------------------- -------------------------- ---------------- ------------------ ------ ------------------ ----------------------------
TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_ {"hostname":"*"} critical onprem-email True 93 Mon Aug 31 20:59:57 2020
UPPER
TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_2 TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_ {"hostname":"hostname^leaf info True 95 Tue Sep 1 18:47:24 2020
UPPER "}
Change, Add, or Remove the Channels on a TCA Rule
-
Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Locate the rule you want to modify and hover over the card.
-
Click
.

- Click Channels.
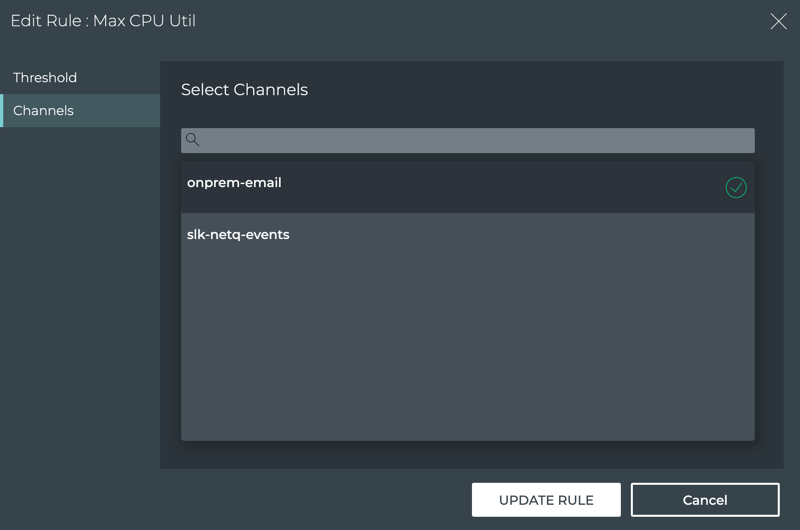
-
Select one or more channels.
Click a channel to select it. Click again to unselect a channel.
-
Click Update Rule.
To change a channel association, run:
netq add tca tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor> channel <text-channel-name-anchor>
This overwrites the existing channel association.
This example shows the channel for the disk utilization 1 rule being changed to a PagerDuty channel pd-netq-events.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca tca_id TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 channel pd-netq-events
Successfully added/updated tca TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1
To remove a channel association (stop sending events to a particular channel), run:
netq add tca tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor> channel drop <text-drop-channel-name>
This example removes the tca_slack_resources channel from the disk utilization 1 rule.
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca tca_id TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 channel drop tca_slack_resources
Successfully added/updated tca TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1
Change the Name of a TCA Rule
You cannot change the name of a TCA rule using the NetQ CLI because the rules are not named. They are given identifiers (tca_id) automatically. In the NetQ UI, to change a rule name, you must delete the rule and re-create it with the new name. Refer to Delete a TCA Rule and then Create a TCA Rule.
Change the Severity of a TCA Rule
TCA rules have either an informational or critical severity.
In the NetQ UI, the severity cannot be changed by itself, the rule must be deleted and re-created using the new severity. Refer to Delete a TCA Rule and then Create a TCA Rule.
In the NetQ CLI, to change the severity, run:
netq add tca tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor> (severity info | severity critical)
This example changes the severity of the maximum CPU utilization 1 rule from critical to info:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca tca_id TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 severity info
Successfully added/updated tca TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1
Suppress a TCA Rule
During troubleshooting or maintenance of switches you may want to suppress a rule to prevent erroneous event messages. This can be accomplished using the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI.
The TCA rules have three possible states iin the NetQ UI:
- Active: Rule is operating, delivering events. This would be the normal operating state.
- Suppressed: Rule is disabled until a designated date and time. When that time occurs, the rule is automatically reenabled. This state is useful during troubleshooting or maintenance of a switch when you do not want erroneous events being generated.
- Disabled: Rule is disabled until a user manually reenables it. This state is useful when you are unclear when you want the rule to be reenabled. This is not the same as deleting the rule.
To suppress a rule for a designated amount of time, you must change the state of the rule.
To suppress a rule:
-
Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Locate the rule you want to suppress.
-
Click Disable.
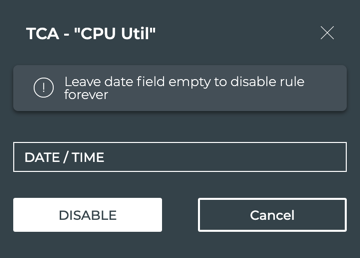
-
Click in the Date/Time field to set when you want the rule to be automatically reenabled.
-
Click Disable.
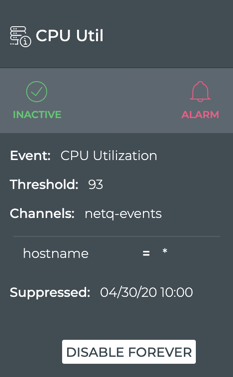
- The state is now marked as Inactive, but remains green
- The date and time that the rule will be enabled is noted in the Suppressed field
- The Disable option has changed to Disable Forever. Refer to Disable a TCA Rule for information about this change.
Using the suppress_until option allows you to prevent the rule from being applied for a designated amout of time (in seconds). When this time has passed, the rule is automatically reenabled.
To suppress a rule, run:
netq add tca tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor> suppress_until <text-suppress-ts>
This example suppresses the maximum cpu utilization event for 24 hours:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca tca_id TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_2 suppress_until 86400
Successfully added/updated tca TCA_CPU_UTILIZATION_UPPER_2
Disable a TCA Rule
Whereas suppression temporarily disables a rule, you can deactivate a rule to disable it indefinitely. You can disable a rule using the NetQ UI or the NetQ CLI.
The TCA rules have three possible states in the NetQ UI:
- Active: Rule is operating, delivering events. This would be the normal operating state.
- Suppressed: Rule is disabled until a designated date and time. When that time occurs, the rule is automatically reenabled. This state is useful during troubleshooting or maintenance of a switch when you do not want erroneous events being generated.
- Disabled: Rule is disabled until a user manually reenables it. This state is useful when you are unclear when you want the rule to be reenabled. This is not the same as deleting the rule.
To disable a rule that is currently active:
-
Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Locate the rule you want to disable.
-
Click Disable.
-
Leave the Date/Time field blank.
-
Click Disable.
- The state is now marked as Inactive and is red
- The rule definition is grayed out
- The Disable option has changed to Enable to reactivate the rule when you are ready
To disable a rule that is currently suppressed:
-
Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Locate the rule you want to disable.
-
Click Disable Forever.
Note the changes in the card:
- The state is now marked as Inactive and is red
- The rule definition is grayed out
- The Disable option has changed to Enable to reactivate the rule when you are ready
To disable a rule, run:
netq add tca tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor> is_active false
This example disables the maximum disk utilization 1 rule:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq add tca tca_id TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1 is_active false
Successfully added/updated tca TCA_DISK_UTILIZATION_UPPER_1
To reenable the rule, set the is_active option to true.
Delete a TCA Rule
You might find that you no longer want to receive event notifications for a particular TCA event. In that case, you can either disable the event if you think you may want to receive them again or delete the rule altogether. Refer to Disable a Rule for the first case. Follow the instructions here to remove the rule using either the NetQ UI or NetQ CLI.
The rule can be in any of the three states, active, suppressed, or disabled.
To delete a rule:
-
Click
to open the Main Menu.
-
Click Threshold Crossing Rules under Notifications.
-
Locate the rule you want to remove and hover over the card.
-
Click
.
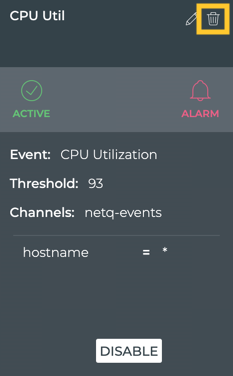
To remove a rule altogether, run:
netq del tca tca_id <text-tca-id-anchor>
This example deletes the maximum receive bytes rule:
cumulus@switch:~$ netq del tca tca_id TCA_RXBYTES_UPPER_1
Successfully deleted TCA TCA_RXBYTES_UPPER_1
Resolve Scope Conflicts
There may be occasions where the scope defined by the multiple rules for a given TCA event may overlap each other. In such cases, the TCA rule with the most specific scope that is still true is used to generate the event.
To clarify this, consider this example. Three events have occurred:
- First event on switch leaf01, interface swp1
- Second event on switch leaf01, interface swp3
- Third event on switch spine01, interface swp1
NetQ attempts to match the TCA event against hostname and interface name with three TCA rules with different scopes:
- Scope 1 send events for the swp1 interface on switch leaf01 (very specific)
- Scope 2 send events for all interfaces on switches that start with leaf (moderately specific)
- Scope 3 send events for all switches and interfaces (very broad)
The result is:
- For the first event, NetQ applies the scope from rule 1 because it matches scope 1 exactly
- For the second event, NetQ applies the scope from rule 2 because it does not match scope 1, but does match scope 2
- For the third event, NetQ applies the scope from rule 3 because it does not match either scope 1 or scope 2
In summary:
| Input Event | Scope Parameters | TCA Scope 1 | TCA Scope 2 | TCA Scope 3 | Scope Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| leaf01,swp1 | Hostname, Interface | '*','*' | leaf*,'*' | leaf01,swp1 | Scope 3 |
| leaf01,swp3 | Hostname, Interface | '*','*' | leaf*,'*' | leaf01,swp1 | Scope 2 |
| spine01,swp1 | Hostname, Interface | '*','*' | leaf*,'*' | leaf01,swp1 | Scope 1 |
Modify your TCA rules to remove the conflict.