Data Center Network Deployments
There are three deployment types that are commonly deployed for network management in the data center:
- Out-of-Band Management (recommended)
- In-band Management
- High Availability
A summary of each type is provided here.
Cumulus NetQ operates over layer 3, and can be used in both layer 2 bridged and layer 3 routed environments. Cumulus Networks always recommends layer 3 routed environments whenever possible.
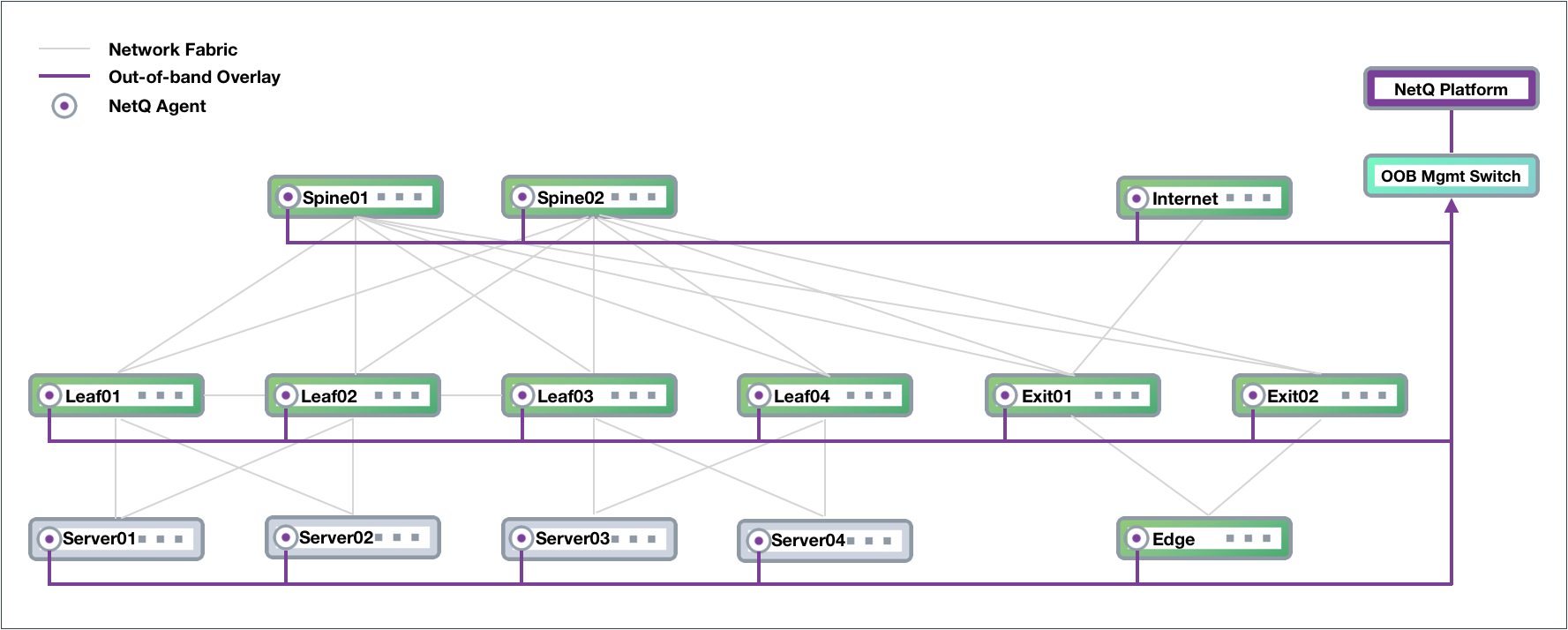
Out-of-band Management Deployment
Cumulus Networks recommends deploying NetQ on an out-of-band (OOB) management network to separate network management traffic from standard network data traffic, but it is not required. This figure shows a sample CLOS-based network fabric design for a data center using an OOB management network overlaid on top, where NetQ is deployed.
The physical network hardware includes:
- Spine switches: where data is aggregated and distributed ; also known as an aggregation switch, end-of-row (EOR) switch or distribution switch
- Leaf switches: where servers connect to the network; also known as a Top of Rack (TOR) or access switch
- Server hosts: where applications are hosted and data served to the user through the network
- Exit switch: where connections to outside the data center occur; also known as Border Leaf or Service Leaf
- Edge server (optional): where the firewall is the demarcation point, peering may occur through the exit switch layer to Internet (PE) devices
- Internet device (PE): where provider edge (PE) equipment communicates at layer 3 with the network fabric
The diagram shows physical connections (in the form of grey lines) between Spine 01 and four Leaf devices and two Exit devices, and Spine 02 and the same four Leaf devices and two Exit devices. Leaf 01 and Leaf 02 are connected to each other over a peerlink and act as an MLAG pair for Server 01 and Server 02. Leaf 03 and Leaf 04 are connected to each other over a peerlink and act as an MLAG pair for Server 03 and Server 04. The Edge is connected to both Exit devices, and the Internet node is connected to Exit 01.
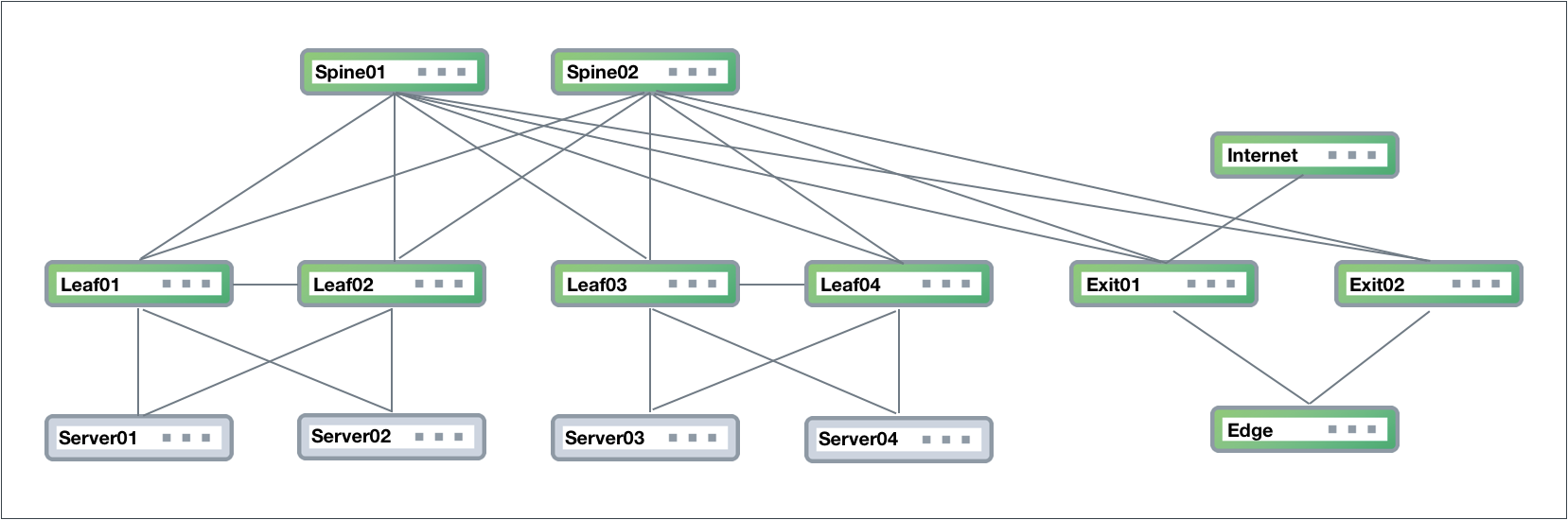
Data Center Network Example
The physical management hardware includes:
- OOB Mgmt Switch: aggregation switch that connects to all of the network devices through communications with the NetQ Agent on each node
- NetQ Platform: hosts the telemetry software, database and user interfaces (refer to description above)
These switches are connected to each of the physical network devices through a virtual network overlay, shown with purple lines.
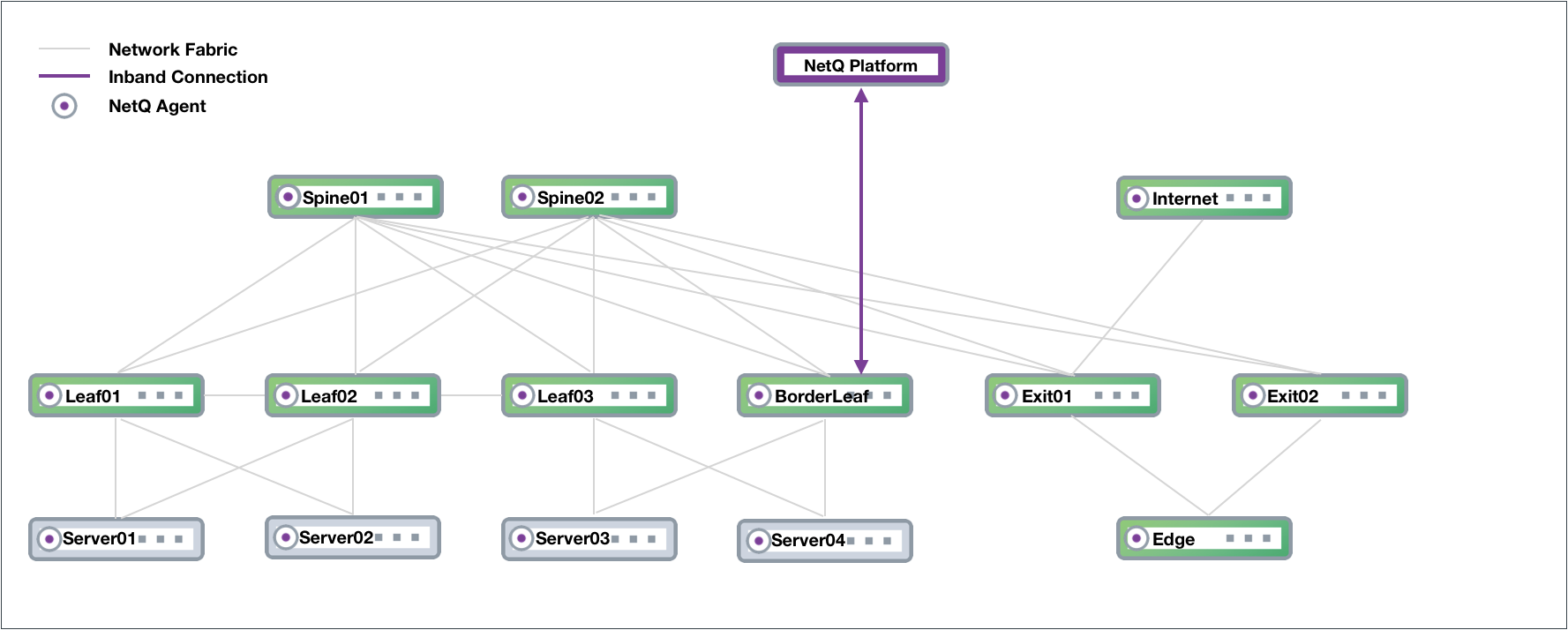
In-band Management Deployment
While not the preferred deployment method, you might choose to implement NetQ within your data network. In this scenario, there is no overlay and all traffic to and from the NetQ Agents and the NetQ Platform traverses the data paths along with your regular network traffic. The roles of the switches in the CLOS network are the same, except that the NetQ Platform performs the aggregation function that the OOB management switch performed. If your network goes down, you might not have access to the NetQ Platform for troubleshooting.
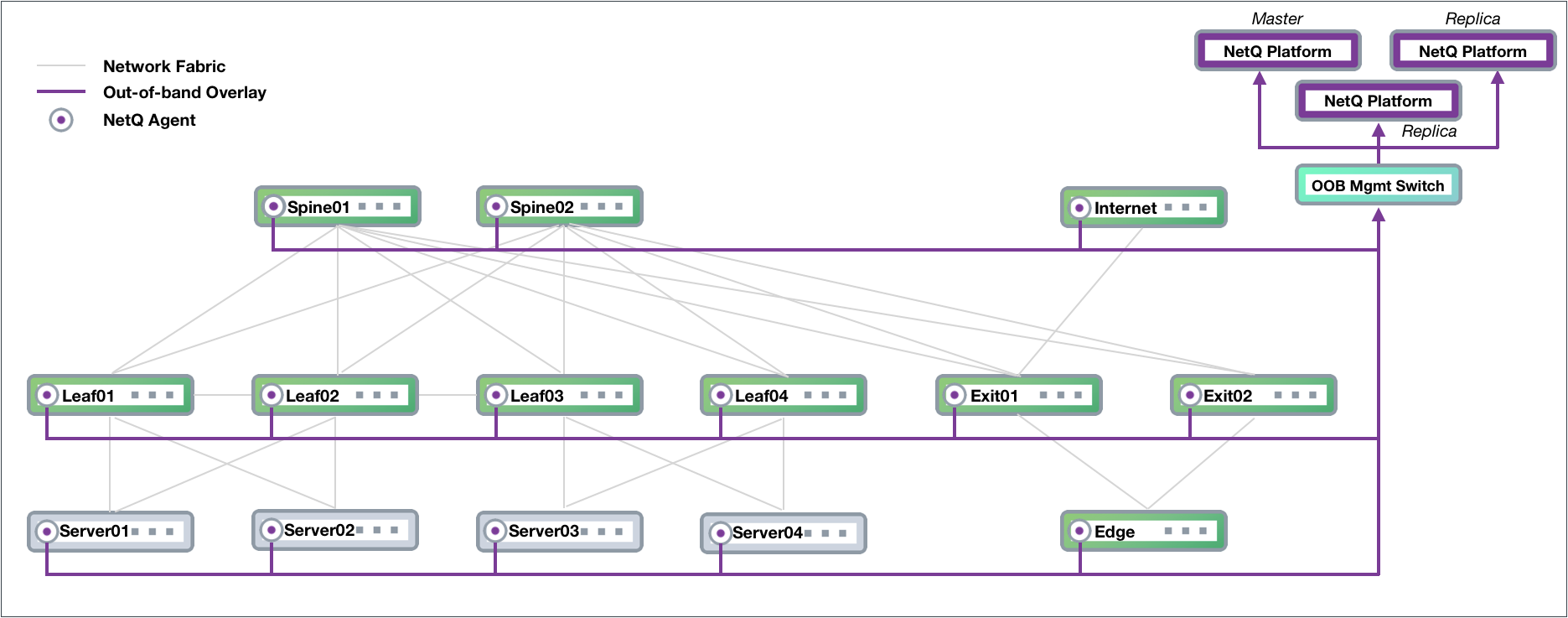
High Availability Deployment
NetQ supports a high availability deployment for users who prefer a solution in which the collected data and processing provided by the NetQ Platform remains available through alternate equipment should the platform fail for any reason. In this configuration, three NetQ Platforms are deployed, with one as the master and two as workers (or replicas). Data from the NetQ Agents is sent to all three switches so that if the master NetQ Platform fails, one of the replicas automatically becomes the master and continues to store and provide the telemetry data. This example is based on an OOB management configuration, and modified to support high availability for NetQ.