Monitor the MLAG Service
The Cumulus NetQ UI enables operators to view the health of the MLAG service on a network-wide and a per session basis, giving greater insight into all aspects of the service. This is accomplished through two card workflows, one for the service and one for the session. They are described separately here.
MLAG or CLAG? The Cumulus Linux implementation of MLAG is referred to by other vendors as MLAG, MC-LAG or VPC. The Cumulus NetQ UI uses the MLAG terminology predominantly.
Monitor the MLAG Service (All Sessions)
With NetQ, you can monitor the number of nodes running the MLAG service, view sessions running, and view alarms triggered by the MLAG service. For an overview and how to configure MLAG in your data center network, refer to Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation - MLAG.
MLAG Service Card Workflow Summary
The small MLAG Service card displays:

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Indicates data is for all sessions of a Network Service or Protocol | |
| Title | MLAG: All MLAG Sessions, or the MLAG Service |
| Total number of switches with the MLAG service enabled during the designated time period | |
| Total number of MLAG-related alarms received during the designated time period | |
| Chart | Distribution of MLAG-related alarms received during the designated time period |
The medium MLAG Service card displays:
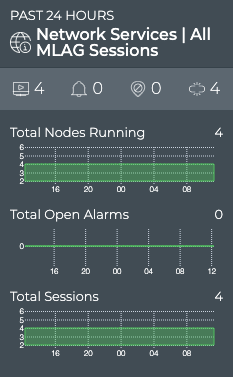
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time period | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes |
| Indicates data is for all sessions of a Network Service or Protocol | |
| Title | Network Services | All MLAG Sessions |
| Total number of switches with the MLAG service enabled during the designated time period | |
| Total number of MLAG-related alarms received during the designated time period | |
| Total number of sessions with an inactive backup IP address during the designated time period | |
| Total number of bonds with only a single connection during the designated time period | |
| Total Nodes Running chart | Distribution of switches and hosts with the MLAG service enabled during the designated time period, and a total number of nodes running the service currently. Note: The node count here may be different than the count in the summary bar. For example, the number of nodes running MLAG last week or last month might be more or less than the number of nodes running MLAG currently. |
| Total Open Alarms chart | Distribution of MLAG-related alarms received during the designated time period, and the total number of current MLAG-related alarms in the network. Note: The alarm count here may be different than the count in the summary bar. For example, the number of new alarms received in this time period does not take into account alarms that have already been received and are still active. You might have no new alarms, but still have a total number of alarms present on the network of 10. |
| Total Sessions chart | Distribution of MLAG sessions running during the designated time period, and the total number of sessions running on the network currently |
The large MLAG service card contains two tabs.
The All MLAG Sessions summary tab which displays:
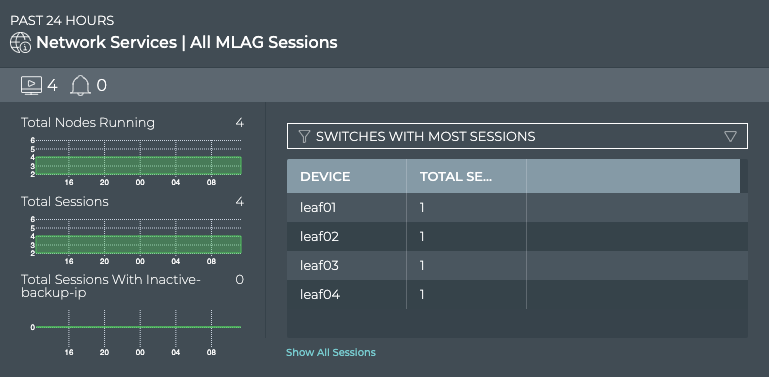
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time period | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes |
| Indicates data is for all sessions of a Network Service or Protocol | |
| Title | All MLAG Sessions Summary |
| Total number of switches with the MLAG service enabled during the designated time period | |
| Total number of MLAG-related alarms received during the designated time period | |
| Total Nodes Running chart | Distribution of switches and hosts with the MLAG service enabled during the designated time period, and a total number of nodes running the service currently. Note: The node count here may be different than the count in the summary bar. For example, the number of nodes running MLAG last week or last month might be more or less than the number of nodes running MLAG currently. |
| Total Sessions chart | Distribution of MLAG sessions running during the designated time period, and the total number of sessions running on the network currently |
| Total Sessions with Inactive-backup-ip chart | Distribution of sessions without an active backup IP defined during the designated time period, and the total number of these sessions running on the network currently |
| Table/Filter options | When the Switches with Most Sessions filter is selected, the table displays switches running MLAG sessions in decreasing order of session count-devices with the largest number of sessions are listed first When the Switches with Most Unestablished Sessions filter is selected, the table displays switches running MLAG sessions in decreasing order of unestablished session count-devices with the largest number of unestablished sessions are listed first |
| Show All Sessions | Link to view all MLAG sessions in the full screen card |
The All MLAG Alarms tab which displays:
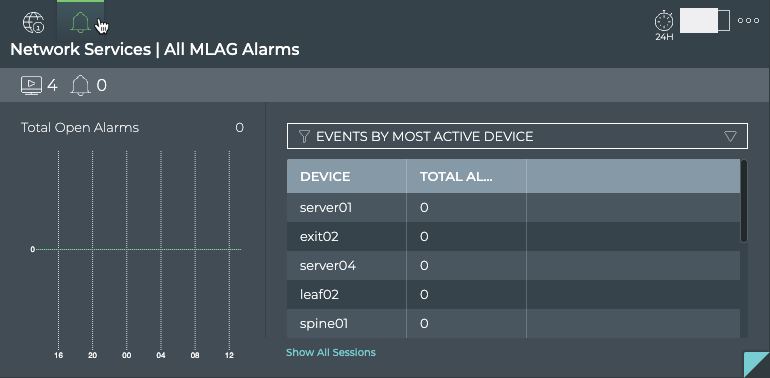
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time period | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes |
| Indicates alarm data for all MLAG sessions | |
| Title | Network Services | All MLAG Alarms (visible when you hover over card) |
| Total number of switches with the MLAG service enabled during the designated time period | |
| Total number of MLAG-related alarms received during the designated time period | |
| Total Alarms chart | Distribution of MLAG-related alarms received during the designated time period, and the total number of current MLAG-related alarms in the network. Note: The alarm count here may be different than the count in the summary bar. For example, the number of new alarms received in this time period does not take into account alarms that have already been received and are still active. You might have no new alarms, but still have a total number of alarms present on the network of 10. |
| Table/Filter options | When the Events by Most Active Device filter is selected, the table displays switches running MLAG sessions in decreasing order of alarm count-devices with the largest number of sessions are listed first |
| Show All Sessions | Link to view all MLAG sessions in the full screen card |
The full screen MLAG Service card provides tabs for all switches, all sessions, and all alarms.
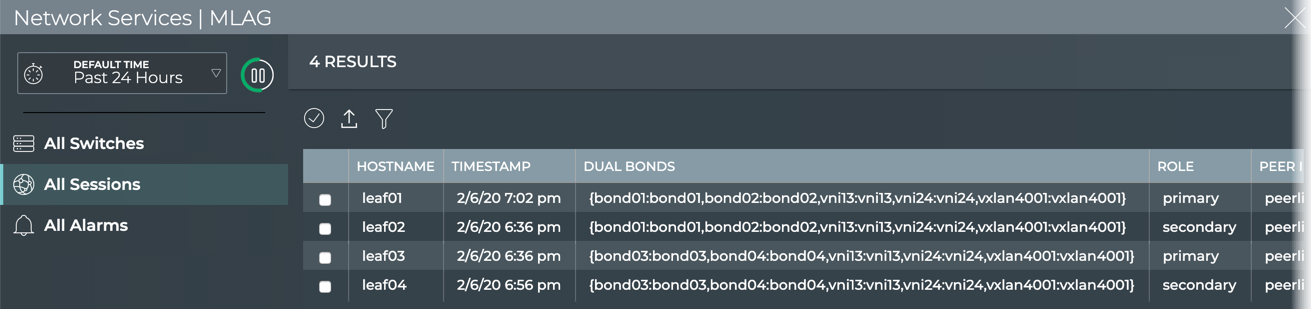
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | Network Services | MLAG |
| Closes full screen card and returns to workbench | |
| Time period | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes; select an alternate time period by clicking |
| Displays data refresh status. Click |
|
| Results | Number of results found for the selected tab |
| All Switches tab | Displays all switches and hosts running the MLAG service. By default, the device list is sorted by hostname. This tab provides the following additional data about each device:
|
| All Sessions tab | Displays all MLAG sessions network-wide. By default, the session list is sorted by hostname. This tab provides the following additional data about each session:
|
| All Alarms tab | Displays all MLAG events network-wide. By default, the event list is sorted by time, with the most recent events listed first. The tab provides the following additional data about each event:
|
| Table Actions | Select, export, or filter the list. Refer to Table Settings. |
View Service Status Summary
A summary of the MLAG service is available from the MLAG Service card workflow, including the number of nodes running the service, the number of MLAG-related alarms, and a distribution of those alarms.
To view the summary, open the small MLAG Service card.

For more detail, select a different size MLAG Service card.
View the Distribution of Sessions and Alarms
It is useful to know the number of network nodes running the MLAG protocol over a period of time, as it gives you insight into the amount of traffic associated with and breadth of use of the protocol. It is also useful to compare the number of nodes running MLAG with the alarms present at the same time to determine if there is any correlation between the issues and the ability to establish a MLAG session.
To view these distributions, open the medium MLAG Service card.

If a visual correlation is apparent, you can dig a little deeper with the large MLAG Service card tabs.
View Devices with the Most CLAG Sessions
You can view the load from MLAG on your switches using the large MLAG Service card. This data enables you to see which switches are handling the most MLAG traffic currently, validate that is what is expected based on your network design, and compare that with data from an earlier time to look for any differences.
To view switches and hosts with the most MLAG sessions:
-
Open the large MLAG Service card.
-
Select Switches with Most Sessions from the filter above the table.
The table content is sorted by this characteristic, listing nodes running the most MLAG sessions at the top. Scroll down to view those with the fewest sessions.
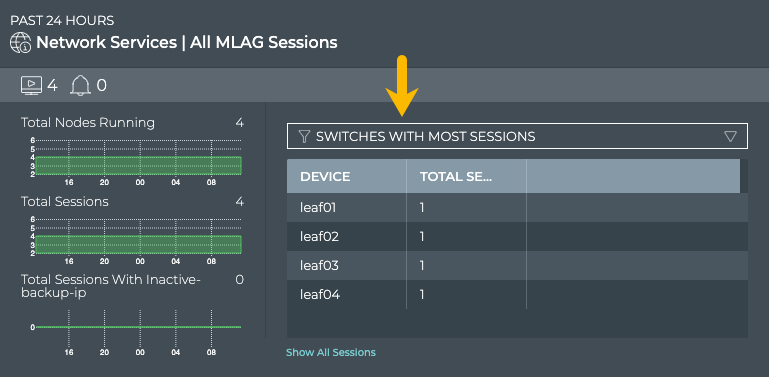
To compare this data with the same data at a previous time:
-
Open another large MLAG Service card.
-
Move the new card next to the original card if needed.
-
Change the time period for the data on the new card by hovering over the card and clicking
.
-
Select the time period that you want to compare with the current time. You can now see whether there are significant differences between this time period and the previous time period.

If the changes are unexpected, you can investigate further by looking at another timeframe, determining if more nodes are now running MLAG than previously, looking for changes in the topology, and so forth.
View Devices with the Most Unestablished MLAG Sessions
You can identify switches that are experiencing difficulties establishing MLAG sessions; both currently and in the past.
To view switches with the most unestablished MLAG sessions:
-
Open the large MLAG Service card.
-
Select Switches with Most Unestablished Sessions from the filter above the table.
The table content is sorted by this characteristic, listing nodes with the most unestablished MLAG sessions at the top. Scroll down to view those with the fewest unestablished sessions.
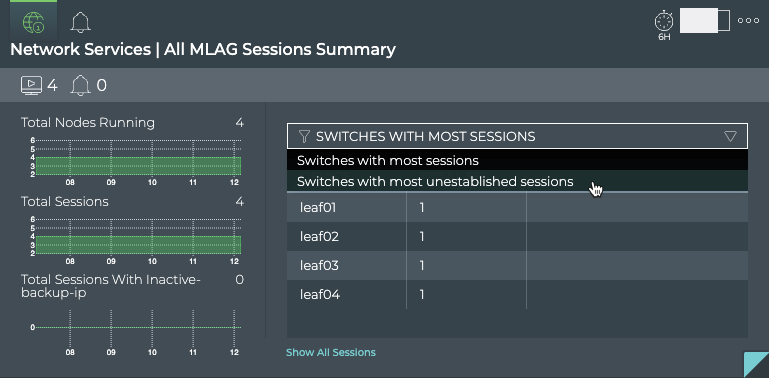
Where to go next depends on what data you see, but a few options include:
-
Change the time period for the data to compare with a prior time. If the same switches are consistently indicating the most unestablished sessions, you might want to look more carefully at those switches using the Switches card workflow to determine probable causes. Refer to Monitor Switches.
-
Click Show All Sessions to investigate all MLAG sessions with events in the full screen card.
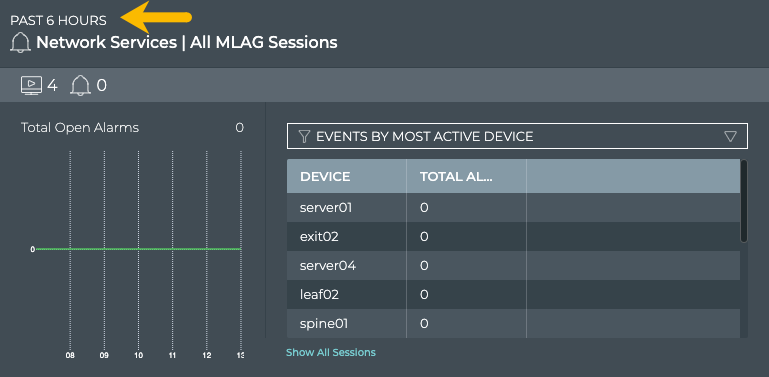
View Switches with the Most MLAG-related Alarms
Switches experiencing a large number of MLAG alarms may indicate a configuration or performance issue that needs further investigation. You can view the switches sorted by the number of MLAG alarms and then use the Switches card workflow or the Alarms card workflow to gather more information about possible causes for the alarms.
To view switches with most MLAG alarms:
-
Open the large MLAG Service card.
-
Hover over the header and click
.
-
Select Events by Most Active Device from the filter above the table.
The table content is sorted by this characteristic, listing nodes with the most MLAG alarms at the top. Scroll down to view those with the fewest alarms.

Where to go next depends on what data you see, but a few options include:
-
Change the time period for the data to compare with a prior time. If the same switches are consistently indicating the most alarms, you might want to look more carefully at those switches using the Switches card workflow.
-
Click Show All Sessions to investigate all MLAG sessions with alarms in the full screen card.
View All MLAG Events
The MLAG Service card workflow enables you to view all of the MLAG events in the designated time period.
To view all MLAG events:
-
Open the full screen MLAG Service card.
-
Click All Alarms tab.
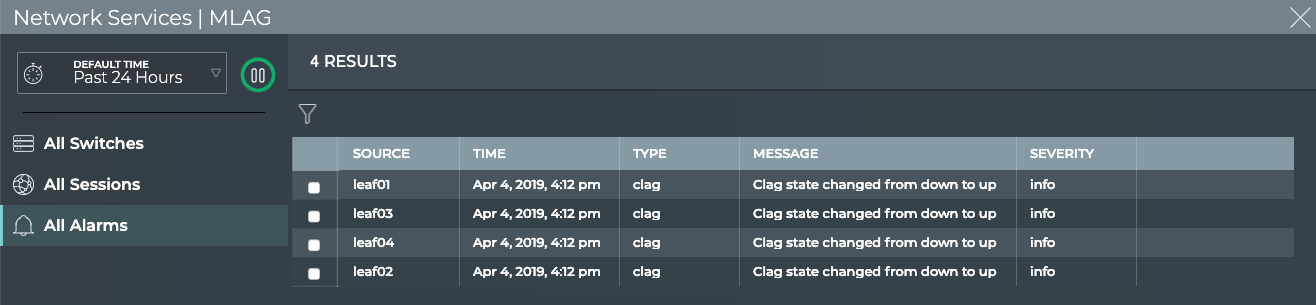
Where to go next depends on what data you see, but a few options include:
- Open the All Switches or All Sessions tabs to look more closely at the alarms from the switch or session perspective.
- Sort on other parameters:
- by Message to determine the frequency of particular events
- by Severity to determine the most critical events
- by Time to find events that may have occurred at a particular time to try to correlate them with other system events
- Export the data to a file by clicking
- Return to your workbench by clicking
in the top right corner
View Details About All Switches Running MLAG
You can view all stored attributes of all switches running MLAG in your network in the full-screen card.
To view all switch details, open the full screen MLAG Service card, and click the All Switches tab.
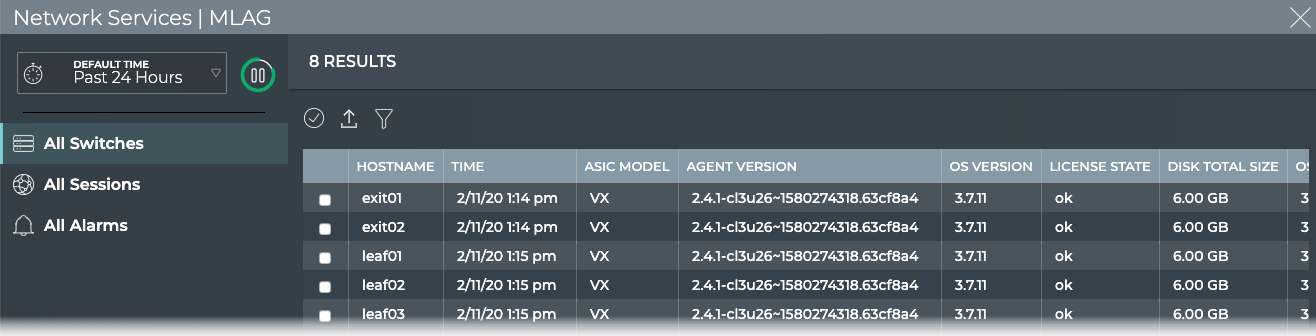
To return to your workbench, click in the top right corner.
Use the icons above the table to select/deselect, filter, and export items in the list. Refer to Table Settings for more detail. To return to original display of results, click the associated tab.
Monitor a Single MLAG Session
With NetQ, you can monitor the number of nodes running the MLAG service, view switches with the most peers alive and not alive, and view alarms triggered by the MLAG service. For an overview and how to configure MLAG in your data center network, refer to Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation - MLAG.
To access the single session cards, you must open the full screen MLAG Service, click the All Sessions tab, select the desired session, then click (Open Cards).
Granularity of Data Shown Based on Time Period
On the medium and large single MLAG session cards, the status of the peers is represented in heat maps stacked vertically; one for peers that are reachable (alive), and one for peers that are unreachable (not alive). Depending on the time period of data on the card, the number of smaller time blocks used to indicate the status varies. A vertical stack of time blocks, one from each map, includes the results from all checks during that time. The results are shown by how saturated the color is for each block. If all peers during that time period were alive for the entire time block, then the top block is 100% saturated (white) and the not alive block is zero percent saturated (gray). As peers that are not alive increase in saturation, the peers that are alive block is proportionally reduced in saturation. An example heat map for a time period of 24 hours is shown here with the most common time periods in the table showing the resulting time blocks.
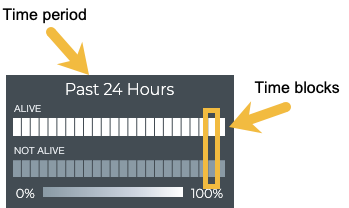
| Time Period | Number of Runs | Number Time Blocks | Amount of Time in Each Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 hours | 18 | 6 | 1 hour |
| 12 hours | 36 | 12 | 1 hour |
| 24 hours | 72 | 24 | 1 hour |
| 1 week | 504 | 7 | 1 day |
| 1 month | 2,086 | 30 | 1 day |
| 1 quarter | 7,000 | 13 | 1 week |
MLAG Session Card Workflow Summary
The small MLAG Session card displays:

| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Indicates data is for a single session of a Network Service or Protocol | |
| Title | CLAG Session |
| Device identifiers (hostname, IP address, or MAC address) for host and peer in session. | |
| Indication of host role, primary |
The medium MLAG Session card displays:
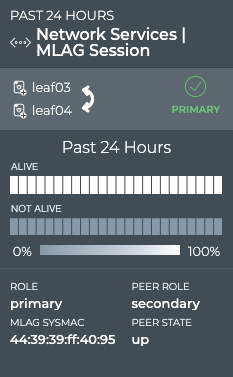
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time period (in header) | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes |
| Indicates data is for a single session of a Network Service or Protocol | |
| Title | Network Services | MLAG Session |
| Device identifiers (hostname, IP address, or MAC address) for host and peer in session. Arrow points from the host to the peer. Click |
|
| Indication of host role, primary |
|
| Time period (above chart) | Range of time for data displayed in peer status chart |
| Peer Status chart | Distribution of peer availability, alive or not alive, during the designated time period. The number of time segments in a time period varies according to the length of the time period. |
| Role | Role that host device is playing. Values include primary and secondary. |
| CLAG sysmac | System MAC address of the MLAG session |
| Peer Role | Role that peer device is playing. Values include primary and secondary. |
| Peer State | Operational state of the peer, up (true) or down (false) |
The large MLAG Session card contains two tabs.
The Session Summary tab displays:
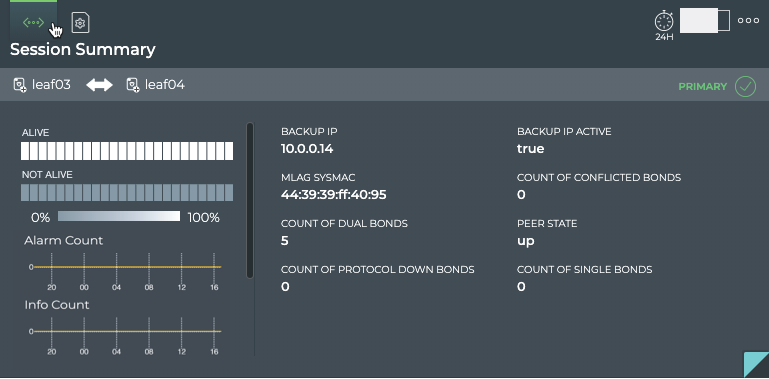
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time period | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes |
| Indicates data is for a single session of a Network Service or Protocol | |
| Title | (Network Services | MLAG Session) Session Summary |
| Device identifiers (hostname, IP address, or MAC address) for host and peer in session. Arrow points from the host to the peer. Click |
|
| Indication of host role, primary |
|
| Alarm Count Chart | Distribution and count of CLAG alarm events over the given time period |
| Info Count Chart | Distribution and count of CLAG info events over the given time period |
| Peer Status chart | Distribution of peer availability, alive or not alive, during the designated time period. The number of time segments in a time period varies according to the length of the time period. |
| Backup IP | IP address of the interface to use if the peerlink (or bond) goes down |
| Backup IP Active | Indicates whether the backup IP address is configured |
| CLAG SysMAC | System MAC address of the MLAG session |
| Peer State | Operational state of the peer, up (true) or down (false) |
| Count of Dual Bonds | Number of bonds connecting to both switches |
| Count of Single Bonds | Number of bonds connecting to only one switch |
| Count of Protocol Down Bonds | Number of bonds with interfaces that were brought down by the clagd service |
| Count of Conflicted Bonds | Number of bonds which have a set of interfaces that are not the same on both switches |
The Configuration File Evolution tab displays:
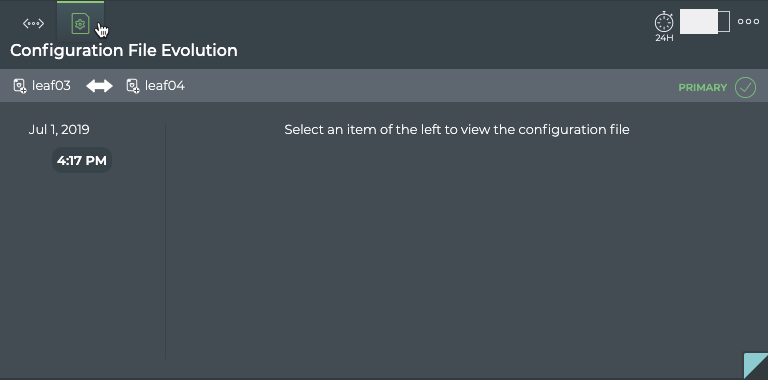
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Time period | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes |
| Indicates configuration file information for a single session of a Network Service or Protocol | |
| Title | (Network Services | MLAG Session) Configuration File Evolution |
| Device identifiers (hostname, IP address, or MAC address) for host and peer in session. Arrow points from the host to the peer. Click |
|
| Indication of host role, primary |
|
| Timestamps | When changes to the configuration file have occurred, the date and time are indicated. Click the time to see the changed file. |
| Configuration File | When File is selected, the configuration file as it was at the selected time is shown. When Diff is selected, the configuration file at the selected time is shown on the left and the configuration file at the previous timestamp is shown on the right. Differences are highlighted. |
The full screen MLAG Session card provides tabs for all MLAG sessions and all events.
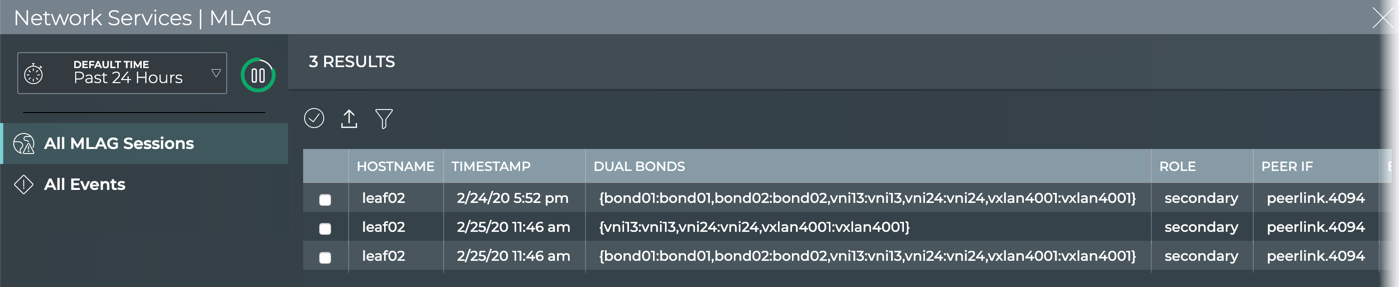
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | Network Services | MLAG |
| Closes full screen card and returns to workbench | |
| Time period | Range of time in which the displayed data was collected; applies to all card sizes; select an alternate time period by clicking |
| Displays data refresh status. Click |
|
| Results | Number of results found for the selected tab |
| All MLAG Sessions tab | Displays all MLAG sessions for the given session. By default, the session list is sorted by hostname. This tab provides the following additional data about each session:
|
| All Events tab | Displays all events network-wide. By default, the event list is sorted by time, with the most recent events listed first. The tab provides the following additional data about each event:
|
| Table Actions | Select, export, or filter the list. Refer to Table Settings. |
View Session Status Summary
A summary of the MLAG session is available from the MLAG Session card workflow, showing the node and its peer and current status.
To view the summary:
-
Open the full screen MLAG Service card.
-
Select a session from the listing to view.
-
Close the full screen card to view the medium MLAG Session card.
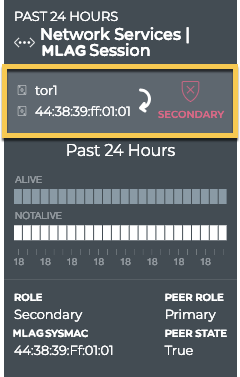
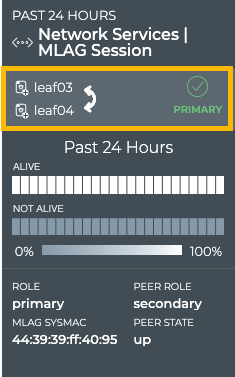
In the left example, we see that the tor1 switch plays the secondary role in this session with the switch at 44:38:39:ff:01:01. In the right example, we see that the leaf03 switch plays the primary role in this session with leaf04.
View MLAG Session Peering State Changes
You can view the peering state for a given MLAG session from the medium and large MLAG Session cards. For a given time period, you can determine the stability of the MLAG session between two devices. If you experienced connectivity issues at a particular time, you can use these cards to help verify the state of the peer. If the peer was not alive more than it was alive, you can then investigate further into possible causes.
To view the state transitions for a given MLAG session:
-
Open the full screen MLAG Service card.
-
Select a session from the listing to view.
-
Close the full screen card to view the medium MLAG Session card.
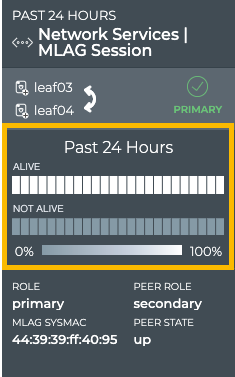
In this example, the peer switch has been alive for the entire 24-hour period.
From this card, you can also view the node role, peer role and state, and MLAG system MAC address which identify the session in more detail.
To view the peering state transitions for a given MLAG session on the large MLAG Session card, open that card.
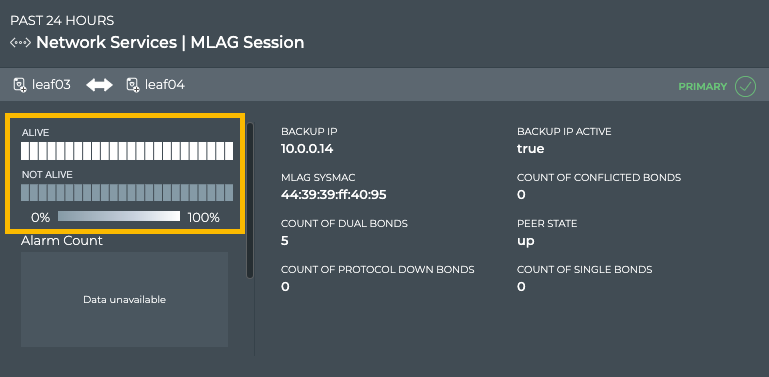
From this card, you can also view the alarm and info event counts, node role, peer role, state, and interface, MLAG system MAC address, active backup IP address, single, dual, conflicted, and protocol down bonds, and the VXLAN anycast address identifying the session in more detail.
View Changes to the MLAG Service Configuration File
Each time a change is made to the configuration file for the MLAG service, NetQ logs the change and enables you to compare it with the last version. This can be useful when you are troubleshooting potential causes for alarms or sessions losing their connections.
To view the configuration file changes:
-
Open the large MLAG Session card.
-
Hover over the card and click
to open the Configuration File Evolution tab.
-
Select the time of interest on the left; when a change may have impacted the performance. Scroll down if needed.
-
Choose between the File view and the Diff view (selected option is dark; File by default).
The File view displays the content of the file for you to review.
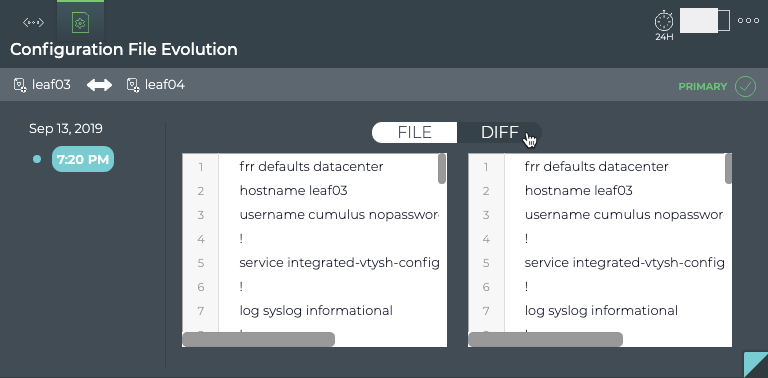
The Diff view displays the changes between this version (on left) and the most recent version (on right) side by side. The changes are highlighted in red and green. In this example, we don’t have any changes after this first creation, so the same file is shown on both sides and no highlighting is present.
All MLAG Session Details
You can view all stored attributes of all of the MLAG sessions associated with the two devices on this card.
To view all session details, open the full screen MLAG Session card, and click the All MLAG Sessions tab.

Where to go next depends on what data you see, but a few options include:
- Open the All Events tabs to look more closely at the alarm and info events fin the network.
- Sort on other parameters:
- by Single Bonds to determine which interface sets are only connected to one of the switches
- by Backup IP and Backup IP Active to determine if the correct backup IP address is specified for the service
- Export the data to a file by clicking
- Return to your workbench by clicking
in the top right corner
View All MLAG Session Events
You can view all of the alarm and info events for the two devices on this card.
To view all events, open the full screen MLAG Session card, and click the All Events tab.
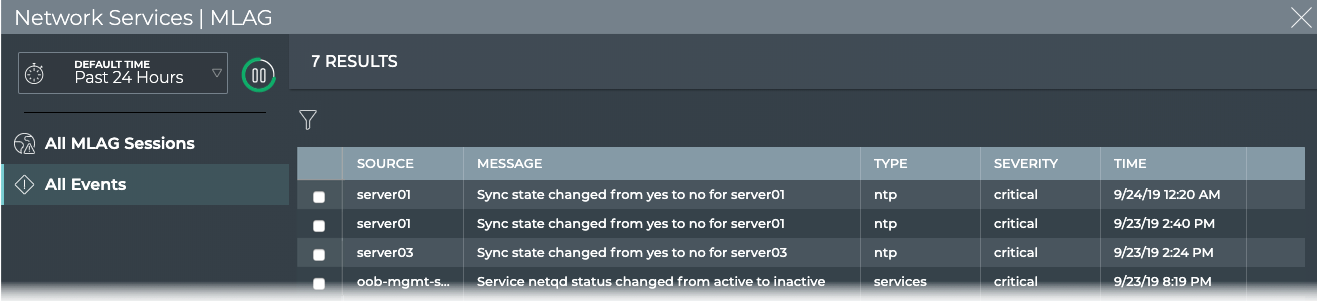
Where to go next depends on what data you see, but a few options include:
- Open the All MLAG Sessions tabs to look more closely at the individual sessions.
- Sort on other parameters:
- by Message to determine the frequency of particular events
- by Severity to determine the most critical events
- by Time to find events that may have occurred at a particular time to try to correlate them with other system events
- Export the data to a file by clicking
- Return to your workbench by clicking
in the top right corner