Set Up Your VMware Virtual Machine for a Single Cloud Server
Follow these steps to setup and configure your VM for a cloud deployment:
-
Verify that your system meets the VM requirements.
Resource Minimum Requirements Processor Four (4) virtual CPUs Memory 8 GB RAM Local disk storage 64 GB Network interface speed 1 Gb NIC Hypervisor VMware ESXi™ 6.5 or later (OVA image) for servers running Cumulus Linux, CentOS, Ubuntu, and RedHat operating systems -
Confirm that the needed ports are open for communications.
You must open the following ports on your NetQ on-premises server:Port or Protocol Number Protocol Component Access 4 IP Protocol Calico networking (IP-in-IP Protocol) 22 TCP SSH 80 TCP Nginx 179 TCP Calico networking (BGP) 443 TCP NetQ UI 2379 TCP etcd datastore 4789 UDP Calico networking (VxLAN) 5000 TCP Docker registry 6443 TCP kube-apiserver 30001 TCP DPU communication 31980 TCP NetQ Agent communication 31982 TCP NetQ Agent SSL communication 32708 TCP API Gateway -
Download the NetQ Platform image.
- On the MyMellanox Downloads page, select NetQ from the Software -> Cumulus Software list.
- Click 3.0 from the Version list, and then select 3.0.0 from the submenu.
- Select VMware (Cloud) from the HyperVisor/Platform list.
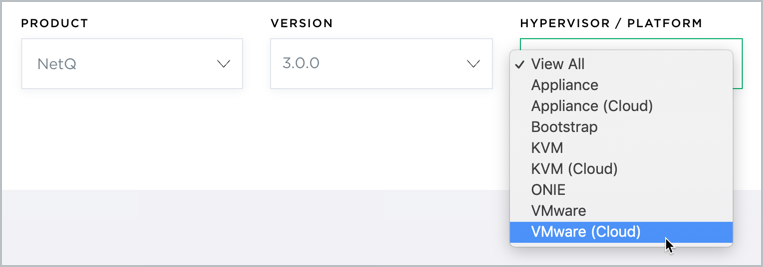
- Scroll down to view the image, and click Download. This downloads the NetQ-3.0.0-opta.tgz installation package.
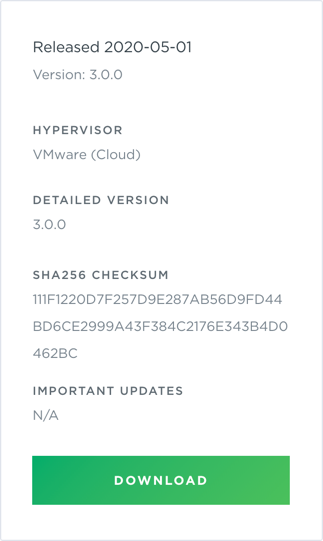
-
Setup and configure your VM.
VMware Example Configuration
This example shows the VM setup process using an OVA file with VMware ESXi.Enter the address of the hardware in your browser.
Log in to VMware using credentials with root access.
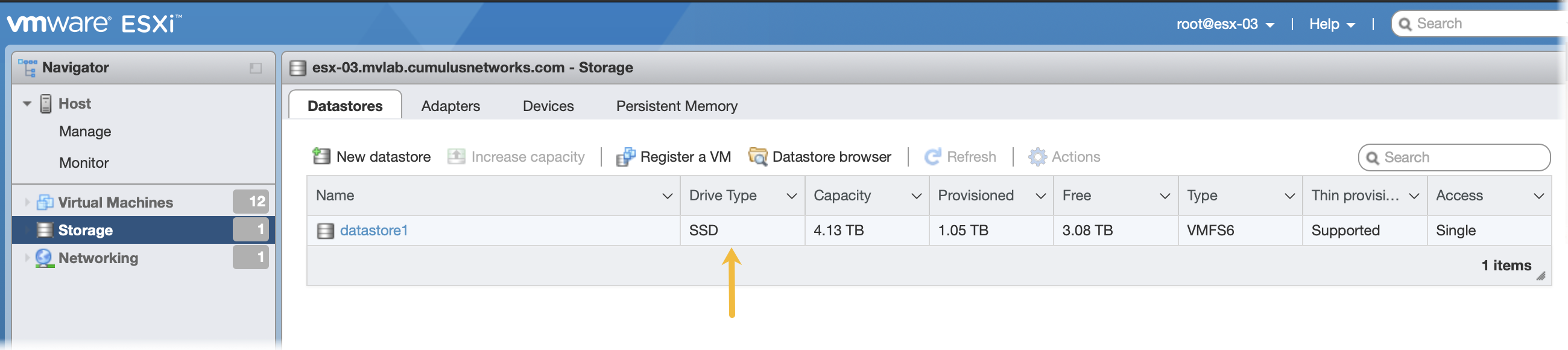
Click Storage in the Navigator to verify you have an SSD installed.
Click Create/Register VM at the top of the right pane.

Select Deploy a virtual machine from an OVF or OVA file, and click Next.
Provide a name for the VM, for example NetQ.
Tip: Make note of the name used during install as this is needed in a later step.
Drag the NetQ image file you downloaded from the NVIDIA Application Hub to the installation wizard, then click Next.
Select the storage type and data store for the image, then click Next.
Accept the default deployment options or modify them according to your network needs. Click Next when you are finished.
Review the configuration summary. Click Back to change any of the settings, or click Finish to continue with the creation of the VM.
The progress of the request is shown in the Recent Tasks window at the bottom of the application. This may take some time. After the VM is deployed, the wizard displays the full hardware and configuration details.
-
Verify the platform is ready for installation. Fix any errors indicated before installing the NetQ software.
cumulus@hostname:~$ sudo opta-check-cloud
-
Change the hostname for the VM from the default value.
The default hostname for the NetQ Virtual Machines is ubuntu. Change the hostname to fit your naming conventions while meeting Internet and Kubernetes naming standards.
Kubernetes requires that hostnames are composed of a sequence of labels concatenated with dots. For example, “en.wikipedia.org” is a hostname. Each label must be from 1 to 63 characters long. The entire hostname, including the delimiting dots, has a maximum of 253 ASCII characters.
The Internet standards (RFCs) for protocols specify that labels may contain only the ASCII letters a through z (in lower case), the digits 0 through 9, and the hyphen-minus character ('-').
Use the following command:
cumulus@hostname:~$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname NEW_HOSTNAME
Add the same NEW_HOSTNAME value to /etc/hosts on your VM for the localhost entry. Example:
127.0.0.1 localhost NEW_HOSTNAME
-
Run the Bootstrap CLI. Be sure to replace the eth0 interface used in this example with the interface on the server used to listen for NetQ Agents.
cumulus@
:~$ netq bootstrap master interface eth0 tarball /mnt/installables/netq-bootstrap-3.0.0.tgz Allow about five to ten minutes for this to complete, and only then continue to the next step.
If this step fails for any reason, you can run
netq bootstrap resetand then try again.If you have changed the IP address or hostname of the NetQ Cloud VM after this step, you need to re-register this address with NetQ as follows:
Reset the VM.
cumulus@hostname:~$ netq bootstrap reset
Re-run the Bootstrap CLI. This example uses interface eth0. Replace this with your updated IP address, hostname or interface using the
interfaceorip-addroption.cumulus@
:~$ netq bootstrap master interface eth0 tarball /mnt/installables/netq-bootstrap-3.0.0.tgz
The final step is to install and activate the Cumulus NetQ software. You can do this using the Admin UI or the CLI.
Click the installation and activation method you want to use to complete installation:
- Use the Admin UI (recommended)
- Use the CLI